Abstract
Objective
Due to minimal tissue violation in percutaneous core needle biopsy (CNB), in contrast to open biopsy, the risk of tumor seeding and subsequent local recurrence (LR) along the biopsy tract remains unclear in extremity soft tissue sarcoma (STS). This study sought to examine the association of CNB tract resection on LR in a large STS institutional database.
Materials and methods
After a retrospective review of the 116 patients who underwent CNB prior to surgery for previously untreated non-metastatic extremity STS, 36 patients who did not have CNB tracts resected (CNB-NR) were matched with 36 who had CNB tracts resected (CNB-R) for the factors that are known to affect LR.
Results
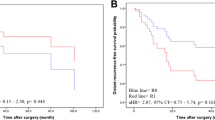
Two patients (6%) developed LR in the CNB-R group, whereas three patients (8%) developed LR in the CNB-NR group (P = 0.643). On Kaplan-Meier analysis, there was no significant difference in LR-free survival between the two groups (94.3% ± 3.9 for the CNB-R group vs. 93.8% ± 4.3 for the CNB-NR group, P = 0.747).
Conclusion
Our data suggest any influence of a CNB tract resection on LR, within the limitations of this study, is likely to be of minor clinical importance in extremity STS. Although it would be prudent to resect the CNB tract in most cases, not resecting the CNB tract is a feasible option if identification or removal of the CNB tract proves difficult.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heslin MJ, Lewis JJ, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF. Core needle biopsy for diagnosis of extremity soft tissue sarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 1997;4(5):425–31.
Strauss DC, Qureshi YA, Hayes AJ, Thway K, Fisher C, Thomas JM. The role of core needle biopsy in the diagnosis of suspected soft tissue tumours. J Surg Oncol. 2010;102(5):523–9.
Mankin HJ, Lange TA, Spanier S. The hazards of biopsy in patients with malignant primary bone and soft-tissue tumors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(8):1121–7.
Cannon S, Dyson P. Relationship of the site of open biopsy of malignant bone-tumors to local recurrence following resection and prosthetic replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69(3):492.
Saghieh S, Masrouha KZ, Musallam KM, et al. The risk of local recurrence along the core-needle biopsy tract in patients with bone sarcomas. Iowa Orthop J. 2010;30:80–3.
Schwartz HS, Spengler DM. Needle tract recurrences after closed biopsy for sarcoma: three cases and review of the literature. Ann Surg Oncol. 1997;4(3):228–36.
Davies NM, Livesley PJ, Cannon SR. Recurrence of an osteosarcoma in a needle biopsy track. J Bone Joint Surg. 1993;75(6):977–8.
Trojani M, Contesso G, Coindre J, et al. Soft-tissue sarcomas of adults; study of pathological prognostic variables and definition of a histopathological grading system. Int J Cancer. 1984;33(1):37–42.
Hoeber I, Spillane AJ, Fisher C, Thomas JM. Accuracy of biopsy techniques for limb and limb girdle soft tissue tumors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8(1):80–7.
Fowler N, Asatiani E, Cheson B. Needle tract seeding after bone marrow biopsy in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49(1):156–8.
Ito Y, Asahi S, Matsuzuka F, Nakamura Y, Amino N, Miyauchi A. Needle tract implantation of follicular neoplasm after fine-needle aspiration biopsy: report of a case. Thyroid Off J Am Thyroid Assoc. 2006;16(10):1059–62.
Kim JE, Kim CY, Kim DG, Jung HW. Implantation metastasis along the stereotactic biopsy tract in anaplastic astrocytoma: a case report. J Neuro-Oncol. 2003;61(3):215–8.
Suzuki K, Takamochi K, Funai K, Kazui T. Needle tract implantation clearly visualized by computed tomography following needle biopsy of malignant mesothelioma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg Off J Eur Assoc Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;29(6):1051.
Kaffenberger BH, Wakely Jr PE, Mayerson JL. Local recurrence rate of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in primary high-grade sarcomas. J Surg Oncol. 2010;101(7):618–21.
Binitie O, Tejiram S, Conway S, Cheong D, Temple HT, Letson GD. Adult soft tissue sarcoma local recurrence after adjuvant treatment without resection of core needle biopsy tract. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(3):891–8.
Wilkinson MJ, Martin JL, Khan AA, Hayes AJ, Thomas JM, Strauss DC. Percutaneous core needle biopsy in retroperitoneal sarcomas does not influence local recurrence or overall survival. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(3):853–8.
Chen AM, Haffty BG, Lee CH. Local recurrence of breast cancer after breast conservation therapy in patients examined by means of stereotactic core-needle biopsy. Radiology. 2002;225(3):707–12.
Fitzal F, Sporn EP, Draxler W, et al. Preoperative core needle biopsy does not increase local recurrence rate in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;97(1):9–15.
Knight R, Horiuchi K, Parker SH, Ratzer ER, Fenoglio ME. Risk of needle-track seeding after diagnostic image-guided core needle biopsy in breast cancer. JSLS J Soc Laparoendosc Surg Soc Laparoendosc Surg. 2002;6(3):207–9.
Robertson EG, Baxter G. Tumour seeding following percutaneous needle biopsy: the real story! Clin Radiol. 2011;66(11):1007–14.
Mohana R, Faisham W, Zulmi W, Nawfar A, Effat O, Salzihan M. The incidence of malignant infiltration in the biopsy tract of osteosarcoma. Malays Orthop J. 2007;1:7–10.
Schotman S, De Man R, Stoker J, Zondervan P, Ijzermans J. Subcutaneous seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous needle biopsy. Gut. 1999;45(4):626–7.
Eilber FC, Brennan MF, Riedel E, Alektiar KM, Antonescu CR, Singer S. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with locally recurrent extremity soft tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005;12(3):228–36.
Trovik CS, Scanadinavian Sarcoma Group P. Local recurrence of soft tissue sarcoma. A Scandinavian Sarcoma Group Project. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 2001;72(300):1–31.
Acknowledgements
No specific funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding sources
No specific funding was disclosed.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have nothing to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqi, M.A., Kim, HS., Jede, F. et al. Association of core needle biopsy tract resection with local recurrence in extremity soft tissue sarcoma. Skeletal Radiol 46, 507–512 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2579-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2579-8