Abstract
Background
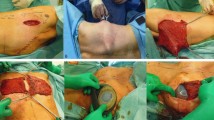
Breast hypoplasia or amastia with pectoralis major muscle defect in female Poland syndrome patients always necessitates surgical intervention. This study aims to introduce an efficient endoscopic technique to perform breast reconstruction in Poland syndrome patients with a latissimus dorsi myo flap and an implant using a single transverse axillary incision (ELDM + IMPLANT) and to evaluate its safety and effectiveness.
Methods
A prospective study was designed to recruit Poland syndrome candidates for ELDM + IMPLANT breast reconstruction. Only one transaxillary incision was made to harvest the LDM flap and create the anterior chest wall pocket. The LDM flap was transposed to the front to reconstruct the breast with a silicone implant. Patient demographics, LDM area, implant size, contralateral symmetry surgery, operative time and post-operative complications were collected. The BREAST-Q reconstruction module was used to evaluate patient quality of life. The disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) outcome questionnaire was used to evaluate patient upper extremity disabilities.
Results
Sixteen eligible patients were recruited and received ELDM + IMPLANT-BR. Mean endoscopic time for LDM flap harvesting was 61.6 min. All of the 16 patients recovered uneventfully without any significant complications. The post-operative scores of satisfaction with breast and psychosocial well-being were significantly higher than the pre-operative ones. The score of DASH was 7.1 pre-operatively and 8.3 post-operatively with no significant difference either. The score of satisfaction with outcome was 80.0.
Conclusions
Our proposed ELDM + IMPLANT technique provides a safe and efficient way to reconstruct breasts in Poland syndrome patients with a high satisfaction rate, optimized aesthetic outcome and minimized donor site morbidity.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these evidence-based medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fokin AA, Robicsek F (2002) Poland’s syndrome revisited. Ann Thorac Surg 74(6):2218–2225
Fodor PB, Khoury F (1980) Latissimus dorsi muscle flap in reconstruction of congenitally absent breast and pectoralis muscle. Ann Plast Surg 4(5):422–425
Fodor PB (1981) Latissimus dorsi flap in Poland’s syndrome. Ann Plast Surg 7(3):258
Seyfer AE, Fox JP, Hamilton CG (2010) Poland syndrome: evaluation and treatment of the chest wall in 63 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 126(3):902–911
Yiyit N, Isitmangil T, Oksuz S (2015) Clinical analysis of 113 patients with Poland syndrome. Ann Thorac Surg 99(3):999–1004
Monticciolo DL, Ross D, Bostwick J 3rd, Eaves F, Styblo T (1996) Autologous breast reconstruction with endoscopic latissimus dorsi musculosubcutaneous flaps in patients choosing breast-conserving therapy: mammographic appearance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167(2):385–389
Cho BC, Lee JH, Ramasastry SS, Baik BS (1997) Free latissimus dorsi muscle transfer using an endoscopic technique. Ann Plast Surg 38(6):586–593
Karp NS, Bass LS, Kasabian AK, Eidelman Y, Hausman MR (1997) Balloon assisted endoscopic harvest of the latissimus dorsi muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg 100(5):1161–1167
Van Buskirk ER, Rehnke RD, Montgomery RL, Eubanks S, Ferraro FJ, Levin LS (1997) Endoscopic harvest of the latissimus dorsi muscle using the balloon dissection technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 99(3):899–903 (discussion 4-5)
Masuoka T, Fujikawa M, Yamamoto H, Ohyama T, Inoue Y, Takao T et al (1998) Breast reconstruction after mastectomy without additional scarring: application of endoscopic latissimus dorsi muscle harvest. Ann Plast Surg 40(2):123–127
Cha W, Jeong WJ, Ahn SH (2013) Latissimus dorsi muscle free flap revisited: a novel endoscope-assisted approach. Laryngoscope 123(3):613–617
Lin CH, Wei FC, Levin LS, Chen MC (1999) Donor-site morbidity comparison between endoscopically assisted and traditional harvest of free latissimus dorsi muscle flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 104(4):1070–1077 (quiz 8)
Guven E, Basaran K, Yazar M, Ozden BC, Kuvat SV, Aydin H (2010) Electrothermal bipolar vessel sealer in endoscope-assisted latissumus dorsi flap harvesting. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech Part A 20(9):735–742
Lee MA, Miteff KG (2014) The scarless latissimus dorsi flap provides effective lower pole prosthetic coverage in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2(5):e147
Yang CE, Roh TS, Yun IS, Kim YS, Lew DH (2014) Immediate partial breast reconstruction with endoscopic latissimus dorsi muscle flap harvest. Arch Plast Surg 41(5):513–519
Serra-Renom JM, Serra-Mestre JM, Martinez L, D’Andrea F (2013) Endoscopic reconstruction of partial mastectomy defects using latissimus dorsi muscle flap without causing scars on the back. Aesthet Plast Surg 37(5):941–949
Missana MC, Pomel C (2007) Endoscopic latissimus dorsi flap harvesting. Am J Surg 194(2):164–169
Iglesias M, Gonzalez-Chapa DR (2013) Endoscopic latissimus dorsi muscle flap for breast reconstruction after skin-sparing total mastectomy: report of 14 cases. Aesthet Plast Surg 37(4):719–727
Pomel C, Missana MC, Atallah D, Lasser P (2003) Endoscopic muscular latissimus dorsi flap harvesting for immediate breast reconstruction after skin sparing mastectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol 29(2):127–131
Pomel C, Missana MC, Lasser P (2002) Endoscopic harvesting of the latissimus dorsi flap in breast reconstructive surgery. Feasibility study and review of the literature. Ann Chir 127(5):337–342
Selber JC, Baumann DP, Holsinger FC (2012) Robotic latissimus dorsi muscle harvest: a case series. Plast Reconstr Surg 129(6):1305–1312
Chung JH, You HJ, Kim HS, Lee BI, Park SH, Yoon ES (2015) A novel technique for robot assisted latissimus dorsi flap harvest. J Plas Reconstr Aesthet Surg JPRAS 68(7):966–972
Pusic AL, Klassen AF, Scott AM, Klok JA, Cordeiro PG, Cano SJ (2009) Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: the BREAST-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg 124(2):345–353
Hudak PL, Amadio PC, Bombardier C (1996) Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand) [corrected] The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG). Am J Ind Med 29(6):602–608
Watfa W, di Summa PG, Raffoul W (2016) Bipolar latissimus dorsi transfer through a single incision: first key-step in poland syndrome chest deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 4(8):e847
Fine NA, Orgill DP, Pribaz JJ (1994) Early clinical experience in endoscopic-assisted muscle flap harvest. Ann Plast Surg 33(5):465–469 (discussion 9-72)
Munoz IVJ, Rodrigues TA, Serra Payro JM, Vinals Vinals JM, Dewever M (2014) Immediate single-stage endoscopic latissimus dorsi breast and nipple reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2(3):e122
Arikawa M, Miyamoto S, Fujiki M, Higashino T, Oshima A, Sakuraba M (2017) Comparison of donor site drainage duration and seroma rate between latissimus dorsi musculocutaneous flaps and thoracodorsal artery perforator flaps. Ann Plast Surg 79(2):183–185
di Santanelli Pompeo F, Laporta R, Sorotos M, Pagnoni M, Falesiedi F, Longo B (2014) Latissimus dorsi flap for total autologous immediate breast reconstruction without implants. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(6):871e–879e
Branford OA, Kelemen N, Hartmann CE, Holt R, Floyd D (2013) Subfascial harvest of the extended latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap in breast reconstruction: a comparative analysis of two techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(4):737–748
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Captital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research 2016-2-4041, PUMC Youth Fund & the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities 3332015156, to Dr. Chunjun Liu, and CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine (CAMS-I2M) (2017-I2M-3-006) to Dr. Jie Luan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights or Ethical Approval
The study has obtained IRB approval from the Ethical Committee of Plastic Surgery Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient prior to the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Dr. Chunjun Liu and Dr. Jie Luan contribute equally as co-corresponding author to this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Endoscopic video of harvesting LDM via transaxillary incision. (MP4 88408 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Luan, J., Ouyang, Y. et al. Breast Reconstruction in Poland Syndrome Patients with Latissimus Dorsi Myo Flap and Implant: An Efficient Endoscopic Approach Using Single Transverse Axillary Incision. Aesth Plast Surg 43, 1186–1194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01346-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01346-0