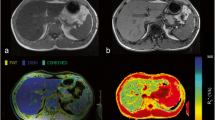
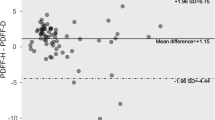
Abstract
Purpose
To compare qualitative results obtained from computer-aided dual-ratio analysis on T1-weighted two-point Dixon, with T2*-corrected multi-echo Dixon and T2-corrected multi-echo single-voxel MR spectroscopy sequence (MRS) for evaluation of liver fat and iron at 3T.
Methods and materials
This retrospective, HIPAA-compliant, IRB-approved study included 479 patients with known or suspected liver disease. Two-point Dixon, multi-echo Dixon, and MR spectroscopy sequences were performed for each patient at 3T. A receiver-operating characteristic analysis was performed to compare the diagnostic performance in 80 patients using biopsy as the standard. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of qualitative two-point Dixon results, multi-echo Dixon (PDFF and R2*), and MRS (fat fraction and R2 water) for detection of hepatic steatosis and siderosis were assessed.
Results
Fat fractions obtained from MRS and multi-echo Dixon have equivalent accuracy for detection of hepatic steatosis (AUC, sensitivity and specificity: 0.90 vs 0.88, 0.77 vs. 0.82, and 0.90 vs. 0.82), but the optimal cutoff value is higher for MRS (6.05% vs. 3.4%). The dual-ratio Dixon discrimination technique showed high negative predictive value for detection of hepatic steatosis and siderosis (0.90 and 0.94, respectively). R2* from multi-echo Dixon and R2water from MRS have equivalent accuracy for detection of iron overload at 3T (AUC 0.89 vs. 0.88). The optimal cutoff for R2* and R2water are 60.5 s−1 and 40.85 s−1, respectively.
Conclusion
The computer-aided dual-ratio discrimination with two-point Dixon is a useful qualitative screening tool with high negative predictive value for hepatic steatosis and iron overload. Multi-echo Dixon and MRS have similar accuracy for detection of hepatic steatosis and iron overload at 3 Tesla.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Association for the Study of the, L., D. European Association for the Study of, and O. European Association for the Study of (2016) EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol, 64(6): p. 1388-402.
Younossi, Z.M., M. Stepanova, M. Afendy, Y. Fang, Y. Younossi, et al. (2011) Changes in the prevalence of the most common causes of chronic liver diseases in the United States from 1988 to 2008. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 9(6): p. 524-530 e1; quiz e60.
Browning, J.D., L.S. Szczepaniak, R. Dobbins, P. Nuremberg, J.D. Horton, et al. (2004) Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology, 40(6): p. 1387-95.
Ratziu, V., F. Charlotte, A. Heurtier, S. Gombert, P. Giral, et al. (2005) Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology, 128(7): p. 1898-906.
Van Beers, B.E., P. Garteiser, B. Leporq, P.E. Rautou, and D. Valla (2017) Quantitative Imaging in Diffuse Liver Diseases. Semin Liver Dis, 37(3): p. 243-258.
Pineda, N., P. Sharma, Q. Xu, X. Hu, M. Vos, et al. (2009) Measurement of hepatic lipid: high-speed T2-corrected multiecho acquisition at 1H MR spectroscopy–a rapid and accurate technique. Radiology, 252(2): p. 568-76.
Yu, H., C.A. McKenzie, A. Shimakawa, A.T. Vu, A.C. Brau, et al. (2007) Multiecho reconstruction for simultaneous water-fat decomposition and T2* estimation. J Magn Reson Imaging, 26(4): p. 1153-61.
Yu, H., A. Shimakawa, C.A. McKenzie, E. Brodsky, J.H. Brittain, et al. (2008) Multiecho water-fat separation and simultaneous R2* estimation with multifrequency fat spectrum modeling. Magn Reson Med, 60(5): p. 1122-34.
Bydder, M., T. Yokoo, G. Hamilton, M.S. Middleton, A.D. Chavez, et al. (2008) Relaxation effects in the quantification of fat using gradient echo imaging. Magn Reson Imaging, 26(3): p. 347-59.
Kuhn, J.P., D. Hernando, B. Mensel, P.C. Kruger, T. Ittermann, et al. (2014) Quantitative chemical shift-encoded MRI is an accurate method to quantify hepatic steatosis. J Magn Reson Imaging, 39(6): p. 1494-501.
Hines, C.D., A. Frydrychowicz, G. Hamilton, D.L. Tudorascu, K.K. Vigen, et al. (2011) T(1) independent, T(2) (*) corrected chemical shift based fat-water separation with multi-peak fat spectral modeling is an accurate and precise measure of hepatic steatosis. J Magn Reson Imaging, 33(4): p. 873-81.
Zhong, X., M.D. Nickel, S.A. Kannengiesser, B.M. Dale, B. Kiefer, et al. (2014) Liver fat quantification using a multi-step adaptive fitting approach with multi-echo GRE imaging. Magn Reson Med, 72(5): p. 1353-65.
Bashir, M.R., E.M. Merkle, A.D. Smith, and D.T. Boll (2012) Hepatic MR imaging for in vivo differentiation of steatosis, iron deposition and combined storage disorder: single-ratio in/opposed phase analysis vs. dual-ratio Dixon discrimination. Eur J Radiol, 81(2): p. e101-9.
Wood, J.C., P. Zhang, H. Rienhoff, W. Abi-Saab, and E.J. Neufeld (2015) Liver MRI is more precise than liver biopsy for assessing total body iron balance: a comparison of MRI relaxometry with simulated liver biopsy results. Magn Reson Imaging, 33(6): p. 761-7.
Rose, C., P. Vandevenne, E. Bourgeois, N. Cambier, and O. Ernst (2006) Liver iron content assessment by routine and simple magnetic resonance imaging procedure in highly transfused patients. Eur J Haematol, 77(2): p. 145-9.
Lin, H., H. Wei, N. He, C. Fu, S. Cheng, et al. (2018) Quantitative susceptibility mapping in combination with water-fat separation for simultaneous liver iron and fat fraction quantification. Eur Radiol, 28(8): p. 3494-3504.
Meisamy, S., C.D. Hines, G. Hamilton, C.B. Sirlin, C.A. McKenzie, et al. (2011) Quantification of hepatic steatosis with T1-independent, T2-corrected MR imaging with spectral modeling of fat: blinded comparison with MR spectroscopy. Radiology, 258(3): p. 767-75.
Henninger, B., H. Zoller, S. Kannengiesser, X. Zhong, W. Jaschke, et al. (2017) 3D Multiecho Dixon for the Evaluation of Hepatic Iron and Fat in a Clinical Setting. J Magn Reson Imaging, 46(3): p. 793-800.
Wood, J.C., C. Enriquez, N. Ghugre, J.M. Tyzka, S. Carson, et al. (2005) MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients. Blood, 106(4): p. 1460-5.
Alam, M.H., D. Auger, L.A. McGill, G.C. Smith, T. He, et al. (2016) Comparison of 3 T and 1.5 T for T2* magnetic resonance of tissue iron. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 18(1): p. 40.
Hetterich, H., C. Bayerl, A. Peters, M. Heier, B. Linkohr, et al. (2016) Feasibility of a three-step magnetic resonance imaging approach for the assessment of hepatic steatosis in an asymptomatic study population. Eur Radiol, 26(6): p. 1895-904.
Liu, C.Y., C.A. McKenzie, H. Yu, J.H. Brittain, and S.B. Reeder (2007) Fat quantification with IDEAL gradient echo imaging: correction of bias from T(1) and noise. Magn Reson Med, 58(2): p. 354-64.
Tang, A., J. Tan, M. Sun, G. Hamilton, M. Bydder, et al. (2013) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: MR imaging of liver proton density fat fraction to assess hepatic steatosis. Radiology, 267(2): p. 422-31.
Idilman, I.S., H. Aniktar, R. Idilman, G. Kabacam, B. Savas, et al. (2013) Hepatic steatosis: quantification by proton density fat fraction with MR imaging versus liver biopsy. Radiology, 267(3): p. 767-75.
Franca, M., A. Alberich-Bayarri, L. Marti-Bonmati, P. Oliveira, F.E. Costa, et al. (2017) Accurate simultaneous quantification of liver steatosis and iron overload in diffuse liver diseases with MRI. Abdom Radiol (NY), 42(5): p. 1434-1443.
Bashir, M.R., X. Zhong, B.M. Dale, R.T. Gupta, D.T. Boll, et al. (2013) Automated patient-tailored screening of the liver for diffuse steatosis and iron overload using MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 201(3): p. 583-8.
Galimberti, S., P. Trombini, D.P. Bernasconi, I. Redaelli, S. Pelucchi, et al. (2015) Simultaneous liver iron and fat measures by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with hyperferritinemia. Scand J Gastroenterol, 50(4): p. 429-38.
Kuhn, J.P., D. Hernando, A. Munoz del Rio, M. Evert, S. Kannengiesser, et al. (2012) Effect of multipeak spectral modeling of fat for liver iron and fat quantification: correlation of biopsy with MR imaging results. Radiology, 265(1): p. 133-42.
Storey, P., A.A. Thompson, C.L. Carqueville, J.C. Wood, R.A. de Freitas, et al. (2007) R2* imaging of transfusional iron burden at 3T and comparison with 1.5T. J Magn Reson Imaging, 25(3): p. 540-7.
Banerjee, R., M. Pavlides, E.M. Tunnicliffe, S.K. Piechnik, N. Sarania, et al. (2014) Multiparametric magnetic resonance for the non-invasive diagnosis of liver disease. J Hepatol, 60(1): p. 69-77.
Henninger, B., H. Zoller, S. Rauch, M. Schocke, S. Kannengiesser, et al. (2015) Automated two-point dixon screening for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis and siderosis: comparison with R2-relaxometry and chemical shift-based sequences. Eur Radiol, 25(5): p. 1356-65.
Lin, H., C. Fu, S. Kannengiesser, S. Cheng, J. Shen, et al. (2018) Quantitative analysis of hepatic iron in patients suspected of coexisting iron overload and steatosis using multi-echo single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Comparison with fat-saturated multi-echo gradient echo sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging, 48(1): p. 205-213.
St Pierre, T.G., P.R. Clark, W. Chua-anusorn, A.J. Fleming, G.P. Jeffrey, et al. (2005) Noninvasive measurement and imaging of liver iron concentrations using proton magnetic resonance. Blood, 105(2): p. 855-61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, C., Olsen, S., Zhang, H.C. et al. Detection of hepatic steatosis and iron content at 3 Tesla: comparison of two-point Dixon, quantitative multi-echo Dixon, and MR spectroscopy. Abdom Radiol 44, 3040–3048 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02118-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02118-9