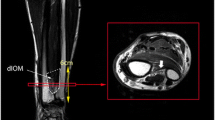
Abstract
The interosseous membrane of the forearm is an important structure to consider in cases of elbow and forearm trauma; it can be injured after elbow or forearm fractures, leading to longitudinal forearm instability. Diagnosis of interosseous membrane injuries is challenging, and failure in diagnosis may result in poor clinical outcomes and complications. Magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound have shown to be valuable methods for the evaluation of this important structure. Both techniques have advantages and limitations, and its use should be adapted to each specific clinical scenario. This article presents an up-to-date literature review regarding the use of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the forearm interosseous membrane evaluation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skahen 3rd JR, Palmer AK, Werner FW, Fortino MD. The interosseous membrane of the forearm: anatomy and function. J Hand Surg Am. 1997;6:981–5.
Davidson PA, Moseley Jr JB, Tullos HS. Radial head fracture. A potentially complex injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;297:224–30.
Hotchkiss RN, An KN, Sowa DT, Basta S and Weiland AJ. An anatomic and mechanical study of the interosseous membrane of the forearm: pathomechanics of proximal migration of the radius. J Hand Surg [Am] 1989; 256–261.
Rabinowitz RS, Light TR, Havey RM, Gourineni P, Patwardhan AG, Sartori MJ, et al. The role of the interosseous membrane and triangular fibrocartilage complex in forearm stability. J Hand Surg Am. 1994;3:385–93.
Wallace AL, Walsh WR, van Rooijen M, Hughes JS, Sonnabend DH. The interosseous membrane in radio-ulnar dissociation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;3:422–7.
Rodriguez-Martin J, Pretell-Mazzini J, Vidal-Bujanda C. Unusual pattern of Essex–Lopresti injury with negative plain radiographs of the wrist: a case report and literature review. Hand Surg. 2010;1:41–5.
Hotchkiss RN. Injuries to the interosseous ligament of the forearm. Hand Clin. 1994;3:391–8.
Marcotte AL, Osterman AL. Longitudinal radioulnar dissociation: identification and treatment of acute and chronic injuries. Hand Clin. 2007;2:195–208.
Skahen 3rd JR, Palmer AK, Werner FW, Fortino MD. Reconstruction of the interosseous membrane of the forearm in cadavers. J Hand Surg Am. 1997;6:986–94.
Stabile KJ, Pfaeffle J, Saris I, Li ZM, Tomaino MM. Structural properties of reconstruction constructs for the interosseous ligament of the forearm. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;2:312–8.
Tejwani SG, Markolf KL, Benhaim P. Graft reconstruction of the interosseous membrane in conjunction with metallic radial head replacement: a cadaveric study. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;2:335–42.
Tejwani SG, Markolf KL, Benhaim P. Reconstruction of the interosseous membrane of the forearm with a graft substitute: a cadaveric study. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;2:326–34.
Tomaino MM, Pfaeffle J, Stabile K, Li ZM. Reconstruction of the interosseous ligament of the forearm reduces load on the radial head in cadavers. J Hand Surg Br. 2003;3:267–70.
Smith AM, Urbanosky LR, Castle JA, Rushing JT, Ruch DS. Radius pull test: predictor of longitudinal forearm instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;11:1970–6.
Sowa DT, Hotchkiss RN, Weiland AJ. Symptomatic proximal translation of the radius following radial head resection. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;317:106–13.
Failla JM, Jacobson J, van Holsbeeck M. Ultrasound diagnosis and surgical pathology of the torn interosseous membrane in forearm fractures/dislocations. J Hand Surg Am. 1999;2:257–66.
Jaakkola JI, Riggans DH, Lourie GM, Lang CJ, Elhassan BT, Rosenthal SJ. Ultrasonography for the evaluation of forearm interosseous membrane disruption in a cadaver model. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;6:1053–7.
Matsuoka J, Beppu M, Nakajima H, Aoki H. Ultrasonography for the interosseous membrane of the forearm. Hand Surg. 2003;2:227–35.
Soubeyrand M, Lafont C, Oberlin C, France W, Maulat I, Degeorges R. The "muscular hernia sign": an original ultrasonographic sign to detect lesions of the forearm’s interosseous membrane. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;4:372–8.
Fester EW, Murray PM, Sanders TG, Ingari JV, Leyendecker J, Leis HL. The efficacy of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound in detecting disruptions of the forearm interosseous membrane: a cadaver study. J Hand Surg Am. 2002;3:418–24.
Hausmann JT, Vekszler G, Breitenseher M, Braunsteiner T, Vecsei V, Gabler C. Mason type-I radial head fractures and interosseous membrane lesions-a prospective study. J Trauma. 2009;2:457–61.
Hodler J, Cotten A, Trudell D, Resnick D. Magnetic resonance imaging of the forearm: cross-sectional anatomy in a cadaveric model. Invest Radiol. 1998;1:6–11.
McGinley JC, Roach N, Gaughan JP, Kozin SH. Forearm interosseous membrane imaging and anatomy. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;10:561–8.
McGinley JC, Roach N, Hopgood BC, Limmer K, Kozin SH. Forearm interosseous membrane trauma: MRI diagnostic criteria and injury patterns. Skeletal Radiol. 2006;5:275–81.
Nakamura T, Yabe Y, Horiuchi Y. In vivo MR studies of dynamic changes in the interosseous membrane of the forearm during rotation. J Hand Surg Br. 1999;2:245–8.
Nakamura T, Yabe Y, Horiuchi Y, Seki T, Yamazaki N. Normal kinematics of the interosseous membrane during forearm pronation-supination–a three-dimensional MRI study. Hand Surg. 2000;1:1–10.
Nakamura T, Yabe Y, Horiuchi Y, Yamazaki N. In vivo motion analysis of forearm rotation utilizing magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon). 1999;5:315–20.
Nakamura T, Yabe Y, Horiuchi Y, Yamazaki N. Three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the interosseous membrane of forearm: a new method using fuzzy reasoning. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;3:463–70.
Starch DW, Dabezies EJ. Magnetic resonance imaging of the interosseous membrane of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;2:235–8.
Hodler J, Yu JS, Steinert HC, Resnick D. MR imaging versus alternative imaging techniques. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1995;4:591–608.
Nazarian LN. The top 10 reasons musculoskeletal sonography is an important complementary or alternative technique to MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;6:1621–6.
Noda K, Goto A, Murase T, Sugamoto K, Yoshikawa H, Moritomo H. Interosseous membrane of the forearm: an anatomical study of ligament attachment locations. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;3:415–22.
Markolf KL, Lamey D, Yang S, Meals R, Hotchkiss R. Radioulnar load-sharing in the forearm. A study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;6:879–88.
McGinley JC, D’Addessi L, Sadeghipour K, Kozin SH. Mechanics of the antebrachial interosseous membrane: response to shearing forces. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;4:733–41.
McGinley JC, Kozin SH. Interosseous membrane anatomy and functional mechanics. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;383:108–22.
Rozental TD, Beredjiklian PK, Bozentka DJ. Longitudinal radioulnar dissociation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;1:68–73.
Allen GM, Wilson DJ. Ultrasound and the diagnosis of orthopaedic disorders. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;6:944–51.
Bianchi S, Martinoli C, Abdelwahab IF. High-frequency ultrasound examination of the wrist and hand. Skeletal Radiol. 1999;3:121–9.
Jacobson JA. Musculoskeletal sonography and MR imaging. A role for both imaging methods. Radiol Clin North Am. 1999;4:713–35.
Zanetti M, Hodler J. Ultrasonography and magnetic resonance tomography (MRI) of tendon injuries. Orthopade. 1995;3:200–8.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez-Martin, J., Pretell-Mazzini, J. The role of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of the forearm interosseous membrane. A review. Skeletal Radiol 40, 1515–1522 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-011-1190-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-011-1190-7