Abstract
Purpose
Purpose of the present cohort study was the determination of lower body function and rotation in patients with symptomatic component mal-rotation after total knee arthroplasty using instrumented 3D gait analysis.
Methods
A consecutive series of 12 patients (61.3 years ± 11.4 years) were included suffering under remaining pain or limited range of motion at least six months after total knee arthroplasty. A CT-scan according to the protocol of Berger et al. and instrumented 3D gait analysis were carried out including clinical examination, videotaping, and kinematic analysis using a Plug-in Gait model. Outcome variables were temporospatial parameters as well as kinematics in sagittal and transversal plane. Data for reference group were collected retrospectively and matched by age and gender.
Results
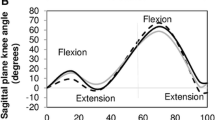
Temporospatial parameters of the study group showed decreased velocity, cadence, and step length as well as increased step time. Single limb support was reduced for the affected limb. In sagittal plane, maximum knee flexion during swing phase was reduced for the replaced knee joint. In transverse plane, there was hardly any difference between affected and non-affected limb. Compared to the reference group, both limbs show significant increased internal ankle rotation and external hip rotation. There were significant strong linear correlations between ankle rotation and hip rotation as well as ankle rotation and radiological tibial mal-rotation.
Conclusions
Patients with symptomatic component mal-rotation after total knee arthroplasty showed typically functional deficits. The affected and non-affected limb showed significant increased internal ankle rotation and external hip rotation, while only the affected, replaced knee showed reduced internal knee rotation. Identification of rotational abnormalities of hip and ankle joints seems to be mandatory in TKA to identify the patient group with external hip rotation, internal ankle rotation, and an elevated risk for symptomatic rotational TKA component mal-alignment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicoll D, Rowley DI (2010) Internal rotational error of the tibial component is a major cause of pain after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(9):1238–1244. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.92b9.23516
Dunbar MJ, Robertsson O, Ryd L, Lidgren L (2000) Translation and validation of the Oxford-12 item knee score for use in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand 71(3):268–274. https://doi.org/10.1080/000164700317411861
Nunez M, Nunez E, del Val JL, Ortega R, Segur JM, Hernandez MV, Lozano L, Sastre S, Macule F (2007) Health-related quality of life in patients with osteoarthritis after total knee replacement: factors influencing outcomes at 36 months of follow-up. Osteoarthr Cartil 15(9):1001–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2007.02.019
Nilsdotter AK, Toksvig-Larsen S, Roos EM (2009) Knee arthroplasty: are patients’ expectations fulfilled? A prospective study of pain and function in 102 patients with 5-year follow-up. Acta Orthop 80(1):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453670902805007
Beswick AD, Wylde V, Gooberman-Hill R, Blom A, Dieppe P (2012) What proportion of patients report long-term pain after total hip or knee replacement for osteoarthritis? A systematic review of prospective studies in unselected patients. BMJ Open 2(1):e000435. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000435
Lim HA, Song EK, Seon JK, Park KS, Shin YJ, Yang HY (2017) Causes of aseptic persistent pain after Total knee arthroplasty. Clinics in orthopedic surgery 9(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.1.50
Jaen F, Sanz-Gallardo MI, Arrazola MP, Garcia de Codes A, de Juanes A, Resines C (2012) Multicentre study of infection incidence in knee prosthesis. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol 56(1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.recot.2011.08.001
Michalik R, Rath B, Springorum HR, Luring C, Tingart M (2016) Anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty: causes, diagnosis and treatment. Der Orthopade 45(5):386–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00132-016-3256-7
Bell SW, Young P, Drury C, Smith J, Anthony I, Jones B, Blyth M, McLean A (2014) Component rotational alignment in unexplained painful primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee 21(1):272–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2012.09.011
Bedard M, Vince KG, Redfern J, Collen SR (2011) Internal rotation of the tibial component is frequent in stiff total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(8):2346–2355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1889-8
De Valk EJ, Noorduyn JC, Mutsaerts EL (2016) How to assess femoral and tibial component rotation after total knee arthroplasty with computed tomography: a systematic review. Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc: Off J ESSKA 24 (11):3517–3528. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4325-5
Hirschmann MT, Konala P, Amsler F, Iranpour F, Friederich NF, Cobb JP (2011) The position and orientation of total knee replacement components: a comparison of conventional radiographs, transverse 2D-CT slices and 3D-CT reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(5):629–633. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.93b5.25893
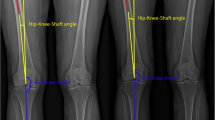
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Sternheim A, Lochab J, Drexler M, Kuzyk P, Safir O, Gross A, Backstein D (2012) The benefit of revision knee arthroplasty for component malrotation after primary total knee replacement. Int Orthop 36(12):2473–2478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1675-6
Pietsch M, Hofmann S (2012) Early revision for isolated internal malrotation of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc: Off J ESSKA 20(6):1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1637-3
Lakstein D, Zarrabian M, Kosashvili Y, Safir O, Gross AE, Backstein D (2010) Revision total knee arthroplasty for component malrotation is highly beneficial: a case control study. J Arthroplast 25(7):1047–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2009.07.004
Wolf SI (2013) Rolle der Bewegungsanalyse in Orthopadie und Unfallchirurgie. Trauma Berufskrankh 15(4):266–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10039-013-2039-1
Miller MC, Berger RA, Petrella AJ, Karmas A, Rubash HE (2001) Optimizing femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:38–45
McClelland JA, Webster KE, Feller JA (2007) Gait analysis of patients following total knee replacement: a systematic review. Knee 14(4):253–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.003
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res (286):40–47
Kadaba MP, Ramakrishnan HK, Wootten ME (1990) Measurement of lower extremity kinematics during level walking. J Orthop Res: Off Publ Orthop Res Soc 8(3):383–392. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.1100080310
Saku SA, Madanat R, Makinen TJ (2018) Reasons and risk factors for ninety day re-admission following primary total knee arthroplasty in a high-volume centre. Int Orthop 42(1):95–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3676-y
Pedraza W, Beckmann J, Mayer C, Mauch F, Huth J, Best R (2016) Partially loaded plain radiographic measurement to evaluate rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 40(12):2519–2526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3247-7
Sailhan F, Jacob L, Hamadouche M (2017) Differences in limb alignment and femoral mechanical-anatomical angles using two dimension versus three dimension radiographic imaging. Int Orthop 41(10):2009–2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3428-z
Bonnefoy-Mazure A, Martz P, Armand S, Sagawa Y Jr, Suva D, Turcot K, Miozzari HH, Lubbeke A (2017) Influence of body mass index on sagittal knee range of motion and gait speed recovery 1-year after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.03.008
Trinler UK, Baty F, Mundermann A, Fenner V, Behrend H, Jost B, Wegener R (2016) Stair dimension affects knee kinematics and kinetics in patients with good outcome after TKA similarly as in healthy subjects. J Orthop Res: Off Publ Orthop Res Soc 34(10):1753–1761. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maier, M.W., Aschauer, S., Wolf, S.I. et al. Three dimensional gait analysis in patients with symptomatic component mal-rotation after total knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 43, 1371–1378 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4118-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4118-1