Abstract
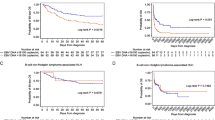
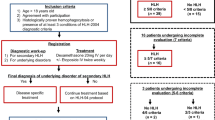
This study investigated the clinical characteristics of Hodgkin lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH-HL). Clinical data of 8 patients with HLH-HL and 20 non-HLH-HL patients were included. All eight HLH-HL patients tested positive for plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-DNA and EBV-encoded small RNA (EBER), and six patients were positive for EBV-DNA in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Two out of the 20 non-HLH-HL patients were confirmed positive for EBER, and the remaining 18 patients were negative. Among the HLH-HL patients, five patients received ABVD (doxorubicin/bleomycin/vinblastine/dacarbazine) chemotherapy regimens in other hospitals, and their conditions were considered to be worse, for which reason they were transferred to our center, and three patients were treated with DEP (doxorubicin-etoposide-methylprednisolone) regimens to target HLH and were alive as of the writing of this article. Two patients were critically ill upon admission and were not able to undergo chemotherapy. Significant differences in survival time were observed between the HLH-HL and non-HLH-HL patients (P = 0.005). HL patients found positive for EBV (plasma/PBMCs EBV-DNA(+)/EBER(+)) may be more likely to develop HLH-HL. It may be beneficial to target HLH during the acute phase of HLH, followed by treating HL once the HLH condition has stabilized. HLH-HL patients have worse prognosis and higher mortality than non-HLH-HL patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HLH-HL:
-
Hodgkin lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- HL:
-
Hodgkin lymphoma
- EBV:
-
Epstein-Barr virus
- EBER:
-
EBV-encoded small RNA
- PBMCs:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- ABVD:
-
doxorubicin/bleomycin/vinblastine/dacarbazine
- DEP:
-
doxorubicin-etoposide-methylprednisolone
- ECOG:
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
- IPS:
-
international prognostic score
- CR:
-
complete response
- PR:
-
partial response
- NR:
-
no response
- ALT:
-
alanine aminotransferase
References
Henter JI, Elinder G, Ost A (1991) Diagnostic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. The FHL Study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Semin Oncol 18:29–33
Rivière S, Galicier L, Coppo P et al (2014) Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome in adults: a retrospective analysis of 162 patients. Am J Med 127:1118–1125
Lehmberg K, Nichols KE, Henter JI et al (2015) Consensus recommendations for the diagnosis and management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with malignancies. Haematologica 100:997–1004
Kanakry JA, Ambinder RF (2013) EBV-related lymphomas: new approaches to treatment. Curr Treat Options in Oncol 14:224–236
Claviez A, Tiemann M, Lüders H et al (2005) Impact of latent Epstein-Barr virus infection on outcome in children and adolescents with Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23:4048–4056
Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M et al (2007) HLH-2004:Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 48:124–131
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA et al (2016) The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 127(20):2375–2390
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC et al (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5:649–655
Hasenclever D, Diehl V (1998) A prognostic score for advanced Hodgkin’s disease. International prognostic factors project on advanced Hodgkin’s disease. N Engl J Med 339:1506–1514
Collaborative study to evaluate the proposed 1st WHO international
Marsh RA, Allen CE, McClain KL et al (2013) Salvage therapy of refractory hemophagocytic lymphohisocytosis with alemtuzumab. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(1):101–109
Wang Y, Huang W, Wang Z et al (2015) Multi-center study of combination DEP regimen as a salvage therapy for adult refractory hemopgagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 126(19):2186–2192
Han AR, Lee HR, Park BB et al (2007) Lymphomaassociated hemophagocytic syndrome: clinical features and treatment outcome. Ann Hematol 86(7):493–498
Li J, Wang Q, Zheng W et al (2014) Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: clinical analysis of 103 adult patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 93(2):100–105
Yu JT, Wang CY, Yang Y et al (2013) Lymphomaassociated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: experience in adults from a single institution. Ann Hematol 92(11):1529–1536
Ishii E, Ohga S, Imashuku S et al (2007) Nationwide survey of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Japan. Int J Hematol 86(1):58–65
Riviere S, Galicier L, Coppo P et al (2014) Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome in adults: a multicenter retrospective analysis of 162 patients. Am J Med 127(11):1118–1125
Veerakul G, Sanpakit K, Tanphaichitr VS et al (2002) Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children: an analysis of etiology and outcome. J Med Assoc Thail 85:530–541
Go RS, Wester SM (2004) Immunophenotypic and molecular features, clinical outcomes, treatments, and prognostic factors associated with subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: a systematic analysis of 156 patients reported in the literature. Cancer 101(6):1404–1413
Willemze R, Jansen PM, Cerroni L et al (2008) Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: definition, classification, and prognostic factors: an EORTC Cutaneous Lymphoma Group Study of 83 cases. Blood 111(2):838–845
Ferreri AJ, Dognini GP, Campo E et al (2007) Variations in clinical presentation, frequency of hemophagocytosis and clinical behavior of intravascular lymphoma diagnosed in different geographical regions. Haematologica 92(4):486–492
Hagihara M, Inoue M, Hua J et al (2012) Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin lymphoma complicating hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis as an initial manifestation: a case report and review of the literature. Intern Med 51(21):3067–3072
Cho EY, Kim KH, Kim WS et al (2008) The spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease in Korea: incidence of disease entities by age groups. J Korean Med Sci 23(2):185–192
Chang YH, Lu PJ, Lu MY et al (2009) Sequential transplants for respective relapse of Hodgkin disease and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a treatment dilemma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 31(10):778–781
Shimazaki C, Inaba T, Nakagawa M (2000) B-cell lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma 38(1-2):121–130
Murase T, Nakamura S, Kawauchi K et al (2000) An Asian variant of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: clinical, pathological and cytogenetic approaches to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Br J Haematol 111(3):826–834
Wang J, Wang Y, Wang Z et al (2016) PEG-aspargase and DEP regimen combination therapy for refractory Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Hematol Oncol 9(1):84
Jin Z, Wang Y, Wang Z et al (2018) Multivariate analysis of prognosis for patients with natural killer/T cell lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematology 23(4):228–234
Parikh SA, Kapoor P, Letendre L et al (2014) Prognostic factors and outcomes of adults with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Mayo Clin Proc 89:484–492
Otrock ZK, Eby CS (2015) Clinical characteristics, prognostic factors, and outcomes of adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Am J Hematol 90:220–224
Daver N, McClain K, Allen C et al (2017) A consensus review on malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Cancer 123(17):3229–3240
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81871633); Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No.7181003); Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Clinical Medicine Development of Special Funding(ZYLX201702); Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals’ Ascent Plan(DFL20180101); Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program(PX2018003); Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Clinical Technology Innovation Project(XMLX201803)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZJ collected and analyzed data, and drafted the manuscript. YW, NW, ZW participated in the design of the study and performed the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Our study was analyzed retrospectively and it conforms to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z., Wang, Y., Wei, N. et al. Hodgkin lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis—a dangerous disease. Ann Hematol 99, 1575–1581 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04093-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04093-4