Abstract
Purpose
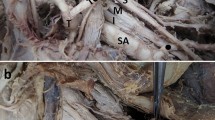
While anatomical variations of the subscapular vessels are frequently encountered during axillary dissection, little is found in the literature. The aim of this cadaveric study was to define arterial and venous anatomical variations and frequencies of the subscapular vascular pedicle and its terminal/afferent vessels in women.
Methods
We performed 80 dissections of the axillary region on forty female formalin-embalmed cadavers. Each anatomical arrangement was photographed and recorded on a scheme before analysis.
Results
We propose a new classification of the subscapular pedicle variations. We observed three types of subscapular arterial variation. The type Ia was the most frequent arrangement (71% of our dissections), the type Ib was observed in 11% and the type II in 18% of cases. We observed four types of subscapular venous variation. The type Ia was observed in 63% of cases, the type Ib in 14%, the type II in 14% and the type III in 10% of cases.
Conclusions
This knowledge of the anatomical variation arrangement and frequencies of the subscapular vascular pedicle will assist the surgeon when dissecting the axillary region for malignant or reconstructive procedures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi B (1928) Das Arteriensystem der Japaner. Verlag der Kai serlich-Japanische Universität zu Kyoto, Kyoto
Adachi B (1933–1940) Das Venensystem der Japaner. Druckanstalt Kenkyusha Tok edn. Druckanstalt Kenkyusha Tok, Kyoto
Allen RJ, Haddock NT, Ahn CY, Sadeghi A (2012) Breast reconstruction with the profunda artery perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:16e–23e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182363d9f
Allen RJ, Treece P (1994) Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap for breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 32:32–38
Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R (1996) Illustrated encyclopedia of human anatomic variation. http://www.anatomyatlases.org/AnatomicVariants/AnatomyHP.shtml#TOC
Bourgery J, Jacob H (1831) Traité complet de l’anatomie de l’homme comprenant la médecine opératoire. C. Delaunay, Paris
Bridges AJ, Holler KA (2007) How many is enough? Determining optimal sample sizes for normative studies in pediatric neuropsychology. Child Neuropsychol 13:528–538. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297040701233875
Chan CY, Tan M (2003) Spatial relations of the angular vein, an important landmark in axillary nodal dissection. Br J Surg 90:948–949. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4147
Chevrel JP, d’Anatomie eMdCMFdP (1991) Anatomie Clinique. 1 Les membres, vol 1. Springer, Paris
Cruveilhier J (1851) Traité d’Anatomie Descriptive. Tome I, vol I. Labé, Paris
Cruveilhier J (1851) Traité d’Anatomie Descriptive. Tome II, vol II. Labé, Paris
Dubreuil-Chambardel L (1926) Variations des artères du membre supérieur. Masson et Cie, Paris
Fontaine C (2001) Some help for literature study in anatomical variation reports. Surg Radiol Anat 23:293–294
Fontaine C (2001) Some thoughts about anatomic variations. Surg Radiol Anat 23:1–2
Goldberg JA, Lineaweaver WC, Buncke HJ (1990) An aberrant independent origin of the serratus anterior pedicle. Ann Plast Surg 25:487–490
Gray H, Carter HV (1858) Anatomy descriptive and surgical. Parker J.W and Son, West Strand., London
Haddad K, Hunsinger V, Obadia D, Hivelin M, Lantieri L (2016) Breast reconstruction with profunda artery perforator flap: A prospective study of 30 consecutive cases. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 61:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anplas.2016.02.004
Hamilton WJ, Boyd JD, Mossman UW (1978) Human embryology, 4th edn. edn. Macmillan Press LTD, London
Hunsinger V, Lhuaire M, Haddad K, Wirz FS, Abedalthaqafi S, Obadia D, Derder M, Marchac A, Benjoar MD, Hivelin M, Lantieri L (2018) Medium- and large-sized autologous breast reconstruction using a Fleur-de-lys Profunda Femoris artery perforator flap design: a report comparing results with the horizontal profunda femoris artery perforator flap. J Reconstr Microsurg. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1649508
Khan A, Chakravorty A, Gui GP (2012) In vivo study of the surgical anatomy of the axilla. Br J Surg 99:871–877. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.8737
Kutiyanawala MA, Stotter A, Windle R (1998) Anatomical variants during axillary dissection. Br J Surg 85:393–394. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00612.x
Lantieri L, Hivelin M, Benjoar MD, Quilichini J, Hutzinger V, Marchac A, Lepage C (2015) [Setting of a breast autologous microsurgical reconstructive surgery evolution in 20 years and review of 1138 cases]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 60:484–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anplas.2015.06.009
Lantieri LA, Mitrofanoff M, Rimareix F, Gaston E, Raulo Y, Baruch JP (1999) Use of circumflex scapular vessels as a recipient pedicle for autologous breast reconstruction: a report of 40 consecutive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:2049–2053
Lepage C, Paraskevas A, Faramarz K, Lantieri L (2006) Reconstruction mammaire par lambeau libre DIEP (deep inferior epigastric perforator). EMC (Elsevier Masson SAS, Paris), Techniques chirurgicales—Chirurgie plastique reconstructrice et esthétique 54-665-G
Lhuaire M (2016) Étude Anatomique des pédicules épigastriques inférieurs, subscapulaire et thoracique interne: applications chirurgicales. Médecine, Université de Reims Champagne-Ardenne, Reims
Lhuaire M, Hivelin M, Drame M, Abrahams P, Kianmanesh R, Fontaine C, Lantieri L (2017) Determining the best recipient vessel site for autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction with DIEP flaps: An anatomical study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 70:781–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2017.01.008
Lhuaire M, Tonnelet R, Renard Y, Piardi T, Sommacale D, Duparc F, Braun M, Labrousse M (2015) Developmental anatomy of the liver from computerized three-dimensional reconstructions of four human embryos (from Carnegie stage 14 to 23). Ann Anat 200:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2015.02.012
Lippert H, Pabst R (1985) Arterial variations in man. Classification and Frequency. J.F. Bergmann Verlag, München
Moriggl B, Fontaine C (2004) Strengthening editors’ policy concerning publication of anatomic variations. Surg Radiol Anat 26:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-003-0211-1
Natsis K, Totlis T, Tsikaras P, Skandalakis P (2006) Bilateral accessory thoracodorsal artery. Ann Anat 188:447–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2006.03.003
O’Rourke MG, Layt CW (1993) Angular vein of the axilla and the anatomy of the subscapular vein important in axillary node dissection. Aust N Zeal J Surg 63:396–398
Rodriguez-Niedenfuhr M, Burton GJ, Deu J, Sanudo JR (2001) Development of the arterial pattern in the upper limb of staged human embryos: normal development and anatomic variations. J Anat 199:407–417
Rouvière H, Delmas A (1974) Anatomie Humaine. Descriptive, topographique et fonctionnelle. Tome III. Membres, système nerveux central, vol Tome III, 11e Édition edn. Masson, Paris
Rowsell AR, Davies DM, Eisenberg N, Taylor GI (1984) The anatomy of the subscapular-thoracodorsal arterial system: study of 100 cadaver dissections. Br J Plast Surg 37:574–576
Soares EW (2014) Anatomical variations of the axilla. SpringerPlus 3:306. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-306
Sollazzo V, Luglio G, Esposito E, Di Micco R, Giglio MC, Peltrini R, Schettino P, Amato B, De Palma GD, Limite G (2017) Venous anomalies of the axilla: a single-institution experience. Aging Clin Exp Res 29:139–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-016-0673-8
Testut L (1921) Traité d’Anatomie Humaine. Tome deuxième: Angéiologie—Système nerveux central, vol II. Septième edn. Gaston Doin, Paris
Tountas CP, Bergman RA (1993) Anatomic variations of the upper extremity. Churchill-Livingstone, New York Edinburg London Melbourne Tokyo
Vesalius A (1543) De humani corporis fabrica libri septem, vol Liber VII, cap. I. Basileæ apud I. Oporinum
Wilke J, Krause F, Niederer D, Engeroff T, Nurnberger F, Vogt L, Banzer W (2015) Appraising the methodological quality of cadaveric studies: validation of the QUACS scale. J Anat 226:440–446. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.12292
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the donors of the Institute of Anatomy and Organogenesis of Lille and their families without whom anatomical studies for medical research advancements and education of future healthcare providers would not be possible. We thank Pr José R. Sañudo from the Department of Human Anatomy and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Complutense University of Madrid, for his instructive comments especially about the genesis of variations during development. We thank Pr Christian Vacher, from the Department of Anatomy, Faculté de Médecine Paris-Diderot, URDIA (EA4465), Paris, for his instructive comments to increase the relevance of the manuscript and especially the correlations between arterial and venous arrangements. We thank Maurice De Meulaere, Fabien Descamps, and Franck Stevendart from the Institute of Anatomy and Organogenesis of Lille for their assistance throughout the dissections.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All persons listed as authors have contributed substantially to the design, performance, analysis, and reporting of this work. ML, MH, MD, VH: collected data, analyzed data, wrote paper. VD, PH, DS, RK: analyzed data, wrote paper. ML, CF, LL: Designed study, analyzed data, wrote paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
This work was a part of: Lhuaire, Martin. Étude anatomique des pédicules épigastriques inférieurs, subscapulaire et thoracique interne: Applications chirurgicales. Thèse de Doctorat en Médecine presented and publicly supported on December 2, 2016. No. 2016REIMM136, 2016, Reims, France.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lhuaire, M., Hivelin, M., Derder, M. et al. Anatomical variations of the subscapular pedicle and its terminal branches: an anatomical study and a reappraisal in the light of current surgical approaches. Surg Radiol Anat 41, 385–392 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2161-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2161-7