Abstract
Purpose
To study the prognostic significance of neutrophil and lymphocyte dynamics in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treated with radioembolization.
Methods
A retrospective, single-center review of clinical records and treatment parameters (liver volume treated, administered activity, and radiation dose) in consecutive patients who received radioembolization for HCC was performed between August 20, 2015, and May 24, 2019. Neutrophil and lymphocyte variables associated with overall survival (OS) were determined by Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage and were correlated with radioembolization treatment parameters. Statistical methods included Wilcoxon signed-rank test, univariate, and multivariate Cox regression analysis; receiver operating characteristic analysis; and the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
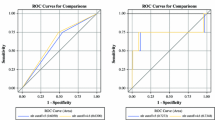
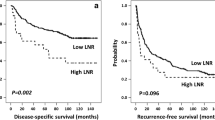
One hundred sixty-three patients with a median 67.0 years of age were included for analysis. Eighty-one percent of patients received segmental radioembolization with a median treatment dose of 358 Gray (interquartile range 256–497). The post-treatment lymphocyte count decreased significantly in 94.5 % (p < 0.001) of patients but was not predictive of OS (p = 0.248). The pre-procedure neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLRpre) was not predictive of OS (p = 0.891), and the 1-month post-procedure NLR was a borderline independent predictor of OS (p = 0.05). The NLR ratio (NLRR = NLRpost-procedure/NLRpre) (Hazard ratio [HR], 1.31; 95% Cl, 1.04-1.66) and change in NLR (ΔNLR= NLRpost-procedure - NLRpre) (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.02–1.15) were associated with worse OS in BCLC C patients. NLRR (> 3.17) and ΔNLR (> 3.74) were independent predictors when adjusted for tumor presentation, treatment parameters, and liver function. Volume of liver treated and administered activity positively correlated with NLRR and ΔNLR (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
A decrease in lymphocyte count is common after radioembolization, but of little clinical impact. Neither pre-treatment or post-treatment NLR was a predictor of survival in our study population. NLRR and ΔNLR were independent predictors of survival in BCLC stage C disease and had positive correlations with volume of liver tissue treated and administered activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AFP:
-
alpha feto protein
- BCLC:
-
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer
- CT:
-
computed tomography
- ECOG:
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HR:
-
hazard ratio
- MIRD:
-
medical internal radiation dose
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- NLR:
-
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
- NLRR:
-
NLRpost-treatment / NLRpre-treatment
- ΔNLR:
-
NLRpost-treatment - NLRpre-treatment
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristic
References
Gaba RC, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik LM, et al. Radiation lobectomy: preliminary findings of hepatic volumetric response to lobar yttrium-90 radioembolization. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(6):1587–96.
Gabr A, Kallini JR, Gates VL, et al. Same-day (90)Y radioembolization: implementing a new treatment paradigm. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43(13):2353–9.
Paramanathan A, Saxena A, Morris DL. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the impact of pre-operative neutrophil lymphocyte ratio on long term outcomes after curative intent resection of solid tumours. Surg Oncol. 2014;23(1):31–9.
Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik L, et al. Radioembolization results in longer time-to-progression and reduced toxicity compared with chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(2):497–507.e492.
Salem R, Miller FH, Yaghmai V, Lewandowski RJ. Response assessment methodologies in hepatocellular carcinoma: complexities in the era of local and systemic treatments. J Hepatol. 2013;58(6):1260–2.
Vouche M, Lewandowski RJ, Atassi R, et al. Radiation lobectomy: time-dependent analysis of future liver remnant volume in unresectable liver cancer as a bridge to resection. J Hepatol. 2013;59(5):1029–36.
Carr BI. Hepatic arterial 90Yttrium glass microspheres (Therasphere) for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: interim safety and survival data on 65 patients. Liver Transpl. 2004;10(2 Suppl 1):S107–10.
Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Atassi B, et al. Treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with use of 90Y microspheres (TheraSphere): safety, tumor response, and survival. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005;16(12):1627–39.
Dunfee BL, Riaz A, Lewandowski RJ, et al. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for liver malignancies: prognostic factors associated with survival. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(1):90–5.
Motomura T, Shirabe K, Mano Y, et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio reflects hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation via inflammatory microenvironment. J Hepatol. 2013;58(1):58–64.
Taussig MD, Irene Koran ME, Mouli SK, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts disease progression following intra-arterial therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 2017;19(5):458–64.
Wang Y, Peng C, Cheng Z, et al. The prognostic significance of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma receiving hepatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;55:73–80.
Wei K, Wang M, Zhang W, et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing TAE combined with Sorafenib. Med Oncol. 2014;31(6):969.
Cruz JC, Watchmaker JM, Albin MM, et al. Neutrophil/Lymphocyte ratio predicts increased risk of immediate progressive disease following chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30:1887–92.
Peng W, Li C, Wen TF, Yan LN, Li B, Wang WT, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio changes predict small hepatocellular carcinoma survival. J Surg Res. 2014;192(2):402–8.
Dolan RD, McSorley ST, Horgan PG, et al. The role of the systemic inflammatory response in predicting outcomes in patients with advanced inoperable cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;116:134–46.
Fan W, Zhang Y, Wang Y, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios as predictors of survival and metastasis for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119312. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119312.
Gao F, Li X, Geng M, Ye X, Liu H, Liu Y, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: an independent predictor of survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(11):e639.
Estrade F, Lescure C, Muzellec L. et.al. Lymphocytes and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio variations after selective internal radiation treatment for HCC: a retrospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2020;43(8):1175–81.
Domouchtsidou A, Barsegian V, Mueller SP, et al. Impaired lymphocyte function in patients with hepatic malignancies after selective internal radiotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018;67(5):843–53.
Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;68(2):723–50.
Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS, Sirlin CB, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, et al. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):358–80.
Toskich BB, Liu DM. Y90 Radioembolization dosimetry: concepts for the interventional radiologist. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;22(2):100–11.
Johnston MP, Khakoo SI. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current and future. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(24):2977–89.
Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894–905.
Erinjeri JP, Fine GC, Adema GJ, et al. Immunotherapy and the interventional oncologist: challenges and opportunities-a society of interventional oncology white paper. Radiology. 2019;292(1):25–34.
Guo RP, Zhong C, Shi M, et al. Expression and clinical significance of certain apoptosis and angiogenesis factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006;44(23):1626–30.
Ménétrier-Caux C, Ray-Coquard I, Blay JY, et al. Lymphopenia in Cancer Patients and its Effects on Response to Immunotherapy: an opportunity for combination with Cytokines? J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):85.
Venkatesulu BP, Mallick S, Lin SH, Krishnan S. A systematic review of the influence of radiation-induced lymphopenia on survival outcomes in solid tumors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018;123:42–51.
Riaz A, Gates VL, Atassi B, et al. Radiation segmentectomy: a novel approach to increase safety and efficacy of radioembolization. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;79(1):163–71.
Najjar M, Agrawal S, Emond JC, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: useful prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2018;5:17–28.
Hung HC, Lee JC, Cheng CH, et al. Impact of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on survival for hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2017;24(10):559–69.
Zheng YB, Zhao W, Liu B, et al. The blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving sorafenib. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5527–31.
Sukato DC, Tohme S, Chalhoub D, et al. The Prognostic Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(6):816–24.e1.
D'Emic N, Engelman A, Molitoris J, et al. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients Treated With Selective Internal Radiation Therapy. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016;7(2):269–77.
Bartlett EK, Flynn JR, Panageas KS, et al. High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with treatment failure and death in patients who have melanoma treated with PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy. Cancer. 2020;126(1):76–85.
Bigot F, Castanon Alvarez E, Hollebecque A, et al. Identification of new prognostic factors in Phase I patients treated by immunotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(6):114–35.
Moschetta M, Kasenda B, Mak G, et al. Dynamics of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Predict Effectiveness of PD1/PDL1 Inhibition. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(6):15–42.
Funding
No funding was used for the purpose of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.L., data gathering, manuscript writing, statistical analysis; S.A.M. data gathering, manuscript writing, statistical analysis; R.P., study design, manuscript writing and editing, data interpretation; C.A.P, data gathering, manuscript writing; W.W., manuscript editing; K.M. manuscript editing; L.R.R., manuscript editing and study design; T.P., manuscript editing and study design; S.K., manuscript editing, data interpretation; B.T., data gathering, manuscript writing, data interpretation, study conception and design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
Dr. Krishnan reports grants from NIH, DoD, CPRIT, clinical research support from Celgene, Elekta outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr. Krishnan has patents pending or issued on radiation minibeams and gold nanoparticles. Dr. Mody reports and Research Support: Astrazeneca/Medimmune; Genentech; Senwha Biociences Inc; Basilea Pharma; Agios; Taiho Oncology; Merck KGa Serono; Puma Biotechnology. Consulting: AstraZeneca, Eisai, Bayer, Celgene, Ipsen. Grant Support: SPORE (NCI/NIH P50 CA210964). Dr. Patel reports grants from NIH, during the conduct of the study. Dr. Toskich is an advisor to Boston Scientific, Johnson and Johnson, Astra Zeneca, and Histosonics. Dr. Roberts reports grants from BTG International, grants from National Cancer Institute Grant P50 CA210964, grants from NIH NCATS Grant UL1 TR002377, during the conduct of the study; grants and other from Bayer, grants and other from Exact Sciences, grants and other from Gilead Sciences, grants from GlycoTest, other from GRAIL, Inc., other from QED Therapeutics, Inc., grants from RedHill Biopharma Ltd., grants from TARGET PharmaSolutions, other from TAVEC, grants from Wako Diagnostics, outside the submitted work. Dr. Li reports personal fees from China Scholarship Council, outside the submitted work. Drs. Padula, Wang, Montazeri, and Paz-Fumagalli have nothing to disclose.
Ethics
IRB approved the study. The need for consent was waived due to the retrospective design of the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xi Li and S. Ali Montazeri were co-first authors.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Oncology - General.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Montazeri, S.A., Paz-Fumagalli, R. et al. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Dynamics in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Radioembolization Using Glass Microspheres. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48, 2624–2634 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-020-05186-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-020-05186-y