Abstract
Purpose
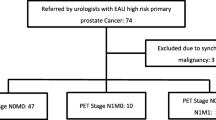
To assess the diagnostic accuracy of 68Ga-PSMA PET in predicting lymph node (LN) metastases in primary N staging in high-risk and very high-risk nonmetastatic prostate cancer in comparison with morphological imaging.
Methods
This was a multicentre trial of the Society of Urologic Oncology in Turkey in conjunction with the Nuclear Medicine Department of Cerrahpasa School of Medicine, Istanbul University. Patients were accrued from eight centres. Patients with high-risk and very high-risk disease scheduled to undergo surgical treatment with extended LN dissection between July 2014 and October 2015 were included. Either MRI or CT was used for morphological imaging. PSMA PET/CT was performed and evaluated at a single centre. Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were calculated for the detection of lymphatic metastases by PSMA PET/CT and morphological imaging. Kappa values were calculated to evaluate the correlation between the numbers of LN metastases detected by PSMA PET/CT and by histopathology.
Results
Data on 51 eligible patients are presented. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of PSMA PET in detecting LN metastases in the primary setting were 53%, 86% and 76%, and increased to 67%, 88% and 81% in the subgroup with of patients with ≥15 LN removed. Kappa values for the correlation between imaging and pathology were 0.41 for PSMA PET and 0.18 for morphological imaging.
Conclusions
PSMA PET/CT is superior to morphological imaging for the detection of metastatic LNs in patients with primary prostate cancer. Surgical dissection remains the gold standard for precise lymphatic staging.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2014;65(2):467–79.
Heesakkers RA, Hovels AM, Jager GJ, van den Bosch HC, Witjes JA, Raat HP, et al. MRI with a lymph-node-specific contrast agent as an alternative to CT scan and lymph-node dissection in patients with prostate cancer: a prospective multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(9):850–6.
Bouchelouche K, Choyke PL, Capala J. Prostate specific membrane antigen – a target for imaging and therapy with radionuclides. Discov Med. 2010;9(44):55–61.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Malcher A, Eder M, Eisenhut M, Linhart HG, Hadaschik BA, et al. PET imaging with a [68Ga]gallium-labelled PSMA ligand for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: biodistribution in humans and first evaluation of tumour lesions. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40(4):486–95.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Zechmann CM, Malcher A, Eder M, Eisenhut M, Linhart HG, et al. Comparison of PET imaging with a (68)Ga-labelled PSMA ligand and (18)F-choline-based PET/CT for the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41(1):11–20.
Budäus L, Leyh-Bannurah SR, Salomon G, Michl U, Heinzer H, Huland H, et al. Initial experience of (68)Ga-PSMA PET/CT imaging in high-risk prostate cancer patients prior to radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2016;69(3):393–6.
Herlemann A, Wenter V, Kretschmer A, Thierfelder KM, Bartenstein P, Faber C, et al. 68Ga-PSMA positron emission tomography/computed tomography provides accurate staging of lymph node regions prior to lymph node dissection in patients with prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2016;70(4):553–7.
Maurer T, Gschwend JE, Rauscher I, Souvatzoglou M, Haller B, Weirich G, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of (68)gallium-PSMA positron emission tomography compared to conventional imaging for lymph node staging of 130 consecutive patients with intermediate to high risk prostate cancer. J Urol. 2016;195(5):1436–43.
van Leeuwen PJ, Emmett L, Ho B, Delprado W, Ting F, Nguyen Q, et al. Prospective evaluation of 68Gallium-prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography/computed tomography for preoperative lymph node staging in prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2017;119(2):209–15.
Comperat E, Camparo P, Srigley J, Delahunt B, Egevad L; ISUP Consensus Working Group. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on handling and staging of radical prostatectomy specimens. Ann Pathol. 2013;33(3):155–61.
Kabasakal L, Demirci E, Ocak M, Akyel R, Nematyazar J, Aygun A, et al. Evaluation of PSMA PET/CT imaging using a 68Ga-HBED-CC ligand in patients with prostate cancer and the value of early pelvic imaging. Nucl Med Commun. 2015;36(6):582–7.
Barrio M, Fendler WP, Czernin J, Herrmann K. Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) ligands for diagnosis and therapy of prostate cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2016;16(11):1177–88.
Jadvar H. PSMA PET in prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(8):1131–2.
Mease RC, Foss CA, Pomper MG. PET imaging in prostate cancer: focus on prostate-specific membrane antigen. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(8):951–62.
Wright GL Jr, Haley C, Beckett ML, Schellhammer PF. Expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen in normal, benign, and malignant prostate tissues. Urol Oncol. 1995;1(1):18–28.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Avtzi E, Giesel FL, Holland-Letz T, Linhart HG, Eder M, et al. The diagnostic value of PET/CT imaging with the (68)Ga-labelled PSMA ligand HBED-CC in the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42(2):197–209.
Kabasakal L, Demirci E, Nematyazar J, Akyel R, Razavi B, Ocak M, et al. The role of PSMA PET/CT imaging in restaging of prostate cancer patients with low prostate-specific antigen levels. Nucl Med Commun. 2017;38(2):149–55.
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA, Hill RE, Liu Q, Reeves JJ, Axford PD, et al. Expression pattern of mouse homolog of prostate-specific membrane antigen (FOLH1) in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate model. Prostate. 2003;55(4):308–16.
Hijazi S, Meller B, Leitsmann C, Strauss A, Meller J, Ritter CO, et al. Pelvic lymph node dissection for nodal oligometastatic prostate cancer detected by 68Ga-PSMA-positron emission tomography/computerized tomography. Prostate. 2015;75(16):1934–40.
Perera M, Papa N, Christidis D, Wetherell D, Hofman MS, Murphy DG, et al. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictors of positive 68Ga-prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography in advanced prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2016;70(6):926–37.
Giesel FL, Fiedler H, Stefanova M, Sterzing F, Rius M, Kopka K, et al. PSMA PET/CT with Glu-urea-Lys-(Ahx)-[68Ga(HBED-CC)] versus 3D CT volumetric lymph node assessment in recurrent prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42(12):1794–800.
Hovels AM, Heesakkers RA, Adang EM, Jager GJ, Strum S, Hoogeveen YL, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of CT and MRI in the staging of pelvic lymph nodes in patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Radiol. 2008;63(4):387–95.
Huang SS, Wang X, Zhang Y, Doke A, DiFilippo FP, Heston WD. Improving the biodistribution of PSMA-targeting tracers with a highly negatively charged linker. Prostate. 2014;74(7):702–13.
Sterzing F, Kratochwil C, Fiedler H, Katayama S, Habl G, Kopka K, et al. (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT: a new technique with high potential for the radiotherapeutic management of prostate cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43(1):34–41.
Bluemel C, Linke F, Herrmann K, Simunovic I, Eiber M, Kestler C, et al. Impact of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT on salvage radiotherapy planning in patients with prostate cancer and persisting PSA values or biochemical relapse after prostatectomy. EJNMMI Res. 2016;6(1):78.
Kolthammer JA, Su KH, Grover A, Narayanan M, Jordan DW, Muzic RF. Performance evaluation of the ingenuity TF PET/CT scanner with a focus on high count-rate conditions. Phys Med Biol. 2014;59(14):3843–59.
Sanchez-Crespo A. Comparison of gallium-68 and fluorine-18 imaging characteristics in positron emission tomography. Appl Radiat Isot. 2013;76:55–62.
Giesel FL, Hadaschik B, Cardinale J, Radtke J, Vinsensia M, Lehnert W, et al. F-18 labelled PSMA-1007: biodistribution, radiation dosimetry and histopathological validation of tumor lesions in prostate cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44(4):678–88.
Giesel FL, Kesch C, Yun M, Cardinale J, Haberkorn U, Kopka K, et al. 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT detects micrometastases in a patient with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15(3):e497–9.
Noto B, Buther F, Auf der Springe K, Avramovic N, Heindel W, Schafers M, et al. Impact of PET acquisition durations on image quality and lesion detectability in whole-body 68Ga-PSMA PET-MRI. EJNMMI Res. 2017;7(1):12.
Suardi N, Briganti A, Gandaglia G, Fossati N, Montorsi F. Salvage lymph node dissection for node-only recurrence of prostate cancer: ready for prime time? Eur Urol. 2017;71(5):693–4.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University, under project number 3264.
We acknowledge the contribution of Polat Türker, Erkan Erkan, Levent Türkeri, Çağ Çal and Haluk Akpınar in providing patients for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Dr. Levent Kabasakal has received a research grant from the Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University, under project number 3264.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the principles of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Öbek, C., Doğanca, T., Demirci, E. et al. The accuracy of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in primary lymph node staging in high-risk prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44, 1806–1812 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3752-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3752-y