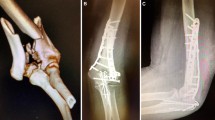
Abstract
Purpose
In distal humerus fractures, the goal is to achieve a functional range of motion of 30°–130° which is not always possible. The aims of the study were to evaluate the functional results after distal humerus fracture operation and to investigate the risk factors for stiffness.
Methods
Between 2005 and 2014, 75 patients with the mean age of 37.8 years (17–80) underwent open reduction and plate fixation for distal humerus fractures. Range of motion (ROM), Mayo elbow performance scores, and quick DASH scores were used for functional evaluation. Patients were divided into two groups according their ROM. Group 1 had > 100° of extension-flexion ROM and group 2 had < 100°. Older age (> 60), AO type C2–3 fracture, open fracture, longer injury-surgery interval, type of plating, and presence of olecranon osteotomy were investigated as risk factors for poor outcome.
Results
At a mean follow-up of 25 months (6–80), 40 patients were in group 1 and 35 patients were in group 2. Group 1 had significantly better functional scores than group 2. AO type C2 and C3 fracture (odds ratio (OR) 16.6, p < 0.0001) and injury-surgery interval longer than 7 days (OR 2.59, p 0.047) were found as significant risk factors for stiffness.
Conclusions
Patients who had distal humerus fracture should be informed about the risk of elbow stiffness especially in AO type C2–C3 fractures and surgical treatment should be planned without any delay.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rose SH, Melton LJ, 3rd, Morrey BF, Ilstrup DM, Riggs BL (1982) Epidemiologic features of humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res (168):24–30
Gupta R, Khanchandani P (2002) Intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus in adults: a critical analysis of 55 cases. Injury 33(6):511–515
Nauth A, McKee MD, Ristevski B, Hall J, Schemitsch EH (2011) Distal humeral fractures in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93(7):686–700. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.00845
Sodergard J, Sandelin J, Bostman O (1992) Mechanical failures of internal fixation in T and Y fractures of the distal humerus. J Trauma 33(5):687–690
Zhang C, Zhong B, Luo CF (2014) Comparing approaches to expose type C fractures of the distal humerus for ORIF in elderly patients: six years clinical experience with both the triceps-sparing approach and olecranon osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134(6):803–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-1983-y
Lawrence TM, Ahmadi S, Morrey BF, Sanchez-Sotelo J (2014) Wound complications after distal humerus fracture fixation: incidence, risk factors, and outcome. J Shoulder Elb Surg 23(2):258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2013.09.014
Morrey BF, Askew LJ, Chao EY (1981) A biomechanical study of normal functional elbow motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 63(6):872–877
Radoicic D, Micic I, Dasic Z, Kosutic M (2014) Does timing of surgery affect the outcome of open articular distal humerus fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24(5):777–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1358-z
Elmadag M, Erdil M, Bilsel K, Acar MA, Tuncer N, Tuncay I (2014) The olecranon osteotomy provides better outcome than the triceps-lifting approach for the treatment of distal humerus fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-012-1149-y
Min W, Ding BC, Tejwani NC (2012) Comparative functional outcome of AO/OTA type C distal humerus fractures: open injuries do worse than closed fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 72(2):E27–E32
Gustilo RB, Anderson JT (1976) Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am 58(4):453–458
Pidhorz L, Alligand-Perrin P, De Keating E, Fabre T, Mansat P, Societe francaise de chirurgie orthopedique et al (2013) Distal humerus fracture in the elderly: does conservative treatment still have a role? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(8):903–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.10.001
Charissoux JL, Vergnenegre G, Pelissier M, Fabre T, Mansat P, Sofcot (2013) Epidemiology of distal humerus fractures in the elderly. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(7):765–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.08.002
Atalar AC, Demirhan M, Salduz A, Kilicoglu O, Seyahi A (2009) Functional results of the parallel-plate technique for complex distal humerus fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 43(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.3944/AOTT.2009.021
Huang TL, Chiu FY, Chuang TY, Chen TH (2005) The results of open reduction and internal fixation in elderly patients with severe fractures of the distal humerus: a critical analysis of the results. J Trauma 58(1):62–69
Muzaffar N, Bhat K, Ahmad R, Wani R, Dar M (2014) Functional results after osteosynthesis of distal humeral fractures with pre-contoured LCP system. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 16(4):381–385. https://doi.org/10.5604/15093492.1119615
Proust J, Oksman A, Charissoux JL, Mabit C, Arnaud JP (2007) Intra-articular fracture of the distal humerus: outcome after osteosynthesis in patients over 60. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 93(8):798–806
Clavert P, Ducrot G, Sirveaux F, Fabre T, Mansat P, Sofcot (2013) Outcomes of distal humerus fractures in patients above 65 years of age treated by plate fixation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(7):771–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.08.001
Begue T (2014) Articular fractures of the distal humerus. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 100(1 Suppl):S55–S63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.11.002
Mansat P, Nouaille Degorce H, Bonnevialle N, Demezon H, Fabre T, Sofcot (2013) Total elbow arthroplasty for acute distal humeral fractures in patients over 65 years old—results of a multicenter study in 87 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(7):779–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.08.003
Obert L, Ferrier M, Jacquot A, Mansat P, Sirveaux F, Clavert P, Charissoux JL, Pidhorz L, Fabre T, Societe Francaise de Chirurgie Orthopedique et al (2013) Distal humerus fractures in patients over 65: complications. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(8):909–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.10.002
Hong CC, Nashi N, Hey HW, Chee YH, Murphy D (2015) Clinically relevant heterotopic ossification after elbow fracture surgery: a risk factors study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 101(2):209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2014.10.021
Werner BC, Rawles RB, Jobe JT, Chhabra AB, Freilich AM (2015) Obesity is associated with increased postoperative complications after operative management of distal humerus fractures. J Shoulder Elb Surg 24(10):1602–1606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.04.019
Chen G, Liao Q, Luo W, Li K, Zhao Y, Zhong D (2011) Triceps-sparing versus olecranon osteotomy for ORIF: analysis of 67 cases of intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus. Injury 42(4):366–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2010.09.004
Atalar AC, Tunali O, Ersen A, Kapicioglu M, Saglam Y, Demirhan MS (2017) Biomechanical comparison of orthogonal versus parallel double plating systems in intraarticular distal humerus fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 51(1):23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aott.2016.11.001
Kollias CM, Darcy SP, Reed JG, Rosvold JM, Shrive NG, Hildebrand KA (2010) Distal humerus internal fixation: a biomechanical comparison of 90 degrees and parallel constructs. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 39(9):440–444
Koonce RC, Baldini TH, Morgan SJ (2012) Are conventional reconstruction plates equivalent to precontoured locking plates for distal humerus fracture fixation? A biomechanics cadaver study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 27(7):697–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2012.03.008
Shin SJ, Sohn HS, Do NH (2010) A clinical comparison of two different double plating methods for intraarticular distal humerus fractures. J Shoulder Elb Surg 19(1):2–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2009.05.003
Lee SK, Kim KJ, Park KH, Choy WS (2014) A comparison between orthogonal and parallel plating methods for distal humerus fractures: a prospective randomized trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24(7):1123–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1286-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of İstanbul University İstanbul Medical Faculty Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tunalı, O., Erşen, A., Pehlivanoğlu, T. et al. Evaluation of risk factors for stiffness after distal humerus plating. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 42, 921–926 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3792-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3792-3