Abstract
Purpose
Our study aims at the evaluation of the recently introduced Lima Promade custom-made acetabular device for the treatment of complex acetabular Paprosky 3B defects.
Methods
Between 2016 and 2018, eight patients with major acetabular osteolysis and multiple revisions history were treated with a custom-made implant in a single centre and by a single surgeon. We assessed patients’ demographics, peri-operative data, and complications and a specific questionnaire was submitted to the surgeon after each procedure.
Results
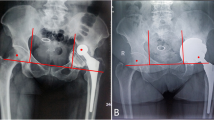
All the devices were correctly positioned. In two over eight cases, a post-operative dislocation occurred, where extensive soft tissue impairment was present. The questionnaire showed a good pre-operative and intra-operative experience of the surgeon.
Conclusions
The Promade custom-made acetabular system showed encouraging results for complex defects and the entire procedure was positively rated. Further analysis with a higher number of cases and a longer follow-up should be performed for a complete clinical and cost-effective evaluation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Australian Orthopedic Association (2017) National joint replacement registry. Annual report 2017
Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M (2007) Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(4):780–785
Kitamura N, Pappedemos PC, Duffy PR 3rd, Stepniewski AS, Hopper RH Jr, Engh CA Jr, Engh CA (2006) The value of anteroposterior pelvic radiographs for evaluating pelvic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 453:239–245
Paprosky WG, Perona PG, Lawrence JM (1994) Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplast 9(1):33–44
Kim DH, Cho SH, Jeong ST, Park HB, Hwang SC, Park JS (2010) Restoration of the center of rotation in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 25(7):1041–1046
Shon WY, Santhanam SS, Choi JW (2016) Acetabular reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis 28(1):1–14
Issack PS, Nousiainen M, Beksac B, Helfet DL, Sculco TP, Buly RL (2009) Acetabular component revision in total hip arthroplasty. Part II: management of major bone loss and pelvic discontinuity. Am J Orthop 38(11):550–556
Myncke I, van Schaik D, Scheerlinck T (2017) Custom-made triflanged acetabular components in the treatment of major acetabular defects. Short-term results and clinical experience. Acta Orthop Belg 83(3):341–350
Paprosky WG, Magnus RE (1994) Principles of bone grafting in revision total hip arthroplasty. Acetabular technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res 298:147–155
Regis D, Sandri A, Bonetti I, Bortolami O, Bartolozzi P (2012) A minimum of 10-year follow-up of the Burch-Schneider cage and bulk allografts for the revision of pelvic discontinuity. J Arthroplast 27(6):1057–1063
Van Kleunen JP, Lee GC, Lementowski PW, Nelson CL, Garino JP (2009) Acetabular revisions using trabecular metal cups and augments. J Arthroplast 24(6):64–68
Petrie J, Sassoon A, Haidukewych GJ (2013) Pelvic discontinuity: current solutions. Bone Joint J 95-B(11 Suppl A):109–113
Taunton MJ, Fehring TK, Edwards P, Bernasek T, Holt GE, Christie MJ (2012) Pelvic discontinuity treated with custom triflange component: a reliable option. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470(2):428–434
Wyatt MC (2015) Custom 3D-printed acetabular implants in hip surgery: innovative breakthrough or expensive bespoke upgrade? Hip Int 25(4):375–379
Sheth NP, Nelson CL, Springer BD, Fehring TK, Paprosky WG (2013) Acetabular bone loss in revision total hip arthroplasty: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 21:128–139
Brubaker SM, Brown TE, Manaswi A et al (2007) Treatment options and allograft use in revision total hip arthroplasty the acetabulum. J Arthroplast 22:52–56
Dammerer D, Putzer D, Glodny B, Petersen J, Arrich F, Krismer M, Biedermann R (2018) Occult intra-operative periprosthetic fractures of the acetabulum may affect implant survival. Int Orthop. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4084-7
Miettinen SS, Mäkinen TJ, Laaksonen I, Mäkelä K, Huhtala H, Kettunen J, Remes V (2017) Early aseptic loosening of cementless monoblock acetabular components. Int Orthop 41(4):715–722
Hansen E, Shearer D, Ries MD (2011) Does a cemented cage improve revision THA for severe acetabular defects? Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:494–502
Schreurs BW, Bolder SB, Gardeniers JW, Verdonschot N, Slooff TJ, Veth RP (2004) Acetabular revision with impacted morsellised cancellous bone grafting and a cemented cup. A 15- to 20-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 86:492–497
Zazgyva A, Zuh SG, Roman CO, Gergely I, Pop TS (2016) Acetabular reconstruction with a reinforcement device and bone grafting in revision arthroplasty-a mean five years of follow-up. Int Orthop 40(8):1631–1638
Mao Y, Xu C, Xu J, Li H, Liu F, Yu D, Zhu Z (2015) The use of customized cages in revision total hip arthroplasty for Paprosky type III acetabular bone defects. Int Orthop 39(10):2023–2030
Massè A, Aprato A, Turchetto L, Rizzi L, Lasagna G, Arrigoni C, Ganz R (2015) Reconstruction with rib graft for acetabular revision in pelvic discontinuity: an extreme solution? Tech Orthop 30(4):269–274
Dewal H, Chen F, Su E, Di Cesare PE (2003) Use of structural bone graft with cementless acetabular cups in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 18:23–28
Flecher X, Appy B, Parratte S, Ollivier M, Argenson JN (2017) Use of porous tantalum components in Paprosky two and three acetabular revision. A minimum five-year follow-up of fifty one hips. Int Orthop 41(5):911–916
Ballester Alfaro JJ, Sueiro Fernández J (2010) Trabecular metal buttress augment and the trabecular metal cup-cage construct in revision hip arthroplasty for severe acetabular bone loss and pelvic discontinuity. Hip Int 20(Suppl 7):S119–S127
Aprato A, D’Amelio A, Marra F, Favuto MM, Mellano D, Massè A (2017) 3D customizing in revision hip replacement. In: Aprato A (ed) 3d applications in hip surgery, 1st edn. Nova biomedical, New York, pp 162–163
Holt GE, Dennis DA (2004) Use of custom triflanged acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 429:209–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aprato, A., Giachino, M., Bedino, P. et al. Management of Paprosky type three B acetabular defects by custom-made components: early results. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 43, 117–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4203-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4203-5