Abstract
Purpose
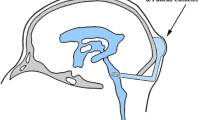
MP470 is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potent activity against mutant c-Kit, PDGFRα, Flt3, c-Met and c-Ret that is being evaluated as an anticancer agent. The plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pharmacokinetics of MP470 were studied in a non-human primate model that is highly predictive of CSF penetration in humans.
Methods
Oral MP470, 300 mg, was administered to four non-human primates. Serial samples of blood were collected from four animals and CSF samples from three animals for pharmacokinetic studies. Plasma and CSF concentrations were measured using an LC–MS/MS assay. Both model-independent and model-dependent methods were used to analyze the pharmacokinetic data.
Results
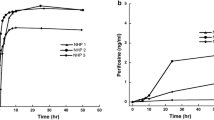
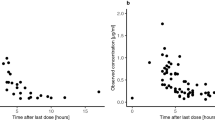
Following a one-time oral dose of 300 mg, the MP470 plasma area under the curve (AUC) was 1,690 ± 821 nM h (mean ± SD). The half-life of MP470 in the plasma was 11.0 ± 3.4 h. There was no measurable MP470 in the CSF.
Conclusions
Although CSF penetration is minimal, MP470 has demonstrated potent activity against cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo, and further clinical investigation is warranted.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinrich MC et al (2002) Inhibition of KIT tyrosine kinase activity: a novel molecular approach to the treatment of KIT-positive malignancies. J Clin Oncol 20(6):1692–1703
Hirota S et al (1998) Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 279(5350):577–580
Lux ML et al (2000) KIT extracellular and kinase domain mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am J Pathol 156(3):791–795
Arber DA, Tamayo R, Weiss LM (1998) Paraffin section detection of the c-kit gene product (CD117) in human tissues: value in the diagnosis of mast cell disorders. Hum Pathol 29(5):498–504
Tian Q et al (1999) Activating c-kit gene mutations in human germ cell tumors. Am J Pathol 154(6):1643–1647
Beghini A et al (2000) C-kit mutations in core binding factor leukemias. Blood 95(2):726–727
Smithey BE, Pappo AS, Hill DA (2002) C-kit expression in pediatric solid tumors: a comparative immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol 26(4):486–492
Qiao GB et al (2005) High-level expression of Rad51 is an independent prognostic marker of survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Br J Cancer 93(1):137–143
Hansen LT et al (2003) The role of RAD51 in etoposide (VP16) resistance in small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 105(4):472–479
Henning W, Sturzbecher HW (2003) Homologous recombination and cell cycle checkpoints: Rad51 in tumour progression and therapy resistance. Toxicology 193(1–2):91–109
NRC (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
D’Argenio D, Schumitzky A (1997) ADAPT II user’s guide: pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic systems analysis software. Biomedical Simulations Resource, University of Southern California, Los Angeles
Kissling C et al (2008) Effects of food on single-dose pharmacokinetics of oral MP-470 capsules (abstract). In: EJC Supplements-20th EORTC-NCI-AACR symposium on molecular targets and cancer therapeutics, Oct 21–24, Geneva Switzerland, p 134 Abstract nr 426
Qi W et al (2009) MP470, a novel receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in combination with Erlotinib inhibits the HER family/PI3K/Akt pathway and tumor growth in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 9(1):142
Tolcher A et al (2009) Clinical responses to MP-470, an oral RAD51 inhibitor, in combination with standard of care doublet chemotherapy, in patients with SCLC and NE malignancies: a phase 1 case series (Abstract). In: Scientific Programme, IASLC: 13th world conference on lung cancer, San Francisco CA, July 13−August 4, 2009, p 101 abstract nr 7936
Advani AS (2005) FLT3 and acute myelogenous leukemia: biology, clinical significance and therapeutic applications. Curr Pharm Des 11(26):3449–3457
Corless CL et al (2005) PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: frequency, spectrum and in vitro sensitivity to imatinib. J Clin Oncol 23(23):5357–5364
Machens A, Lorenz K, Dralle H (2009) Constitutive RET tyrosine kinase activation in hereditary medullary thyroid cancer: clinical opportunities. J Intern Med 266(1):114–125
Lanzi C et al (2009) Targeting RET for thyroid cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol 77(3):297–309
You WK, McDonald DM (2008) The hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling pathway as a therapeutic target to inhibit angiogenesis. BMB Rep 41(12):833–839
Ke AW et al (2009) Role of overexpression of CD151 and/or c-Met in predicting prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49(2):491–503
Heimans JJ et al (1994) Paclitaxel (Taxol) concentrations in brain tumor tissue. Ann Oncol 5(10):951–953
Welsh J et al (2009) The c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor MP470 radiosensitizes glioblastoma cells. J Radiat Oncol 4(69). doi:10.1186/1748-717X-4-69
Acknowledgments
The contributors Shi, C., Inloes R., Choy G. and Redkar S. are employees of SuperGen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baxter, P.A., Thompson, P.A., McGuffey, L.M. et al. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of MP470 in non-human primates. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67, 809–812 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1380-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1380-3