Abstract
A better understanding of the risks and benefits of extracolonic findings and radiation dose will aid in the safe and proper implementation of CT colonography in clinical practice. The majority of extracolonic findings in screening patients are benign and can be ignored by referring physicians. Radiologists also need to be responsible in reporting extracolonic findings. Referring providers must be knowledgeable about the theoretic risks and controversies regarding the use of ionizing radiation. Screening CT colonography imparts a low-level of radiation to patients that is equivalent or less than annual background dose.



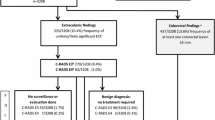
Reproduced with permission from the American Journal of Roentgenology (Pooler et al. [35])



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zalis ME, Barish MA, Choi JR, et al. (2005) CT colonography reporting and data system: a consensus proposal. Radiology 236:3–9
Pickhardt PJ, Choi JR, Hwng I, et al. (2003) Computed tomographic virtual colonoscopy to screen for colorectal neoplasia in asymptomatic adults. N Engl J Med 349:2191–2200
Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al. (2008) Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:130–160
US Preventative Task Force (2008) Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventative Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Intern Med 149:627–637
US Preventative Services Task Force (2016) Screening for colorectal cancer–US Preventative Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2016:2564–2575
Lin JS, Piper M, Perdue LA, et al. (2016) Screening for colorectal cancer: updated evidence report and systemic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA 315:2576–2594
Hara AK, Johnson CD, MacCarty RL, Welch TJ (2000) Incidental extracolonic findings at CT colonography. Radiology 215:353–357
Gluecker TM, Johnson CD, Wilson LA, et al. (2003) Extracolonic findings at CT colonography: evaluation of prevalence and cost in a screening population. Gastroenterology 124:911–916
Chin M, Mendelson R, Edwards J, Foster N, Forbes G (2005) Computed tomographic colonography: prevalence, nature, and clinical significance of extracolonic findings in a community screening program. Am J Gastroenterol 100:2771–2776
Yee J, Kumar NN, Godara S, et al. (2005) Extracolonic abnormalities discovered incidentally at CT colonography in a male population. Radiology 236:519–526
Kim DH, Pickhardt PJ, Taylor AJ, et al. (2007) CT colonography versus colonoscopy for the detection of advanced neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 357(14):1403–1412
Flicker MS, Tsoukas AT, Hazra A, Dachman AH (2008) Economic impact of extracolonic findings at computed tomographic colonography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 32:497–503
Johnson CD, Chen MH, Toledano AY, et al. (2008) The national CT colonography trial: multicenter assessment of accuracy for detection of large adenomas and cancers. N Engl J Med 359:1207–1217
Pickhardt PJ, Hanson ME, Vanness DJ, et al. (2008) Unsuspected extracolonic findings at screening CT colonography: clinical and economic impact. Radiology. 249:151–159
Pickhardt PJ, Kim DH, Meiners RJ, et al. (2010) Colorectal and extracolonic cancers detected at screening CT colonography in 10,286 asymptomatic adults. Radiology 255(1):83–88
Veerappan GR, Ally MR, Choi JH, et al. (2010) Extracolonic findings on CT colonography increases yield of colorectal cancer screening. AJR 195:677–686
Kim DH, Pickhardt PJ, Hanson ME, Hinshaw JL (2010) CT colonography: performance and program outcome measures in an older screening population. Radiology. 254(2):493–500
Macari M, Nevsky G, Bonavita J, et al. (2011) CT colonography in senior versus nonsenior patients: extracolonic findings, recommendations for additional imaging, and polyp prevalence. Radiology 259(3):767–774
Zalis ME, Blake MA, Cai W, et al. (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of laxative-free computed tomographic colonography for detection of adenomatous polyps in asymptomatic adults: a prospective evaluation. Ann Intern Med 156:692–702
Cash BD, Riddle M, et al. (2012) Observed outcomes with computerized tomographic colonography in a Medicare-aged screening population: an analysis of over 1,400 patients. AJR 199:W27–W34
Stoop EM, de Haan MC, de Wijkerslooth TR, et al. (2012) Participation and yield of colonoscopy vs non-cathartic CT colonography in population-based screening for colorectal cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 13:55–64
Pooler BD, Kim DH, Pickhardt PJ (2016) Potentially important extracolonic findings at screening CT colonography: incidence and outcomes data from a clinical screening program. AJR 206:313–318
Pooler BD, Kim DH, Pickhardt PJ (2016) Indeterminate but likely unimportant extracolonic findings at screening CT colonography (C-RADS category E3): incidence and outcomes data from a clinical screening program. AJR 207:996–1001
Khan KY, Xiong T, McCafferty I, et al. (2007) Frequency and impact of extracolonic findings detected at computed tomographic colonography in a symptomatic patient. Br J Radiol 94:355–361
Spreng A, Netzer P, Mattich J, et al. (2005) Importance of extracolonic findings at IV contrast medium-enhanced CT colonography versus those at non-enhanced CT colonography. Eur Radiol 15:2088–2095
Hellstrom M, Svensson MH, Lasson A (2004) Extracolonic and incidental findings on CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy). AJR 182:631–638
Edwards JT, Wood CJ, Mendelson RM, Forbes GM (2001) Extracolonic findings at virtual colonoscopy: implications for screening programs. Am J Gastroenterol 96:3009–3012
Wonhainen A, Lundkvist J, Bergqvist D, Bjorck M (2005) Cost-effectiveness of different screening strategies for abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 41:741–751
Wilmink AB, Quick CR, Hubbard CS, Day NE (2003) Effectiveness and cost of screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm-results of a population screening program. J Vasc Surg 38:72–77
Hassan C, Pickhardt PJ, Laghi A, et al. (2008) Computed tomographic colonography to screen for colorectal cancer, extracolonic cancer, and aortic aneurysm: model simulation with cost-effectiveness analysis. Arch Intern Med. 168(7):696–705
Fletcher RH, Pignone M (2008) Extracolonic findings with computed tomographic colonography, asset or liability? Arch Intern Med 168:685–686
Harris RP, Helfand M, Woolf SH, et al. (2001) Methods Working Group; third US Preventive Services Task Force. Current methods for the US Preventative Services Task Force-a review of the process. Am J Prev Med 20:21–35
Cochrane AL, Holland WW (1971) Validation of screening procedures. Br Med Bull 27:3–8
Pooler DB, Kim DH, Pickhardt PJ (2017) Extracolonic findings at screening CT colonography: prevalence, benefits, challenges and opportunities. AJR 209:1–9
Chin J, Syrek Jensen T, Ashby L, et al. (2015) Screening for lung cancer with low dose CT-translating science into Medicare coverage policy. NEJM 372:2083–2085
Berland LL, Silverman SG, Gore RM, et al. (2010) Managing incidental findings on abdominal CT: white paper of the ACR incidental findings committee. J Am Coll Radiol 7:754–773
Patel MD, Ascher SM, Paspulati RM, et al. (2013) Managing incidental findings on abdominal and pelvic CT and MRI, part 1: white paper of the ACR incidental findings committee II on adnexal findings. J Am Coll Radiol 10:675–681
Heller MT, Harisinghani M, Neitlich JD, Yeghiayan P, Berland LL (2013) Managing incidental findings on abdominal and pelvic CT and MRI, part 3: white paper of the ACR incidental findings committee II on splenic and nodal findings. J Am Coll Radiol 10:833–839
Sebastian S, Araujo C, Neitlich JD, Berland LL (2013) Managing incidental findings on abdominal and pelvic CT and MRI, part 4: white paper of the ACR incidental findings committee II on gallbladder and biliary findings. J Am Coll Radiol 10:953–956
Doshi AM, Kiritsy M, Rosenkrantz AB (2015) Strategies for avoiding recommendations for additional imaging through a comprehensive comparison with prior studies. J Am Coll Radiol 12:657–663
https://www.acr.org/Quality-Safety/National-Radiology-Data-Registry/CT-Colonography/Registry
Radiation Control: Health Facilities and Clinics, SB1237, February 19, 2010. http://www.leginfo.ca.gov/pub/09-10/bill/sen/sb_12011250/sb1237bill_20100929chaptered.html.
Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams. Effective radiation dose in adults. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=safety-xray.
Health Physics Society (2016) Radiation risk in perspective. Position Statement of the Health Physics Society. http://hps.org/documents/risk_ps010-3.pdf.
American Association of Physicists in Medicine (2017) Position statement on radiation risks from medical imaging procedures. http://www.aapm.org/org/policies/details.asp?id=318&type=PP¤t=true.
Berrington de González A, Kim KP, Knudsen AB, et al. (2011) Radiation-related cancer risks from CT colonography screening: a risk-benefit analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:816–823
Brink JA, Amis ES (2010) Image wisely: a campaign to increase awareness about adult radiation protection. Radiology 257:601–602
Applegate K, Frush DP (2017) Image gently: a decade of international collaborations to promote appropriate imaging for children. J Am Coll Radiol 14:956–957
McCollough CH, Leng S, Yu L, et al. (2011) CT dose index and patient dose: they are not the same thing. Radiology 259:311–316
Thakur Y, McLaughlin PD, Mayo JR (2013) Strategies for radiation dose optimization. Curr Radiol Rep 1:1–10
AAPM Report No. 96: the measurement, reporting, and management of radiation dose in CT. (2008). https://www.aapm.org/pubs/reports/RPT_96.pdf.
Flicek KT, Hara AK, Silva AC, et al. (2010) Reducing the radiation dose for CT colonography using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: a pilot study. AJR 195:126–131
ACR-SAR-SCBT-MR practice parameter for the performance of computed tomography (CT) colonography in adults. https://www.acr.org/~/media/ACR/Documents/PGTS/guidelines/CT_Colonography.pdf.
Habibzadeh MA, Ay MR, Asl AR, Ghadiri H, Zaidi H (2012) Impact of miscentering on patient dose and image noise in x-ray CT imaging: phantom and clinical studies. Phys Med 28:191–199
Chang KJ, Yee J (2013) Dose reduction methods for CT colonography. Abdom Imaging 38:224–232
Vogt C, Cohnen M, Beck A, et al. (2004) Detection of colorectal polyps by multislice CT colonography with ultra-low-dose technique: comparison with high-resolution videocolonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 60:201–209
Iannaccone R, Catalano C, Mangiapane F, et al. (2005) Colorectal polyps: detection with low-dose multidetector row helical CT colonography versus two sequential colonoscopies. Radiology 237:927–937
Ginsburg M, Obara P, Wise L, et al. (2013) BMI-based radiation dose reduction in CT colonography. Acad Radiol 20:486–492
McMillan K, Bostani M, Cagnon CH, et al. (2017) Estimating patient dose from CT exams that use automatic exposure control: development and validation of methods to accurately estimate tube current values. Med Phys 44:4262–4275
Elojeimy S, Tipnis S, Huda W (2010) Relationship between radiographic techniques (kilovolt and milliampere-second) and CTDI(VOL). Radiat Prot Dosimetry 141(1):43–49
Seyal AR, Arslanoglu A, Abboud SF, et al. (2015) CT of the abdomen with reduced tube voltage in adults: a practical approach. Radiographics 35:1922–1939
Chang KJ, Caovan DB, Grand DJ, et al. (2013) Reducing radiation dose at CT colonography: decreasing tube voltage to 100 kVp. Radiology 266:791–800
Shin CI, Kim SH, Lee ES, et al. (2014) Ultra-low peak voltage CT colonography: effect of iterative reconstruction algorithms on performance of radiologists who use anthropomorphic colonic phantoms. Radiology 273:759–771
Beister M, Kolditz D, Kalender WA (2012) Iterative reconstruction methods in X-ray CT. Phys Med 28:94–108
Fletcher JG, Grant KL, Fidler JL, et al. (2012) Validation of dual-source single-tube reconstruction as a method to obtain half-dose images to evaluate radiation dose and noise reduction: phantom and human assessment using CT colonography and sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction (SAFIRE). J Comput Assist Tomogr 36:560–569
Nagata K, Fujiwara M, Kanazawa H, et al. (2015) Evaluation of dose reduction and image quality in CT colonography: comparison of low-dose CT with iterative reconstruction and routine-dose CT with filtered back projection. Eur Radiol 25:221–229
Millerd PJ, Paden RG, Lund JT, et al. (2015) Reducing the radiation dose for computed tomography colonography using model-based iterative reconstruction. Abdom Imaging 40:1183–1189
Lambert L, Ourednicek P, Jahoda J, et al. (1048) Model-based vs hybrid iterative reconstruction technique in ultralow-dose submillisievert CT colonography. Br J Radiol 2015(88):20140667
Lubner MG, Pooler BD, Kitchin DR, et al. (2015) Sub-milliSievert (sub-mSv) CT colonography: a prospective comparison of image quality and polyp conspicuity at reduced-dose versus standard-dose imaging. Eur Radiol 25:2089–2102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was provided for this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Judy Yee, MD, FACR has received research Grants from Echopixel and Philips. Elizabeth McFarland, MD is a member of the Medical Advisory Board for Vital Images.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yee, J., McFarland, E. Extracolonic findings and radiation at CT colonography: what the referring provider needs to know. Abdom Radiol 43, 554–565 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1461-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1461-z