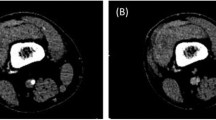
Abstract
High-pressure injection injuries occur when equipment capable of achieving high pressure injects its contents into the human body. These injuries are largely occupational and may present as small entrance wounds with very few symptoms. However, they represent a surgical emergency, often requiring amputation. They characteristically involve the upper extremities, but other regions of the body may be injured. We present the case of a 26-year-old man who sustained a high-pressure injection injury with hydraulic oil to the knee and a literature review of this type of accident. To our knowledge, this report is the first to describe such an injury to the knee, with magnetic resonance imaging findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith GD. High-pressure injection injuries. Trauma. 2005;7:95–103.
Hogan CJ, Ruland RT. High-pressure injection injuries to the upper extremity: a review of the literature. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(7):503–11.
Schoo MJ, Scott FA, Boswick JA. High pressure injection injuries of the hand. J Trauma. 1980;20:229–38.
Amsdell SL, Hammert WC. High-pressure injection injuries in the hand: current treatment concepts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132(4):586e–91e.
Pappou IP, Deal DN. High-pressure injection injuries. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(11):2404–7.
Mason ML, Queen FB. Grease gun injuries to the hand—pathology and treatment of injuries (oleomas) following the injection of grease under high pressure. Q Bull Northwest Univ Med Sch. 1941;15(2):122–32.
Mills C, Wilson P, Watts T, Manushakian H. High pressure paint injection injury of the hand. Injury Extra. 2007;38:298–300.
Neal NC, Burke FD. High-pressure injection injuries. Injury. 1991;6:467–70.
Subramaniam RM, Clearwater GM. High-pressure water injection injury: emergency presentation and management. Emerg Med (Fremantle). 2002;14(3):324–7.
Kaufman HD. High pressure injection injuries, the problems, pathogenesis and management. Hand. 1970;1(2):63–73.
Moore B. Oleogranuloma; the late effects of accidental injection of mineral oil under pressure. Br J Ind Med. 1946;3(4):250–2.
Llauger J, Palmer J, Rosón N, Bagué S, Camins A, Cremades R. Nonseptic monoarthritis: imaging features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2000;20:263–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noronha, P.A., Lomelino, R.O., Dinoá, V. et al. Synovitis of the knee following a high-pressure injection injury with hydraulic oil. Skeletal Radiol 47, 1701–1704 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-2969-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-2969-6