Abstract
Background
The superomedial vertical scar breast reduction (SVBR) described by Hall-Findlay is gaining popularity among surgeons worldwide. The aim of this study was to evaluate its long-term aesthetic outcome, the extent of quality of life improvement and the factors that influence patient satisfaction and reviewers’ evaluation of aesthetic/surgical outcome.
Methods
In this historical prospective study, we included women who underwent SVBR at least one year prior to enrollment and responded to a quality of life questionnaire. Their breasts were photographed, measured and evaluated by the plastic surgery staff.
Results
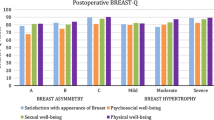
A total of 40 patients responded to the questionnaire, and the breasts of 31 of them were measured and photographed. All 31 patients had good breast symmetry according to objective breast measurements. There was a clear correlation between the patients’ and the reviewers’ scores of breast symmetry, scar appearance and breast shape (r = 0.4–0.65, r = 0.432–0.495 and r = 0.335–0.403, respectively). The factor that most influenced reviewers’ and patients’ satisfaction with the overall aesthetic outcome was the breast-to-body proportion.
Conclusions
The proportions between the breast size and the patient’s body habitus are pivotal to patient satisfaction and should be taken into consideration when planning a reduction mammaplasty. The SVBR technique for breast reduction provided good cosmetic outcome and symmetry over a long-term follow-up.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzalez F, Walton RL, Shafer B et al (1993) Reduction mammaplasty improves symptoms of macromastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 91:1270–1279
Letterman G, Schurter M (1980) The effects of mammary hypertrophy on the skeletal system. Ann Plast Surg 5:425–431
Davis GM, Ringler SL, Short K et al (1995) Reduction mammaplasty: long term efficacy, morbidity, and patient satisfaction. Plast Reconstr Surg 96:1106–1110
Atterhem H, Holmner S, Janson PE (1998) Reduction mammaplasty: symptoms, complications, and late results. Scand J Plast Reconstr Hand Surg 32:281–286
Eggert E, Schuss R, Edsander-Nord A (2009) Clinical outcome, quality of life, patient’s satisfaction, and aesthetic results, after reduction mammaplasty. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 43:201–206
Serletti JM, Reading G, Caldwell E et al (1992) Long term patient satisfaction following reduction mammaplasty. Ann Plast Surg 28:363–365
Wise RJ (1956) A preliminary report of a method of planning the mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 17:367–375
Strombeck JO (1960) Mammaplasty: report of a new technique based on the two-pedicle procedure. Br J Plast Surg 13:79–90
Dufourmentel C, Mouly R (1961) Plastie mammaire par la methode oblique (in French). Ann Chir Plast 6:45–58
Skoog T (1963) A technique of breast reduction: transposition of the nipple on a cutaneous vascular pedicle. Acta Chir Scand 126:453–465
Pitanguy I (1967) Surgical treatment of breast hypertrophy. Br J Plast Surg 20:78–85
Lassus C (1970) A technique for breast reduction. Int Surg 53:69–72
McKissock PK (1972) Reduction mammaplasty with a vertical dermal flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 49:245–252
Regnault P (1974) Reduction mammaplasty by the “B” technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 53:19–24
Ribeiro L (1975) A new technique for reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 55:330–334
Robbins TH (1977) A reduction mammoplasty with the areola-nipple based on an inferior dermal pedicle. Plast Reconstr Surg 59:64–67
Marchac D, de Olarte G (1982) Reduction mammaplasty and correction of ptosis with a short inframammary scar. Plast Reconstr Surg 69:45–55
Hester TR Jr, Bostwick J III, Miller L et al (1985) Breast reduction utilizing the maximally vascularized central breast pedicle. Plast Reconstr Surg 76:890–900
Lejour M, Abboud M, Declety A et al (1990) Reduction of mammaplasty scars: from a short inframammary scar to a vertical scar (in French). Ann Chir Plast Esthet 35:369–379
Benelli L (1990) A new periareolar mammaplasty: the “round block” technique. Aesthet Plast Surg 14:93–100
Hammond DC (1999) Short scar periareolar inferior pedicle reduction (SPAIR) mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:890–891
Hall-Findlay EJ (1999) A simplified vertical reduction mammaplasty: shortening the learning curve. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:748–759
Sampaio Goes JC (2002) Periareolar mammaplasty: double skin technique with application of mesh support. Clin Plast Surg 29:349–364
Blondeel PN, Hamdi M, Van de Sijpe KA et al (2003) The latero-central glandular pedicle technique for breast reduction. Br J Plast Surg 56:48–359
Antony AK, Yegiyants SS, Danielson KK et al (2013) A matched cohort study of superomedial pedicle vertical scar breast reduction (100 breasts) and traditional inferior pedicle wise-pattern reduction (100 breasts): an outcomes study over 3 years. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:1068–1076
Serra P, Longhi P, Sinha M (2010) Breast reduction with a superomedial pedicle and a vertical scar (Hall-Findlay’s technique): experience with 210 consecutive patients. Ann Plast Surg 64:275–278
Lista F, Austin RE, Singh Y et al (2015) Vertical scar reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:23–25
Finger RE, Vasquez B, Drew GS et al (1989) Superomedial pedicle technique of reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 83:471–480
Spear SL, Howard MA (2003) Evolution of the vertical reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:855–868
Chen CM, White C, Warren SM et al (2004) Simplifying the vertical reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:162–172
Yuksel F, Karagoz H, Sever C et al (2012) Experience with vertical mammaplasty: advantages and drawbacks of Hall-Findlay’s superomedial pedicle technique and improving the results by adding modifications to the technique. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36:1329–1333
Birtchnell S, Whitfield P, Lacey JH (1990) Motivational factors in women requesting augmentation and reduction mammaplasty. J Psychosom Res 34:509–514
Catanuto G, Patete P, Spano A et al (2009) New technologies for the assessment of breast surgical outcomes. Aesthet Surg J 29:505–508
Strasser EJ (1999) An objective grading system for the evaluation of cosmetic surgical results. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:2282–2285
Goldwin Y, Wood SH, O’Neill TJ (1998) A comparison of the patient and surgeon opinion on the long-term aesthetic outcome of reduction mammaplasty. Br J Plast Surg 51:444–449
Berg A, Plamer B (1997) Quality assurance in plastic surgery: reduction mammaplasty. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 31:327–331
Westreich M (1997) Anthromorphic breast measurement: protocol and results in 50 women with aesthetically perfect breasts and clinical application. Plast Reconstr Surg 100:468–479
Grossman AJ, Roudner LA (1980) A simple means for accurate breast volume determination. Plast Reconstr Surg 66:851–852
Loughry CW, Sheffer DB, Price TE et al (1989) Breast volume measurement of 598 women using biostereometric analysis. Ann Plast Surg 22:380–385
Daly SE, Kent JC, Huynh DQ et al (1992) The determination of short-term breast volume changes and the rate of synthesis of human milk using computerized breast measurement. Exp Physiol 77:79–87
Herold C, Reichelt A, Stieglitz LH et al (2010) MRI-based breast volumetry-evaluation of three different software solutions. J Digit Imaging 23:603–610
Choppin SB, Wheat JS, Gee M et al (2016) The accuracy of breast volume measurement methods: a systematic review. Breast 28:121–129
Malata CM, Boot JC, Bradbury ET et al (1994) Congenital breast asymmetry: subjective and objective assessment. Br J Plast Surg 47:95–102
Smith DJ, Paline WE, Katch V et al (1986) Surgical treatment of congenital breast asymmetry. Ann Plast Surg 17:92–101
Stark B, Olivary N (1991) Breast asymmetry: an objective analysis of postoperative results. Eur J Plast Surg 14:173–176
Pusic AL, Klassen AF, Scott AM et al (2009) Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: the BREAST-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:345–353
Coriddi M, Nadeau M, Taghizadeh M et al (2013) Analysis of satisfaction and well-being following breast reduction using a validated survey instrument: the BREAST-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:285–290
Meshulam-Derazon S, Barnea Y, Zaretski A et al (2009) Large-volume breast reduction: long-term results. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 43:65–70
Acknowledgements
No outside funding was provided for this paper. Dr. Barnea is a speaker for Johnson Medical. We thank Esther Eshkol for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ron, O., Inbal, A., Arad, E. et al. Superomedial Pedicle Vertical Scar Breast Reduction: Objective and Subjective Assessment of Breast Symmetry and Aesthetics. Aesth Plast Surg 42, 639–647 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-1015-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-1015-8