Abstract
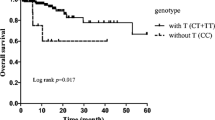
To investigate the possible role of functional single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in circadian genes as prognostic markers of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). We conducted a prospective study using data from Huashan Hospital 2006–2015 and followed up 91 PCNSL patients until June 30, 2016. The survival of patients with different prognostic factors was compared by log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed by Cox regression. During a long-term follow-up (6–110 months), overall survival (OS) was 32 months (95% CI, 13.3–91.1) and progression-free survival (PFS) was 23 months (95% CI, 9.0–41.0) for the entire cohort. Age (P = 0.046, P = 0.001) and performance status (PS) score (P = 0.013, P = 0.003) showed differences in OS and PFS. ABCB1 rs1045642 variant showed significant difference in PFS between patients with CC genotype and those with CT/TT genotypes (P = 0.020). In multivariate analysis, age (HR = 2.3; 95% CI, 1.2–4.2, P = 0.008), PS (HR = 2.4; 95% CI, 1.3–4.4, P = 0.007), and ABCB1 rs1045642 (HR = 1.9; 95% CI, 1.0–3.3, P = 0.036) were the independent risk factors for PFS. In our results, the most important prognostic factors associated with higher risk of progression were ABCB1 rs1045642 CC genotype, PS > 2, and older age.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCNSL:
-
primary central nervous system lymphoma
- NHL:
-
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- DLBCL:
-
diffuse large B cell lymphomas
- SNP:
-
single nucleotide polymorphism
- OS:
-
overall survival
- PFS:
-
progression-free survival
- PS:
-
performance status
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- HD-MTX:
-
high-dose methotrexate
- WBRT:
-
whole-brain radiotherapy
- R:
-
rituximab
- IDA:
-
idarubicin
- Vm26:
-
teniposide
- FDG-PET:
-
18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- β2-MG:
-
β2-microglobulin
- ALL:
-
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
References
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE, Kruchko C (2012) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005-2009. Neuro-Oncology 14(Suppl 5):v1–v49. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos218
Camilleri-Broet S, Criniere E, Broet P, Delwail V, Mokhtari K, Moreau A, Kujas M, Raphael M, Iraqi W, Sautes-Fridman C, Colombat P, Hoang-Xuan K, Martin A (2006) A uniform activated B-cell-like immunophenotype might explain the poor prognosis of primary central nervous system lymphomas: analysis of 83 cases. Blood 107(1):190–196. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-03-1024
Carbone A, Gloghini A, Larocca LM, Capello D, Pierconti F, Canzonieri V, Tirelli U, Dalla-Favera R, Gaidano G (2001) Expression profile of MUM1/IRF4, BCL-6, and CD138/syndecan-1 defines novel histogenetic subsets of human immunodeficiency virus-related lymphomas. Blood 97(3):744–751
Kreher S, Johrens K, Strehlow F, Martus P, Borowiec K, Radke J, Heppner F, Roth P, Thiel E, Pietsch T, Weller M, Korfel A (2015) Prognostic impact of B-cell lymphoma 6 in primary CNS lymphoma. Neuro-Oncology 17(7):1016–1021. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nov046
Ferreri AJ, Blay JY, Reni M, Pasini F, Spina M, Ambrosetti A, Calderoni A, Rossi A, Vavassori V, Conconi A, Devizzi L, Berger F, Ponzoni M, Borisch B, Tinguely M, Cerati M, Milani M, Orvieto E, Sanchez J, Chevreau C, Dell’Oro S, Zucca E, Cavalli F (2003) Prognostic scoring system for primary CNS lymphomas: the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol 21(2):266–272
Abrey LE, Ben-Porat L, Panageas KS, Yahalom J, Berkey B, Curran W, Schultz C, Leibel S, Nelson D, Mehta M, DeAngelis LM (2006) Primary central nervous system lymphoma: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model. J Clin Oncol 24(36):5711–5715. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2006.08.2941
Roth P, Keller A, Hoheisel JD, Codo P, Bauer AS, Backes C, Leidinger P, Meese E, Thiel E, Korfel A, Weller M (2015) Differentially regulated miRNAs as prognostic biomarkers in the blood of primary CNS lymphoma patients. Eur J Cancer 51(3):382–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2014.10.028
Mao X, Sun Y, Tang J (2014) Serum miR-21 is a diagnostic and prognostic marker of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurol Sci 35(2):233–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1491-9
Kasenda B, Haug V, Schorb E, Fritsch K, Finke J, Mix M, Hader C, Weber WA, Illerhaus G, Meyer PT (2013) 18F-FDG PET is an independent outcome predictor in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Nucl Med 54(2):184–191. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.112.108654
Lee KM, Lan Q, Kricker A, Purdue MP, Grulich AE, Vajdic CM, Turner J, Whitby D, Kang D, Chanock S, Rothman N, Armstrong BK (2007) One-carbon metabolism gene polymorphisms and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in Australia. Hum Genet 122(5):525–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0431-2
Wang SS, Maurer MJ, Morton LM, Habermann TM, Davis S, Cozen W, Lynch CF, Severson RK, Rothman N, Chanock SJ, Hartge P, Cerhan JR (2009) Polymorphisms in DNA repair and one-carbon metabolism genes and overall survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. Leukemia 23(3):596–602. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.240
Al-Dayel F, Al-Rasheed M, Ibrahim M, Bu R, Bavi P, Abubaker J, Al-Jomah N, Mohamed GH, Moorji A, Uddin S, Siraj AK, Al-Kuraya K (2008) Polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes CYP1A1, GSTT and GSTP contribute to the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma risk in the Saudi Arabian population. Leuk Lymphoma 49(1):122–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428190701704605
Gra OA, Glotov AS, Nikitin EA, Glotov OS, Kuznetsova VE, Chudinov AV, Sudarikov AB, Nasedkina TV (2008) Polymorphisms in xenobiotic-metabolizing genes and the risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in adult Russian patients. Am J Hematol 83(4):279–287. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.21113
Morton LM, Schenk M, Hein DW, Davis S, Zahm SH, Cozen W, Cerhan JR, Hartge P, Welch R, Chanock SJ, Rothman N, Wang SS (2006) Genetic variation in N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1) and 2 (NAT2) and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Pharmacogenet Genomics 16(8):537–545. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.fpc.0000215071.59836.29
Cerhan JR, Habermann TM, Maurer MJ, Wooldridge JE, Ansell SM, Nowakowski GS, Micallef IN, Thompson CA, Wang AH, Macon WR, Syrbu SI, Slager SL, Witzig TE, Link B (2010) Genetic polymorphisms in genes involved in R-CHOP metabolism and event-free and overall survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 116(21):439–439
Chen BB, Xu XP, Shen L, Han TJ, Lin ZG, Chen Z, Kang H, Huang B, Lin GW (2013) Prognostic value of clinical characteristics and immunophenotypic biomarkers in 115 patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Chin Med J 126(3):482–487
Aller SG, Yu J, Ward A, Weng Y, Chittaboina S, Zhuo R, Harrell PM, Trinh YT, Zhang Q, Urbatsch IL, Chang G (2009) Structure of P-glycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug binding. Science (New York, NY) 323(5922):1718–1722. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1168750
Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Oh JM, Kim IW, Sauna ZE, Calcagno AM, Ambudkar SV, Gottesman MM (2007) A “silent” polymorphism in the MDR1 gene changes substrate specificity. Science (New York, NY) 315(5811):525–528. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1135308
Bogacz A, Mrozikiewicz PM, Deka-Pawlik D, Seremak-Mrozikiewicz A, Bartkowiak-Wieczorek J, Barlik M, Drews K, Kowalska A, Grzeskowiak E (2013) Frequency of G2677T/A and C3435T polymorphisms of MDR1 gene in preeclamptic women. Ginekol Pol 84(9):781–787
Vinolas N, Provencio M, Reguart N, Cardenal F, Alberola V, Sanchez-Torres JM, Baron FJ, Cobo M, Maestu I, Moreno I, Mesia C, Izquierdo A, Felip E, Lopez-Brea M, Marquez A, Sanchez-Ronco M, Taron M, Santarpia MC, Rosell R (2011) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in MDR1 gen correlates with outcome in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with cisplatin plus vinorelbine. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 71(2):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2010.05.005
Ma CX, Sun YH, Wang HY (2015) ABCB1 polymorphisms correlate with susceptibility to adult acute leukemia and response to high-dose methotrexate. Tumour Biol 36(10):7599–7606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3403-5
Li Y, Yan PW, Huang XE, Li CG (2011) MDR1 gene C3435T polymorphism is associated with clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients treated with postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 12(9):2405–2409
Wang Z, Wang T, Bian J (2013) Association between MDR1 C3435T polymorphism and risk of breast cancer. Gene 532(1):94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.050
Ni Y, Yin G, Xiao Z, Fan L, Wang L, Wu Y, Wu H, Qian S, Xu W, Li J, Miao K, Qiu H (2016) MDR1 polymorphisms have an impact on the prognosis of Chinese diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients. Tumour Biol 37(1):1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3930-0
Gregers J, Green H, Christensen IJ, Dalhoff K, Schroeder H, Carlsen N, Rosthoej S, Lausen B, Schmiegelow K, Peterson C (2015) Polymorphisms in the ABCB1 gene and effect on outcome and toxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J 15(4):372–379. https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2014.81
Yang YL, Lin DT, Chang SK, Lin SR, Lin SW, Chiou RJ, Yen CT, Lin KH, Jou ST, Lu MY, Chang HH, Chang WH, Lin KS, Hu CY (2010) Pharmacogenomic variations in treatment protocols for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 54(2):206–211. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.22292
Rao DN, Anuradha C, Vishnupriya S, Sailaja K, Surekha D, Raghunadharao D, Rajappa S (2010) Association of an MDR1 gene (C3435T) polymorphism with acute leukemia in India. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 11(4):1063–1066
Jamroziak K, Mlynarski W, Balcerczak E, Mistygacz M, Trelinska J, Mirowski M, Bodalski J, Robak T (2004) Functional C3435T polymorphism of MDR1 gene: an impact on genetic susceptibility and clinical outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Eur J Haematol 72(5):314–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2004.00228.x
Kishi S, Cheng C, French D, Pei D, Das S, Cook EH, Hijiya N, Rizzari C, Rosner GL, Frudakis T, Pui CH, Evans WE, Relling MV (2007) Ancestry and pharmacogenetics of antileukemic drug toxicity. Blood 109(10):4151–4157. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-10-054528
Suthandiram S, Gan GG, Zain SM, Bee PC, Lian LH, Chang KM, Ong TC, Mohamed Z (2014) Effect of polymorphisms within methotrexate pathway genes on methotrexate toxicity and plasma levels in adults with hematological malignancies. Pharmacogenomics 15(11):1479–1494. https://doi.org/10.2217/pgs.14.97
Dervieux T, Greenstein N, Kremer J (2006) Pharmacogenomic and metabolic biomarkers in the folate pathway and their association with methotrexate effects during dosage escalation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54(10):3095–3103. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22129
Organista-Nava J, Gomez-Gomez Y, Saavedra-Herrera MV, Rivera-Ramirez AB, Teran-Porcayo MA, Alarcon-Romero Ldel C, Illades-Aguiar B, Leyva-Vazquez MA (2010) Polymorphisms of the gamma-glutamyl hydrolase gene and risk of relapse to acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Mexico. Leuk Res 34(6):728–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2009.11.027
Garcia-Bournissen F, Moghrabi A, Krajinovic M (2007) Therapeutic responses in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and haplotypes of gamma glutamyl hydrolase (GGH) gene. Leuk Res 31(7):1023–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2006.08.007
Funding
This research was supported/funded by the Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (Grant No. 2014JP003A), the Science and Technology Development Fund of Bao Shan District (Grant No. 13-E-34), and the Shanghai Hospital Development Center (Grant No.16CR2043B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bobin Chen, Hui Kang, and Xiaoping Xu designed the research. Hui Kang, Dongxiao Zhuang, and Dina Suolitiken collected the clinical data. Ting Wu, Hui Kang, Yan Ma, and Zhiguang Lin performed the research. Ting Wu analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Huashan Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 366 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, T., Kang, H., Zhuang, D. et al. The role of ABCB1 polymorphism as a prognostic marker for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ann Hematol 98, 923–930 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03629-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03629-7



