Abstract
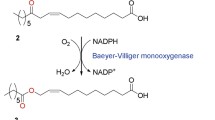
ω-Hydroxyundec-9-enoic acid (ω-HUA) was reported as a valuable medium-chain fatty acid with industrial potentials. For bioconversion of ricinoleic acid to ω-HUA, in this study, an alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh) from Micrococcus luteus, a Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase (BVMO) from Pseudomonas putida KT2440 and an esterase (Pfe1) from Pseudomonas fluorescens SIK WI were overexpressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). In order to enhance accessibility of Pfe1 to the (E)-11-(heptanoyloxy) undec-9-enoic acid (11-HOUA) substrate, a truncated PelB signal sequence without the recognition site of signal peptidase (tPelB) was attached to the N-terminus of Pfe1, resulting in the construction of E. coli AB-tPE strain expressing Adh, BVMO and the tPelB-Pfe1 fusion protein. A batch-type biotransformation of ricinoleic acid by E. coli AB-tPE resulted in 1.8- and 2.2-fold increases in ω-HUA conversion yield and productivity, respectively, relative to those for the control strain without the PelB sequence (AB-E). By fed-batch-type biotransformation with glycerol feeding, the AB-tPE strain produced 23.7 mM (equivalent to 4.7 g/L) of ω-HUA with 60.8%(mol/mol) of conversion yield and 1.2 mM/h of productivity, which were 13.2, 2.9, and 2.6 times higher than those in a batch-type biotransformation using the AB-E strain. In conclusion, combination of the truncated PelB-Pfe1 fusion and fed-batch process with glycerol feeding provided the highest efficiency of ω-HUA biotransformation, of which strategies might be applicable for biotransformation of hydrophobic substances.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayorinde FO, Nana EY, Nicely PD, Woods AS, Price EO, Nwaonicha CP (1997) Syntheses of 12-aminododecanoic and 11-aminoundecanoic acids from vernolic acid. J Am Oil Chem Soc 74(5):531–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-997-0176-z
Biermann U, Bornscheuer U, Meier MAR, Metzger JO, Schafer HJ (2011) Oils and fats as renewable raw materials in chemistry. Angew Chem Int Edit 50(17):3854–3871. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201002767
Cho Y-H, Lee H-J, Lee J-E, Kim S-J, Park K, Lee DY, Park Y-C (2015) Fast determination of multiple-reaction intermediates for long-chain dicarboxylic acid biotransformation by gas chromatography-flame ionization detector. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(5):704–708. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1502.02026
Cho Y-H, Kim S-J, Kim H-W, Kim JY, Gwak JS, Chung D, Kim KH, Park K, Park Y-C (2017) Continuous supply of glucose and glycerol enhances biotransformation of ricinoleic acid to (E)-11-(heptanoyloxy) undec-9-enoic acid in recombinant Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 253:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.05.014
Desbois AP, Smith VJ (2010) Antibacterial free fatty acids: activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biot 85(6):1629–1642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2355-3
Henke E, Bornscheuer UT (2002) Esterases from Bacillus subtilis and B. stearothermophilus share high sequence homology but differ substantially in their properties. Appl Microbiol Biot 60(3):320–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1126-1
Jang HY, Jeon EY, Baek AH, Lee SM, Park JB (2014) Production of ω-hydroxyundec-9-enoic acid and n-heptanoic acid from ricinoleic acid by recombinant Escherichia coli-based biocatalyst. Process Biochem 49(4):617–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.01.025
Jang HY, Singha K, Kim HH, Kwon YU, Park JB (2016) Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of 11-hydroxyundecanoic acid and 1,11-undecanedioic acid from ricinoleic acid. Green Chem 18(4):1089–1095. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC01017A
John GT, Heinzle E (2001) Quantitative screening method for hydrolases in microplates using pH indicators: determination of kinetic parameters by dynamic pH monitoring. Biotechnol Bioeng 72(6):620–627. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0290(20010320)72:6<620::AID-BIT1027>3.0.CO;2-W
Jung SM, Seo JH, Lee JH, Park JB, Seo JH (2015) Fatty acid hydration activity of a recombinant Escherichia coli-based biocatalyst is improved through targeting the oleate hydratase into the periplasm. Biotechnol J 10(12):1887–1893. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201500141
Kim SJ, Seo SO, Jin YS, Seo JH (2013) Production of 2,3-butanediol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 146:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.081
Kim SK, Park YC, Lee HH, Jeon ST, Min WK, Seo JH (2015) Simple amino acid tags improve both expression and secretion of Candida antarctica lipase B in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 112(2):346–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25361
Kim H, Lee H-S, Park H, Lee D-H, Boles E, Chung D, Park Y-C (2017) Enhanced production of xylitol from xylose by expression of Bacillus subtilis arabinose:H+ symporter and Scheffersomyces stipitis xylose reductase in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzym Microb Technol 107:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2017.07.014
Lee YA, Jeon EY, Lee SM, Bornscheuer UT, Park JB (2014) Engineering the substrate-binding domain of an esterase enhances its hydrolytic activity toward fatty acid esters. Process Biochem 49(12):2101–2106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.09.019
Lei SP, Lin HC, Wang SS, Callaway J, Wilcox G (1987) Characterization of the Erwinia carotovora pelB gene and its product pectate lyase. J Bacteriol 169(9):4379–4383. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.169.9.4379-4383.1987
Martinez-Rojas E, Kurt T, Schmidt U, Meyer V, Garbe L-A (2014) A bifunctional enzyme from Rhodococcus erythropolis exhibiting secondary alcohol dehydrogenase-catalase activities. Appl Microbiol Biot 98(22):9249–9258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5808-2
Singh P, Sharma L, Kulothungan SR, Adkar BV, Prajapati RS, Ali PSS, Krishnan B, Varadarajan R (2013) Effect of signal peptide on stability and folding of Escherichia coli thioredoxin. Plos One 8(5). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063442
Song JW, Jeon EY, Song DH, Jang HY, Bornscheuer UT, Oh DK, Park JB (2013) Multistep enzymatic synthesis of long-chain alpha,omega-dicarboxylic and omega-hydroxycarboxylic acids from renewable fatty acids and plant oils. Angew Chem Int Edit 52(9):2534–2537. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201209187
Song JW, Lee JH, Bornscheuer UT, Park JB (2014) Microbial synthesis of medium-chain α,ω-dicarboxylic acids and ω-aminocarboxylic acids from renewable long-chain fatty acids. Adv Synth Catal 356(8):1782–1788. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201300784
Stillwell W (2016) Introduction to Biological Membranes. In: An introduction to biological membranes: composition, structure and function. Elsevier, London
Suzuki Y, Kurita O, Kono Y, Hyakutake H, Sakurai A (1995) Structure of a new antifungal C11-hydroxyfatty acid isolated from leaves of wild rice (Oryza officinalis). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59(11):2049–2051. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.59.2049
Yang YX, Lu WH, Zhang XY, Xie WC, Cai MM, Gross RA (2010) Two-step biocatalytic route to biobased functional polyesters from ω-carboxy fatty acids and diols. Biomacromolecules 11(1):259–268. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm901112m
Yang KM, Kim BM, Park JB (2014) ω-Hydroxyundec-9-enoic acid induces apoptosis through ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biochem Bioph Res Co 448(3):267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.111
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the R&D Program of MOTIE/KEIT (10044647 and 10048684) and The Advanced Biomass R&D Center (ABC) of Korea Grant (2011-0031359) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1298 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, YH., Kim, SJ., Kim, JY. et al. Effect of PelB signal sequences on Pfe1 expression and ω-hydroxyundec-9-enoic acid biotransformation in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 7407–7416 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9139-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9139-6