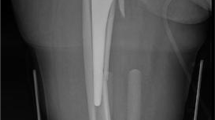
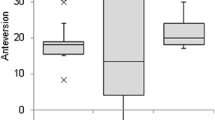
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore the indications for the two most frequently applied surgical procedures for benign lesions in the proximal femur.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 142 patients with benign lesions in the proximal femur from January 2010 to January 2015. Internal fixation (IF) was adopted in 110 patients, while endoprosthetic replacement (EPR) was applied in 32 patients. Clinical data, including operation time, blood loss, hospitalization time, and hospitalization expenses, were compared between the groups. Limb mobilization was evaluated by the Musculoskeletal Tumor Society Score-93 (MSTS-93) and Harris Hip Score (HHS). Local recurrences and complications were statistically compared.
Results
The average follow-up was 66 months (range 32–84 months). In the EPR group, operation time and hospitalization time were significantly shorter (p < 0.05 and p < 0.05, respectively), while blood loss and hospitalization expenses were significantly higher (p < 0.05 and p < 0.05, respectively). Functional outcomes of the MSTS-93 and HHS were higher at the three week follow-up in the EPR group (p < 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively) but lower at 6 months (p = 0.031 and p = 0.042, respectively). No differences were observed in the two scores at three months (p = 0.261 and p = 0.134, respectively). Local recurrence and complication rates were similar in the two groups (p = 0.895 and p = 0.942, respectively).
Conclusion
The strategy for benign proximal femur lesions should depend on the site, size, initial diagnosis, and thinning degree of cortical bone. IF and EPR both result in satisfactory local control and functional and radiological results, while EPR is more suitable for aggressive and recurrent lesions and serves as an effective measure after IF failure.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wai EK, Davis AM, Griffin A, Bell RS, Wunder JS (2001) Pathologic fractures of the proximal femur secondary to benign bone tumors. Clin Orthop Relat Res 393:279–286
Shih HN, Cheng CY, Chen YJ, Huang TJ, Hsu RW (1996) Treatment of the femoral neck amd trochanteric benign lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 328:220–226
Jaffe KA, Dunham WK (1990) Treatment of benign lesions of the femoral head and neck. Clin Orthop Relat Res 257:134–137
Zhang X, Chen C, Duan H, Tu C (2015) Radiographic classification and treatment of fibrous dysplasia of the proximal femur: 227 femurs with a mean follow-up of 6 years. J Orthop Surg Res 10:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-015-0313-6
Wijsbek AE, Vazquez-Garcia BL, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, Abudu AA, Tillman RM, Jeys L (2014) Giant cell tumour of the proximal femur: is joint-sparing management ever successful? Bone Joint J 96-B(1):127–131. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.96B1.31763
Chen F, Xia J, Wang S, Wei Y, Wu J, Huang G, Chen J, Shi J (2013) Use of extended curettage with osteotomy and fenestration followed by reconstruction with conservation of muscle insertion in the treatment of Enneking stage II locally aggressive bone tumor of the proximal extremities: resection and treatment of bone tumors. World J Surg Oncol 11:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7819-11-54
Shin SH, Yeo I, Seo SW (2013) Can certain benign lesions of the proximal femur be treated without surgery? Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(10):3319–3325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3048-x
Carvallo PI, Griffin AM, Ferguson PC, Wunder JS (2015) Salvage of the proximal femur following pathological fractures involving benign bone tumors. J Surg Oncol 112(8):846–852. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.24072
Erol B, Topkar MO, Aydemir AN, Okay E, Caliskan E, Sofulu O (2016) A treatment strategy for proximal femoral benign bone lesions in children and recommended surgical procedures: retrospective analysis of 62 patients. Arch Orthop Traum Surg 136(8):1051–1061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-016-2486-9
Jeys LM, Suneja R, Chami G, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, Tillman RM (2006) Impending fractures in giant cell tumours of the distal femur: incidence and outcome. Int Orthop 30(2):135–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-005-0061-z
Farid Y, Lin PP, Lewis VO, Yasko AW (2006) Endoprosthetic and allograft-prosthetic composite reconstruction of the proximal femur for bone neoplasms. Clin Orthop Relat Res 442:223–229
Mirels H (1989) Metastatic disease in long bones. A proposed scoring system for diagnosing impending pathologic fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 249:256–264
Enneking WF, Dunham W, Gebhardt MC, Malawar M, Pritchard DJ (1993) A system for the functional evaluation of reconstructive procedures after surgical treatment of tumors of the musculoskeletal system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:241–246
Mac NR, Quinlan JF, Stapleton RD, Hurson B, Dudeney S, O'Toole GC (2011) Inter- and intra-observer variability associated with the use of the Mirels’ scoring system for metastatic bone lesions. Int Orthop 35(1):83–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0941-8
Cumming D, Cumming J, Vince A, Benson R (2009) Metastatic bone disease: the requirement for improvement in a multidisciplinary approach. Int Orthop 33(2):493–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0556-5
Guille JT, Kumar SJ, MacEwen GD (1998) Fibrous dysplasia of the proximal part of the femur. Long-term results of curettage and bone-grafting and mechanical realignment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80(5):648–658
Riha D, Bartonicek J (2010) Internal fixation of pertrochanteric fractures using DHS with a two-hole side-plate. Int Orthop 34(6):877–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0840-z
Hu YC, Lun DX, Zhao SK (2012) Combined anterior and lateral approaches for bone tumors of the femoral neck and head. Orthopedics 35(5):e628–e634. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20120426-14
Nakamura T, Matsumine A, Asanuma K, Matsubara T, Sudo A (2015) Treatment of the benign bone tumors including femoral neck lesion using compression hip screw and synthetic bone graft. SICOT J 1:15. https://doi.org/10.1051/sicotj/2015009
Han N, Sun G, Li Z, Li G, Lu Q, Han Q, Wei X (2011) Comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation blade and reverse less invasive stabilization system-distal femur systems in the treatment of proximal femoral fractures. Orthop Surg 3(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1757-7861.2010.00118.x
Zhang Y, Li JZ, Lu XC, Zhang Y, Zhang HS, Shi HL, Lei Z, Feng G, Fu WP (2017) Intramedullary nailing combined with bone grafting for benign lesions of the proximal femur. Orthop Surg 9(1):97–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/os.12311
Niu X, Zhang Q, Hao L, Ding Y, Li Y, Xu H, Liu W (2012) Giant cell tumor of the extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(5):461–467. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.01922
Sakayama K, Sugawara Y, Kidani T, Miyawaki J, Fujibuchi T, Kamei S, Aizawa J, Yamamoto H (2007) Diagnostic and therapeutic problems of giant cell tumor in the proximal femur. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127(10):867–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-007-0419-3
Han I, Choi ES, Kim HS (2014) Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the proximal femur: natural history and predisposing factors for disease progression. Bone Joint J 96-B(5):673–676. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.96B5.33281
Sierra RJ, Cabanela ME (2009) Total hip arthroplasty in patients with underlying fibrous dysplasia. Orthopedics 32(5):320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures in studies involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research community and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Fang, X., Yu, Z. et al. Surgical strategy for benign lesions in proximal femur: internal fixation or endoprosthetic replacement. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 42, 2691–2698 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3922-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3922-y