Abstract
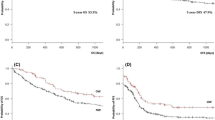
Obesity adversely affects outcome in pediatric acute lymphocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). We asked if obesity, measured by body mass index (BMI), affected outcome in 329 adult AML patients treated with high-dose cytarabine and idarubicin-containing regimens administered according to actual body weight. Age ≥ 60, unfavorable karyotype, secondary AML, and positive smoking status had adverse impact on overall survival in a multivariate analysis, while BMI did not. We conclude that high BMI should not be a barrier to administer high-dose cytarabine-containing regimens for AML induction.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calle EE et al (2003) Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 348(17):1625–1638
Lichtman MA (2010) Obesity and the risk for a hematological malignancy: leukemia, lymphoma, or myeloma. Oncologist 15(10):1083–1101
Hunter RJ et al (2009) Dosing chemotherapy in obese patients: actual versus assigned body surface area (BSA). Cancer Treat Rev 35(1):69–78
Sparreboom A et al (2007) Evaluation of alternate size descriptors for dose calculation of anticancer drugs in the obese. J Clin Oncol 25(30):4707–4713
Lange BJ et al (2005) Mortality in overweight and underweight children with acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA 293(2):203–211
Lange BJ et al (2008) Outcomes in CCG-2961, a children's oncology group phase 3 trial for untreated pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the children's oncology group. Blood 111(3):1044–1053
(2004) Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 363(9403): p. 157–63
Cheson BD et al (2003) Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes, and Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 21(24):4642–4649
Byrd JC et al (2002) Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 8461). Blood 100(13):4325–4336
Larsson SC, Wolk A (2008) Overweight and obesity and incidence of leukemia: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int J Cancer 122(6):1418–1421
Ross JA et al (2004) Body mass index and risk of leukemia in older women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13(11 Pt 1):1810–1813
Tedesco J et al (2011) High prevalence of obesity in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): implications for differentiating agents in APL and metabolic syndrome. Ther Adv Hematol 2(3):141–145
Wang A et al (2005) Obesity and weight control practices in 2000 among veterans using VA facilities. Obes Res 13(8):1405–1411
(2009) Obesity trends among U.S. adults. CDC
Must A, Dallal GE, Dietz WH (1991) Reference data for obesity: 85th and 95th percentiles of body mass index (wt/ht2) and triceps skinfold thickness. Am J Clin Nutr 53(4):839–846
Appel SJ, Harrell JS, Davenport ML (2005) Central obesity, the metabolic syndrome, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in young adults. J Am Acad Nurse Pract 17(12):535–541
Frezza EE, Wachtel MS, Chiriva-Internati M (2006) Influence of obesity on the risk of developing colon cancer. Gut 55(2):285–291
Haydon AM et al (2006) Effect of physical activity and body size on survival after diagnosis with colorectal cancer. Gut 55(1):62–67
Busetto L et al (2005) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in morbid obesity: effects of intragastric balloon. Chest 128(2):618–623
Hatipoglu N et al (2010) Neck circumference: an additional tool of screening overweight and obesity in childhood. Eur J Pediatr 169(6):733–739
Ashwell M, Hsieh SD (2005) Six reasons why the waist-to-height ratio is a rapid and effective global indicator for health risks of obesity and how its use could simplify the international public health message on obesity. Int J Food Sci Nutr 56(5):303–307
Estey E et al (1997) Association between increased body mass index and a diagnosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 11(10):1661–1664
Jeddi R et al (2010) High body mass index is an independent predictor of differentiation syndrome in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leuk Res 34(4):545–547
Jeddi R et al (2008) Predictive factors of all-trans-retinoic acid related complications during induction therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. Hematology 13(3):142–146
Navarro WH et al (2010) Obesity does not preclude safe and effective myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) in adults. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl 16(10):1442–1450
Haque AK et al (2008) Pulmonary and cardiovascular complications of obesity: an autopsy study of 76 obese subjects. Arch Pathol Lab Med 132(9):1397–1404
Mathieu P, Lemieux I, Despres JP (2010) Obesity, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87(4):407–416
Derolf AR et al (2009) Improved patient survival for acute myeloid leukemia: a population-based study of 9729 patients diagnosed in Sweden between 1973 and 2005. Blood 113(16):3666–3672
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partially by grants from the National Cancer Institute Grant CA16056 (HJL, ASL, AJH, LAF, SNJS, AWB, MB, MRB, ESW, MW), the Szefel Foundation, Roswell Park Cancer Institute (ESW), the Nancy C. Cully Endowment for Leukemia Research (MW), and the Heidi Leukemia Research Fund, Buffalo, NY (MW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H.J., Licht, A.S., Hyland, A.J. et al. Is obesity a prognostic factor for acute myeloid leukemia outcome?. Ann Hematol 91, 359–365 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-011-1319-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-011-1319-8