Abstract
Objective
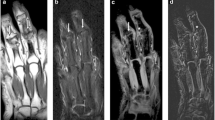
To evaluate the diagnostic potential of susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) for the detection of erosions of the hand, compared to T1-weighted (T1w) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Computed tomography (CT) was used as a reference standard.
Materials and methods
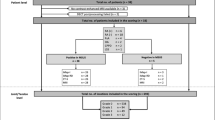
We prospectively investigated 37 patients with suspected arthritic activity of the hand. All patients underwent T1w, SWI, and CT on the same day. Patients were randomized to MRI or CT first. CT, T1w, SWI, and T1w/SWI were scored for erosions according to OMERACT RAMRIS guidelines. Specificity, sensitivity, and diagnostic accuracy were separately calculated for T1w, SWI, and T1w/SWI on a per-patient and per-bone basis using CT as reference. The one-tailed McNemar test was performed to test the number of erosion-positive patients in T1w, SWI, and T1w/SWI for non-inferiority. Measured erosion sizes were compared using Pearson’s test.
Results
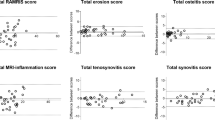
CT was positive for erosions in 16 patients and 55 bones. SWI and T1w/SWI had superior diagnostic accuracy (91.2 and 93.8%) compared to T1w (87.8%) driven by a higher specificity (93.8 and 96.5%) compared to T1w (88.8%). On the patient level, SWI and T1w/SWI showed non-inferiority (p = 0.11 and p = 0.38) but not T1w alone (p < 0.0001). The lesion size on CT correlated better with SWI (Pearson’s r = 0.92) compared to T1w (r = 0.69).
Conclusions
Adding SWI to a standard MRI protocol has the potential to improve erosion detection in hands by increasing specificity. SWI depicts bony erosions more accurately compared to standard MRI techniques.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkmann GH, Norli ES, Bøyesen P, van der Heijde D, Grøvle L, Haugen AJ, et al. Role of erosions typical of rheumatoid arthritis in the 2010 ACR/EULAR rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: results from a very early arthritis cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(11):1911–4.
Knevel R, Lukas C, van der Heijde D, Rincheval N, Combe B, van der Helm-van Mil AH. Defining erosive disease typical of RA in the light of the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria for rheumatoid arthritis; results of the data driven phase. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(4):590–5.
Lee CH, Srikhum W, Burghardt AJ, Virayavanich W, Imboden JB, Link TM, et al. Correlation of structural abnormalities of the wrist and metacarpophalangeal joints evaluated by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography, 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging and conventional radiographs in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18(6):628–39.
Scheel AK, Hermann KG, Ohrndorf S, Werner C, Schirmer C, Detert J, et al. Prospective 7-year follow-up imaging study comparing radiography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis finger joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(5):595–600.
Diekhoff T, Hermann KG, Greese J, Schwenke C, Poddubnyy D, Hamm B, et al. Comparison of MRI with radiography for detecting structural lesions of the sacroiliac joint using CT as standard of reference: results from the SIMACT study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(9):1502–8.
Østergaard M, Peterfy CG, Bird P, Gandjbakhch F, Glinatsi D, Eshed I, et al. The OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scoring system: updated recommendations by the OMERACT MRI in arthritis working group. J Rheumatol. 2017;44(11):1706–12.
Chang G, Boone S, Martel D, Rajapakse CS, Hallyburton RS, Valko M, et al. MRI assessment of bone structure and microarchitecture. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;46(2):323–37.
Shah LM, Hanrahan CJ. MRI of spinal bone marrow: part I, techniques and normal age-related appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(6):1298–308.
Goldbach-Mansky R, Woodburn J, Yao L, Lipsky PE. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis: a more precise image or just a more expensive one? Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(3):585–9.
McQueen F, Lassere M, Edmonds J, Conaghan P, Peterfy C, Bird P, et al. OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging studies. Summary of OMERACT 6 MR imaging module. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(6):1387–92.
Wycliffe ND, Choe J, Holshouser B, Oyoyo UE, Haacke EM, Kido DK. Reliability in detection of hemorrhage in acute stroke by a new three-dimensional gradient recalled echo susceptibility-weighted imaging technique compared to computed tomography: a retrospective study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;20(3):372–7.
Thomas B, Somasundaram S, Thamburaj K, Kesavadas C, Gupta AK, Bodhey NK, et al. Clinical applications of susceptibility weighted MR imaging of the brain—a pictorial review. Neuroradiology. 2008;50(2):105–16.
Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Cheng YC. Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(1):19–30.
Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Haacke EM. Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(2):232–52.
Yamada N, Imakita S, Sakuma T, Takamiya M. Intracranial calcification on gradient-echo phase image: depiction of diamagnetic susceptibility. Radiology. 1996;198(1):171–8.
Böker SM, Adams LC, Bender YY, Wagner M, Diekhoff T, Fallenberg E, et al. Evaluation of vertebral body fractures using susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol. 2018;28(5):2228–35.
Nörenberg D, Armbruster M, Bender YN, Walter T, Ebersberger HU, Diederichs G, et al. Diagnostic performance of susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of sub-coracoacromial spurs causing subacromial impingement syndrome. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(3):1286–94.
Wu Z, Mittal S, Kish K, Yu Y, Hu J, Haacke EM. Identification of calcification with MRI using susceptibility-weighted imaging: a case study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29(1):177–82.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(9):1580–8.
Østergaard M, Edmonds J, McQueen F, Peterfy C, Lassere M, Ejbjerg B, et al. An introduction to the EULAR-OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(Suppl 1):i3–7.
Tan YK, Conaghan PG. Imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25(4):569–84.
Lee DM, Weinblatt ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001;358(9285):903–11.
Aletaha D, Smolen J, Ward MM. Measuring function in rheumatoid arthritis: identifying reversible and irreversible components. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(9):2784–92.
Baum R, Gravallese EM. Bone as a target organ in rheumatic disease: impact on osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;51(1):1–15.
Heinlen L, Humphrey MB. Skeletal complications of rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(10):2801–12.
McQueen FM, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Tan PL, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals progression of erosions despite clinical improvement. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58(3):156–63.
Husberg M, Bernfort L, Hallert E. Costs and disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis in 1996-2000 and 2006-2011, improved outcome and shift in distribution of costs: a two-year follow-up. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(5):378–383.
Døhn UM, Ejbjerg BJ, Court-Payen M, Hasselquist M, Narvestad E, Szkudlarek M, et al. Are bone erosions detected by magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography true erosions? A comparison with computed tomography in rheumatoid arthritis metacarpophalangeal joints. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(4):R110.
Hoving JL, Buchbinder R, Hall S, Lawler G, Coombs P, McNealy S, et al. A comparison of magnetic resonance imaging, sonography, and radiography of the hand in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(4):663–75.
Saran S, Bagarhatta M, Saigal R. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography in detection of destructive changes in small joints of hands in patients of rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. J Assoc Physicians India. 2016;64(11):26–30.
Døhn UM, Terslev L, Szkudlarek M, Hansen MS, Hetland ML, Hansen A, et al. Detection, scoring and volume assessment of bone erosions by ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with CT. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(4):530–4.
Bai Y, Wang MY, Han YH, Dou SW, Lin Q, Guo Y, et al. Susceptibility weighted imaging: a new tool in the diagnosis of prostate cancer and detection of prostatic calcification. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53237.
Zhu WZ, Qi JP, Zhan CJ, Shu HG, Zhang L, Wang CY, et al. Magnetic resonance susceptibility weighted imaging in detecting intracranial calcification and hemorrhage. Chin Med J. 2008;121(20):2021–5.
Gupta RK, Rao SB, Jain R, Pal L, Kumar R, Venkatesh SK, et al. Differentiation of calcification from chronic hemorrhage with corrected gradient echo phase imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2001;25(5):698–704.
Nörenberg D, Ebersberger HU, Walter T, Ockert B, Knobloch G, Diederichs G, et al. Diagnosis of calcific tendonitis of the rotator cuff by using susceptibility-weighted MR imaging. Radiology. 2016;278(2):475–84.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs. Bettina Herwig for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulas, S.T., Diekhoff, T., Hermann, K.G.A. et al. Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging to improve the specificity of erosion detection: a prospective feasibility study in hand arthritis. Skeletal Radiol 48, 721–728 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-3116-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-3116-0