Abstract
Purpose
The olfactory nerve (OlfN) is a small neural structure with inconsistent visualization on neuroimages. The aim of this study was to delineate the intracranial course of the OlfN using constructive interference in steady state magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
Methods
A total of 168 patients were enrolled in this study. Following initial examinations with conventional MR sequences, constructive interference in steady-state sequence (CISS) was performed in coronal and axial sections.
Results
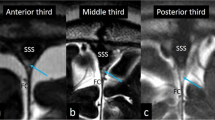
On coronal sections, the OlfN was entirely visualized in 90 % of patients on the right and 92 % on the left, coursing along the olfactory sulcus. Complete visualization of the OlfN occurred in 100 % of patients on serial axial images. The OlfN was classified into four portions based on the topographical differences and surrounding structures. The olfactory fossa exhibited considerable variability at the midlevel of the olfactory bulb on coronal images. Characteristic appearance of the OlfN with respect to age range or gender was not observed.
Conclusions
The OlfN follows a highly consistent course along the olfactory sulcus. Thin-sliced, CISS sequences are useful for consistent visualization of the OlfN.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolmaali N, Gudziol V, Hummel T (2008) Pathology of the olfactory nerve. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 18:233–242
Buschhüter D, Smitka M, Puschmann S, Gerber JC, Witt M, Abolmaali ND, Hummel T (2008) Correlation between olfactory bulb volume and olfactory function. Neuroimage 42:498–502
Cardali S, Romano A, Angileri FF, Conti A, La Torre D, de Divitiis O, d’Avella D, Tschabitscher M, Tomasello (2005) Microsurgical anatomic features of the olfactory nerve: relevance to olfaction preservation in the pterional approach. Neurosurgery 57(1 Suppl):17–21
Castillo M (2002) Imaging of the upper cranial nerves, I, III-VIII, and the cavernous sinus. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 10:415–431
Coello AF, Canals AG, Gonzalez JM, Martin JJ (2010) Cranial nerve injury after minor head trauma. J Neurosurg 113:547–555
Cömert A, Uğur HC, Kahiloğullar G, Elhan A, Tekdemir I (2011) Microsurgical anatomy for intraoperative preservation of the olfactory bulb and tract. J Craniofac Surg 22:1080–1082
Duprez TP, Rombaux P (2010) Imaging the olfactory tract (cranial nerve #1). Eur J Radiol 74:288–298
Favre JJ, Chaffanjon JG, Chirossel JP (1995) Blood supply of the olfactory nerve. Meningeal relationships and surgical relevance. Sur Radiol Anat 17:133–138
Held P, Seitz J, Fründ R, Nitz WR, Haffke T, Hees H, Bonkowsky V (2000) MRI detection of olfactory bulb and tract. J Neuroradiol 27:112–118
Pellicanò G, Capaccioli L, Petacchi D, Dal Pozzo G, Villari N, Gheri G, Bryk SG (1994) Magnetic resonance in the study of cranial nerves. Ital J Anat Embryol 99:229–241
Shiga H, Taki J, Washiyama K, Yamamoto J, Kinase S, Okuda K, Kinuya S, Watanabe N, Tonami H, Koshida K, Amano R, Fukukawa M, Miwa T (2013) Assessment of olfactory nerve by SPECT-MRI image with nasal thallium-201 administration in patients with olfactory impairments in comparison to healthy volunteers. PLoS One 8:e57671
Suzuki M, Takashima T, Kadoya M, Takahashi S, Miyayama S, Taira S (1989) MR imaging of olfactory bulbs and tracts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 10:955–957
Tsuchiya K, Yamakami N, Hachiya J, Kassai Y (1998) MR cisternography using a three-dimensional half-fourier single-shot fast spin-echo sequence. Eur Radiol 8:424–426
Wang SS, Zheng HP, Zhang X, Zhang FH, Jing JJ, Wang RM (2008) Microanatomy and surgical relevance of the olfactory cistern. Microsurgery 28:65–70
Xu F, Kida I, Hyder F, Shulman RG (2000) Assessment and discrimination of odor stimuli in rat olfactory bulb by dynamic functional MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10601–10606
Yousem DM, Maldjian JA, Siddigi F, Hummel T, Aisop DC, Geckle RJ, Bilker WB, Doty RL (1999) Gender effects on odor-stimulated functional magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Res 818:480–487
Zhang Z, Meng Q, Chen Y, Li Z, Luo B, Yang Z, Mao L, Lin E (2008) 3-T imaging of the cranial nerves using three-dimensional reversed FISP with diffusion-weighted MR sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:454–458
Acknowledgments
This work was not supported by grant funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings presented in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsutsumi, S., Ono, H. & Yasumoto, Y. Visualization of the olfactory nerve using constructive interference in steady state magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat 39, 315–321 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1731-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1731-9