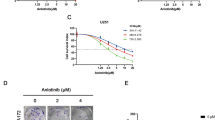
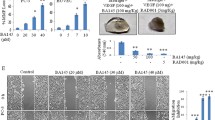
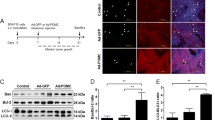
Abstract
Glioblastoma, characterized by extensive microvascular proliferation and invasive tumor growth, is one of the most common and lethal malignancies in adults. Benefits of the conventional anti-angiogenic therapy were only observed in a subset of patients and limited by diverse relapse mechanism. Fortunately, recent advances in cancer immunotherapy have offered new hope for patients with glioblastoma. Herein, we reported a novel dual-targeting therapy for glioblastoma through simultaneous blockade of VEGF and CD47 signaling. Our results showed that VEGFR1D2-SIRPαD1, a VEGF and CD47 bispecific fusion protein, exerted potent anti-tumor effects via suppressing VEGF-induced angiogenesis and activating macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. Meanwhile, autophagy was activated by VEGFR1D2-SIRPαD1 through inactivating Akt/mTOR and Erk pathways in glioblastoma cells. Importantly, autophagy inhibitor or knockdown of autophagy-related protein 5 potentiated VEGFR1D2-SIRPαD1-induced macrophage phagocytosis and cytotoxicity against glioblastoma cells. Moreover, suppression of autophagy led to increased macrophage infiltration, angiogenesis inhibition, and tumor cell apoptosis triggered by VEGF and CD47 dual-targeting therapy, thus eliciting enhanced anti-tumor effects in glioblastoma. Our data revealed that VEGFR1D2-SIRPαD1 alone or in combination with autophagy inhibitor could effectively elicit potent anti-tumor effects, highlighting potential therapeutic strategies for glioblastoma through disrupting angiogenetic axis and CD47-SIRPα anti-phagocytic axis alone or in combination with autophagy inhibition.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen E, Jabouille A, Rivera LB, Lodewijckx I, Missiaen R, Steri V, Feyen K, Tawney J, Hanahan D, Michael IP, Bergers G (2017) Combined antiangiogenic and anti-PD-L1 therapy stimulates tumor immunity through HEV formation. Sci Transl Med 9. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aak9679
Bakas S, Akbari H, Pisapia J, Martinez-Lage M, Rozycki M, Rathore S, Dahmane N, O’Rourke DM, Davatzikos C (2017) In vivo detection of EGFRvIII in glioblastoma via perfusion magnetic resonance imaging signature consistent with deep peritumoral infiltration: the phi-index. Clin Cancer Res 23:4724–4734. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1871
Boucher JM, Bautch VL (2014) Antiangiogenic VEGF-A in peripheral artery disease. Nat Med 20:1383–1385. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3767
Boya P, Codogno P, Rodriguez-Muela N (2018) Autophagy in stem cells: repair, remodelling and metabolic reprogramming. Development 145. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.146506
Chao MP, Majeti R, Weissman IL (2011) Programmed cell removal: a new obstacle in the road to developing cancer. Nat Rev. Cancer 12:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3171
Cioffi M, Trabulo S, Hidalgo M, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Erkan M, Kleeff J, Sainz B Jr, Heeschen C (2015) Inhibition of CD47 effectively targets pancreatic cancer stem cells via dual mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res 21:2325–2337. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1399
De Henau O, Rausch M, Winkler D, Campesato LF, Liu C, Cymerman DH, Budhu S, Ghosh A, Pink M, Tchaicha J, Douglas M, Tibbitts T, Sharma S, Proctor J, Kosmider N, White K, Stern H, Soglia J, Adams J, Palombella VJ, McGovern K, Kutok JL, Wolchok JD, Merghoub T (2016) Overcoming resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy by targeting PI3Kgamma in myeloid cells. Nature 539:443–447. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20554
Diaz RJ, Ali S, Qadir MG, De La Fuente MI, Ivan ME, Komotar RJ (2017) The role of bevacizumab in the treatment of glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 133:455–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2477-x
Ellingson BM, Gerstner E, Smits M, Huang RY, Colen RR, Abrey LE, Aftab DT, Schwab GM, Hessel C, Harris RJ, Chakhoyan A, Gahrmann R, Pope WB, Leu K, Raymond C, Woodworth DC, de Groot JF, Wen PY, Batchelor T, van den Bent MJ, Cloughesy TF (2017) Diffusion MRI phenotypes predict overall survival benefitfrom anti-VEGF monotherapy in recurrent glioblastoma:Converging evidence from phase II trials. Clin Cancer Res 23:5745–5756. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2844
Gholamin S, Mitra SS, Feroze AH, Liu J, Kahn SA, Zhang M, Esparza R, Richard C, Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Volkmer AK, Willingham S, Ponnuswami A, McCarty A, Lovelace P, Storm TA, Schubert S, Hutter G, Narayanan C, Chu P, Raabe EH, Harsh Gt, Taylor MD, Monje M, Cho YJ, Majeti R, Volkmer JP, Fisher PG, Grant G, Steinberg GK, Vogel H, Edwards M, Weissman IL, Cheshier SH (2017) Disrupting the CD47-SIRPalpha anti-phagocytic axis by a humanized anti-CD47 antibody is an efficacious treatment for malignant pediatric brain tumors. Sci Transl Med 9. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf2968
Guo G, Gong K, Ali S, Ali N, Shallwani S, Hatanpaa KJ, Pan E, Mickey B, Burma S, Wang DH, Kesari S, Sarkaria JN, Zhao D, Habib AA (2017) A TNF-JNK-Axl-ERK signaling axis mediates primary resistance to EGFR inhibition in glioblastoma. Nat Neurosci 20:1074–1084. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4584
Hagberg CE, Mehlem A, Falkevall A, Muhl L, Fam BC, Ortsater H, Scotney P, Nyqvist D, Samen E, Lu L, Stone-Elander S, Proietto J, Andrikopoulos S, Sjoholm A, Nash A, Eriksson U (2012) Targeting VEGF-B as a novel treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 490:426–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11464
Hu B, Wang Q, Wang YA, Hua S, Sauve CG, Ong D, Lan ZD, Chang Q, Ho YW, Monasterio MM, Lu X, Zhong Y, Zhang J, Deng P, Tan Z, Wang G, Liao WT, Corley LJ, Yan H, Zhang J, You Y, Liu N, Cai L, Finocchiaro G, Phillips JJ, Berger MS, Spring DJ, Hu J, Sulman EP, Fuller GN, Chin L, Verhaak RG, DePinho RA (2016) Epigenetic activation of WNT5A drives glioblastoma stem cell differentiation and invasive growth. Cell 167:1281–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.039
Hu YL, DeLay M, Jahangiri A, Molinaro AM, Rose SD, Carbonell WS, Aghi MK (2012) Hypoxia-induced autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and adaptation to antiangiogenic treatment in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 72:1773–1783. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3831
Jalali S, Chung C, Foltz W, Burrell K, Singh S, Hill R, Zadeh G (2014) MRI biomarkers identify the differential response of glioblastoma multiforme to anti-angiogenic therapy. Neuro Onco 16:868–879. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou040
Jeanbart L, Swartz MA (2015) Engineering opportunities in cancer immunotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:14467–14,472. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1508516112
Jung K, Heishi T, Khan OF, Kowalski PS, Incio J, Rahbari NN, Chung E, Clark JW, Willett CG, Luster AD, Yun SH, Langer R, Anderson DG, Padera TP, Jain RK, Fukumura D (2017) Ly6Clo monocytes drive immunosuppression and confer resistance to anti-VEGFR2 cancer therapy. J Clin Invest 127:3039–3051. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI93182
Kim D, Fiske BP, Birsoy K, Freinkman E, Kami K, Possemato RL, Chudnovsky Y, Pacold ME, Chen WW, Cantor JR, Shelton LM, Gui DY, Kwon M, Ramkissoon SH, Ligon KL, Kang SW, Snuderl M, Vander Heiden MG, Sabatini DM (2015) SHMT2 drives glioma cell survival in ischaemia but imposes a dependence on glycine clearance. Nature 520:363–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14363
Lee H, Lee JK, Park MH, Hong YR, Marti HH, Kim H, Okada Y, Otsu M, Seo EJ, Park JH, Bae JH, Okino N, He X, Schuchman EH, Bae JS, Jin HK (2014) Pathological roles of the VEGF/SphK pathway in Niemann-Pick type C neurons. Nat Commun 5:5514. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6514
Lombardi G, Pambuku A, Bellu L, Farina M, Della Puppa A, Denaro L, Zagonel V (2017) Effectiveness of antiangiogenic drugs in glioblastoma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 111:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.01.018
Mondal A, Kumari Singh D, Panda S, Shiras A (2017) Extracellular vesicles as modulators of tumor microenvironment and disease progression in glioma. Front Oncol 7:144. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2017.00144
Peng QX, Han YW, Zhang YL, Hu J, Fan J, Fu SZ, Xu S, Wan Q (2017) Apatinib inhibits VEGFR-2 and angiogenesis in an in vivo murine model of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 8:52813–52,822. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17264
Ramagopal UA, Liu W, Garrett-Thomson SC, Bonanno JB, Yan Q, Srinivasan M, Wong SC, Bell A, Mankikar S, Rangan VS, Deshpande S, Korman AJ, Almo SC (2017) Structural basis for cancer immunotherapy by the first-in-class checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E4223–E4232. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1617941114
Rubinsztein DC, Codogno P, Levine B (2012) Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:709–730. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3802
Sagiv-Barfi I, Kohrt HE, Czerwinski DK, Ng PP, Chang BY, Levy R (2015) Therapeutic antitumor immunity by checkpoint blockade is enhanced by ibrutinib, an inhibitor of both BTK and ITK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E966–E972. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1500712112
Sareddy GR, Viswanadhapalli S, Surapaneni P, Suzuki T, Brenner A, Vadlamudi RK (2017) Novel KDM1A inhibitors induce differentiation and apoptosis of glioma stem cells via unfolded protein response pathway. Oncogene 36:2423–2434. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.395
Selvakumaran M, Amaravadi RK, Vasilevskaya IA, O’Dwyer PJ (2013) Autophagy inhibition sensitizes colon cancer cells to antiangiogenic and cytotoxic therapy. Clin Cancer Res 19:2995–3007. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1542
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF (1983) Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science 219:983–985. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6823562
Shen W, Zhang X, Fu X, Fan J, Luan J, Cao Z, Yang P, Xu Z, Ju D (2017) A novel and promising therapeutic approach for NSCLC: recombinant human arginase alone or combined with autophagy inhibitor. Cell Death Dis 8:e2720. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.137
Sockolosky JT, Dougan M, Ingram JR, Ho CC, Kauke MJ, Almo SC, Ploegh HL, Garcia KC (2016) Durable antitumor responses to CD47 blockade require adaptive immune stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E2646–E2654. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1604268113
Stanton MJ, Dutta S, Zhang H, Polavaram NS, Leontovich AA, Honscheid P, Sinicrope FA, Tindall DJ, Muders MH, Datta K (2013) Autophagy control by the VEGF-C/NRP-2 axis in cancer and its implication for treatment resistance. Cancer Res 73:160–171. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3635
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 60:166–193. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20069
Vonderheide RH (2015) CD47 blockade as another immune checkpoint therapy for cancer. Nat Med 21:1122–1123. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3965
Wen Y, Graybill WS, Previs RA, Hu W, Ivan C, Mangala LS, Zand B, Nick AM, Jennings NB, Dalton HJ, Sehgal V, Ram P, Lee JS, Vivas-Mejia PE, Coleman RL, Sood AK (2015) Immunotherapy targeting folate receptor induces cell death associated with autophagy in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21:448–459. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1578
Willingham SB, Volkmer JP, Gentles AJ, Sahoo D, Dalerba P, Mitra SS, Wang J, Contreras-Trujillo H, Martin R, Cohen JD, Lovelace P, Scheeren FA, Chao MP, Weiskopf K, Tang C, Volkmer AK, Naik TJ, Storm TA, Mosley AR, Edris B, Schmid SM, Sun CK, Chua MS, Murillo O, Rajendran P, Cha AC, Chin RK, Kim D, Adorno M, Raveh T, Tseng D, Jaiswal S, Enger PO, Steinberg GK, Li G, So SK, Majeti R, Harsh GR, van de Rijn M, Teng NN, Sunwoo JB, Alizadeh AA, Clarke MF, Weissman IL (2012) The CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPa) interaction is a therapeutic target for human solid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:6662–6667. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1121623109
Zeng X, Zhao H, Li Y, Fan J, Sun Y, Wang S, Wang Z, Song P, Ju D (2015) Targeting Hedgehog signaling pathway and autophagy overcomes drug resistance of BCR-ABL-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Autophagy 11:355–372. https://doi.org/10.4161/15548627.2014.994368
Zhang B, Fan J, Zhang X, Shen W, Cao Z, Yang P, Xu Z, Ju D (2016) Targeting asparagine and autophagy for pulmonary adenocarcinoma therapy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:9145–9161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7640-3
Zhang X, Chen W, Fan J, Wang S, Xian Z, Luan J, Li Y, Wang Y, Nan Y, Luo M, Li S, Tian W, Ju D (2018) Disrupting CD47-SIRPα axis alone or combined with autophagy depletion for the therapy of glioblastoma. Carcinogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgy041
Zhang X, Fan J, Wang S, Li Y, Wang Y, Li S, Luan J, Wang Z, Song P, Chen Q, Tian W, Ju D (2017) Targeting CD47 and autophagy elicited enhanced antitumor effects in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 5:363–375. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0398
Zhu Y, Li H, Ding S, Wang Y (2018) Autophagy inhibition promotes phagocytosis of macrophage and protects mice from methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26677
Funding
The work was funded by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (grant number 2015CB931800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81573332 and 81773620), and the Special Research Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Medical Genomics and Collaborative Innovation Center of Systems Biomedicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Wenzhi Tian is the founder and Song Li is the employee of ImmuneOnco Biopharma (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Others declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures involving animals were conducted in accordance with the standards approved by Animal Ethical Committee of School of Pharmacy at Fudan University.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1507 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Wang, S., Nan, Y. et al. Inhibition of autophagy potentiated the anti-tumor effects of VEGF and CD47 bispecific therapy in glioblastoma. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 6503–6513 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9069-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9069-3