Abstract
Purpose
Vγ9Vδ2 (γδ) T lymphocytes, a critical peripheral blood lymphocyte subset, are directly cytotoxic against many solid and hematologic tumor types. Vγ9Vδ2 T lymphocytes can be selectively expanded in vivo with BrHPP (IPH1101) and IL-2. The present phase I trial was conducted with the aim of determining the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD) and safety of IPH1101 combined with a low dose of IL-2 in patients with solid tumors.
Experimental design
A 1-h intravenous infusion of IPH11 was administered alone at cycle 1, combined with a low dose of SC IL-2 (1 MIU/M2 d1 to d7) in the subsequent cycles (day 1 every 3 weeks). The dose of IPH1101 was escalated from 200 to 1,800 mg/m2.
Results
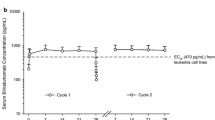
As much as 28 patients with solid tumors underwent a total of 109 treatment cycles. Pharmacodynamics data demonstrate that γδ T lymphocyte amplification in humans requires the co-administration of IL-2 and is dependent on IPH 1101 dose. Dose-limiting toxicity occurred in two patients at a dose of 1,800 mg/m2: one grade 3 fever (1 patient) and one grade 3 hypotension (1 patient) suggesting cytokine release syndrome immediately following the first infusion. At lower doses the treatment was well tolerated; the most frequent adverse events were mild fever, chills and abdominal pain, without exacerbation in the IL-2 combined cycles.
Conclusion
IPH1101 in combination with SC low-dose IL-2 is safe, well tolerated and induces a potent γδ T lymphocyte expansion in patients. Its clinical activity will be evaluated in phase II clinical trials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choudhary A, Davodeau F, Moreau A, Peyrat MA, Bonneville M, Jotereau F (1995) Selective lysis of autologous tumor cells by recurrent gamma delta tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from renal carcinoma. J Immunol 154:3932–3940
Viey E, Fromont G, Escudier B et al (2005) IPH1101-activated gamma delta T cells kill autologous metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Immunol 174:1338–1347
Bachelez H, Flageul B, Degos L, Boumsell L, Bensussan A (1992) TCR gamma delta bearing T lymphocytes infiltrating human primary cutaneous melanomas. J Invest Dermatol 98:369–374
Bouet-Toussaint F, Cabillic F, Toutirais O, Le Gallo M, Thomas de la Pintière C, Daniel P, Genetet N, Meunier B, Dupont-Bierre E, Boudjema K, Catros V (2008) Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell-mediated recognition of human solid tumors Potential for immunotherapy of hepatocellular and colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:531–539
Wrobel P, Shojaei H, Schittek B, Gieseler F, Wollenberg B, Kalthoff H, Kabelitz D, Wesch D (2007) Lysis of a broad range of epithelial tumour cells by human gamma delta T cells: involvement of NKG2D ligands and T-cell receptor-versus NKG2D-dependent recognition. Scand J Immunol 66:320–328
Corvaisier M, Moreau-Aubry A, Diez E, Bennouna J, Mosnier JF, Scotet E, Bonneville M, Jotereau F (2005) V gamma 9V delta 2 T cell response to colon carcinoma cells. J Immunol 175:5481–5488
Murayama M, Tanaka Y, Yagi J, Uchiyama T, Ogawa K (2008) Antitumor activity and some immunological properties of gammadelta T-cells from patients with gastrointestinal carcinomas. Anticancer Res 28:2921–2931
Bryant NL, Suarez-Cuervo C, Gillespie GY, Markert JM, Nabors LB, Meleth S, Lopez RD, Lamb LS Jr (2009) Characterization and immunotherapeutic potential of gammadelta T-cells in patients with glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 11:3557–3567
Todaro M, D’Asaro M, Caccamo N, Iovino F, Francipane MG, Meraviglia S, Orlando V, La Mendola C, Gulotta G, Salerno A, Dieli F, Stassi G (2009) Efficient killing of human colon cancer stem cells by gammadelta T lymphocytes. J Immunol 182:7287–7296
Chen J, Niu H, He W, Ba D (2001) Antitumor activity of expanded human tumor-infiltrating gammadelta T lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 125:256–263
Kang N, Zhou J, Zhang T, Wang L, Lu F, Cui Y, Cui L, He W (2009) Adoptive immunotherapy of lung cancer with immobilized anti-TCR gammadelta antibody-expanded human gammadelta T-cells in peripheral blood. Cancer Biol Ther 8:1540–1549
Viey E, Lucas C, Romagne F, Escudier B, Chouaib S, Caignard A (2008) Chemokine receptors expression and migration potential of tumor-infiltrating and peripheral-expanded Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells from renal cell carcinoma patients. J Immunother 31:313–323
Espinosa E, Belmant C, Pont F, Luciani B, Poupot R, Romagné F, Brailly H, Bonneville M, Fournié JJ (2001) Chemical synthesis and biological activity of bromohydrin pyrophosphate, a potent stimulator of human gamma delta T cells. J Biol Chem 276:18337–18344
Wilhelm M, Kunzmann V, Eckstein S, Reimer P, Weissinger F, Ruediger T, Tony HP (2003) Gammadelta T cells for immune therapy of patients with lymphoid malignancies. Blood 102:200–206
Dieli F, Vermijlen D, Fulfaro F, Caccamo N, Meraviglia S, Cicero G, Roberts A, Buccheri S, D’Asaro M, Gebbia N, Salerno A, Eberl M, Hayday AC (2007) Targeting human gammadelta T cells with zoledronate and interleukin-2 for immunotherapy of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res 67:7450–7457
Sicard H, Ingoure S, Luciani B, Serraz C, Fournié JJ, Bonneville M, Tiollier J, Romagné F (2005) In vivo immunomanipulation of V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells with a synthetic phosphoantigen in a preclinical nonhuman primate model. J Immunol 175:5471–5480
Bennouna J, Bompas E, Neidhardt EM, Rolland F, Philip I, Galéa C, Salot S, Saiagh S, Audrain M, Rimbert M, Lafaye-de Micheaux S, Tiollier J, Négrier S (2008) Phase-I study of Innacell gammadelta, an autologous cell-therapy product highly enriched in gamma9delta2 T lymphocytes, in combination with IL-2, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:1599–1609
Casetti R, Perretta G, Taglioni A, Mattei M, Colizzi V, Dieli F, D’Offizi G, Malkovsky M, Poccia F (2005) Drug-induced expansion and differentiation of V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells in vivo: the role of exogenous IL-2. J Immunol 175:1593–1598
Laurent G, Lafaye de Micheaux S, Solal-Celigny P, Soubeyran P, Delwail V, Ghesquieres H, Thieblemont C, Jourdan E, Beautier L, Audibert F, Squiban P, Sicard H, Rossi JF (2009) Phase I/II study of IPH1101, γδ T cell agonist, combined with rituximab, in low grade follicular lymphoma patients. Blood 114:658–659
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennouna, J., Levy, V., Sicard, H. et al. Phase I study of bromohydrin pyrophosphate (BrHPP, IPH 1101), a Vγ9Vδ2 T lymphocyte agonist in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59, 1521–1530 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-010-0879-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-010-0879-0