Abstract
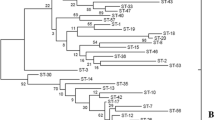
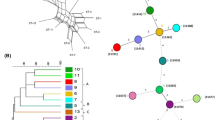
In the present study, 35 Leuconostoc mesenteroides strains isolated from vegetables and food products from South Korea were studied by multilocus sequence typing (MLST) of seven housekeeping genes (atpA, groEL, gyrB, pheS, pyrG, rpoA, and uvrC). The fragment sizes of the seven amplified housekeeping genes ranged in length from 366 to 1414 bp. Sequence analysis indicated 27 different sequence types (STs) with 25 of them being represented by a single strain indicating high genetic diversity, whereas the remaining 2 were characterized by five strains each. In total, 220 polymorphic nucleotide sites were detected among seven housekeeping genes. The phylogenetic analysis based on the STs of the seven loci indicated that the 35 strains belonged to two major groups, A (28 strains) and B (7 strains). Split decomposition analysis showed that intraspecies recombination played a role in generating diversity among strains. The minimum spanning tree showed that the evolution of the STs was not correlated with food source. This study signifies that the multilocus sequence typing is a valuable tool to access the genetic diversity among L. mesenteroides strains from South Korea and can be used further to monitor the evolutionary changes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegría Á, Delgado S, Flórez AB, Mayo B (2013) Identification, typing, and functional characterization of Leuconostoc spp. strains from traditional, starter-free cheeses. Dairy Sci Technol 93:657–673
Axelsson L (2004) Lactic acid bacteria: classification and physiology. In: Salminen S, Wright AV, Ouwehand A (eds) Lactic acid bacteria: microbiological and functional aspects. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–66
Bain JM, Tavanti A, Davidson AD, Jacobsen MD, Shaw D, Gow NAR, Odds FC (2007) Multilocus sequence typing of the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. J Clinic Microbiol 45(5):1469–1477
Bilhere E, Lucas PM, Claisse O, Lonvaud-Funel A (2009) Multilocus sequence typing of Oenococcus oeni: detection of two subpopulations shaped by intergenic recombination. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1291–1300
Björkroth KJ, Geisen R, Schillinger U, Weiss N, De Vos P, Holzapfel WH, Korkeala HJ, Vandamme P (2000) Characterization of Leuconostoc gasicomitatum sp. nov., associated with spoiled raw tomato-marinated broiler meat strips packaged under modified-atmosphere conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(9):3764–3772
Botina SG, Tsygankov YD, Sukhodolets VV (2006) Identification of industrial strains of lactic acid bacteria by methods of molecular genetic typing. Russ J Genet 42(12):1367–1379
de Bruyne K, Schillinger U, Caroline L, Boehringer B, Cleenwerck I, Vancanneyt M, Vuyst LD, Franz MAPC, Vandamme P (2007) Leuconostoc holzapfelii sp. nov., isolated from Ethiopian coffee fermentation and assessment of sequence analysis of housekeeping genes for delineation of Leuconostoc species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2952–2959
Cai H, Rodriguez BT, Zhang W, Broadbent JR, Steele JL (2007) Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Lactobacillus casei strains isolated from different ecological niches suggests frequent recombination and niche specificity. Microbiology 153:2655–2665
Calmin G, Lefort F, Belbahri L (2008) Multi-loci sequence typing for two lacto-acid bacteria (LAB) species: Pediococcus paryulus and P. damnosus. Mol Biotechnol 40:170–179
Chaillou S, Lucquin I, Najjari A, Zagorec M, Champomier-Vergès MC (2013) Population genetics of Lactobacillus sakei reveals three lineages with distinct evolutionary histories. PLoS One 8(9):e73253
Cibik R, Lepage E, Talliez P (2000) Molecular diversity of Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Leuconostoc citreum isolated from traditional French cheeses as revealed by RAPD fingerprinting, 16S rDNA sequencing and 16S rDNA fragment amplification. Syst Appl Microbiol 23(2):267–278
Dan T, Liu W, Sun Z, Lv Q, Xu H, Song Y, Zhang H (2014) A novel multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) protocol for Leuconostoc lactis isolates from traditional dairy products in China and Mongolia. BMC Microbiol 14:150
Dan T, Liu W, Song Y, Xu H, Menghe B, Zhang H, Sun Z (2015) The evolution and population structure of Lactobacillus fermentum from different naturally fermented products as determined by multilocus sequence typing (MLST). BMC Microbiol 15:107
Dingle KE, Colles FM, Wareing DRA, Ure R, Fox AJ, Bolton FE, Bootsma HJ, Willems RJL, Urwin R, Maiden MCJ (2001) Multilocus sequence typing system for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clinic Microbiol 39:14–23
Farfán M, Miñana-Galbis D, Fusté MC, Lorén JG (2002) Allelic diversity and population structure in Vibrio cholera O139 Bengal based on nucleotide sequence analysis. J Bacteriol 184:1304–1313
Feil EJ, Enright MC (2004) Analyses of clonality and the evolution of bacterial pathogens. Curr Opin Microbiol 7(3):308–313
Gemechu T (2015) Review on lactic acid bacteria function in milk fermentation and preservation. Afr J Food Sci 9(4):170–175
Glaeser P, Kämpfer P (2014) Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) in prokaryotic taxonomy. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:237–245
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hayek SA, Ibrahim SA (2013) Current limitations and challenges with lactic acid bacteria: a review. Food Nutr Sci 4:73–87
Helgason E, Tourasse NJ, Meisal R, Caugant DA, Kolsto AB (2004) Multilocus sequence typing scheme for bacteria of the Bacillus cereus group. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:191–201
Hemme D, Foucaud-Scheunemann C (2004) Leuconostoc, characteristics, use in dairy technology and prospects in functional foods. Int Dairy J 14:467–494
Huson DH, Bryant D (2006) Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol Bio Evol 23(2): 254–267
Jeong SJ, Park JY, Lee HJ, Kim JH (2007) Characterization of pFMBL1, a small cryptic plasmid isolated from Leuconostoc mesenteroides SY2. Plasmid 57(3):314–323
Jolley KA, Feil EJ, Chan MS, Maiden MC (2001) Sequence type analysis and recombinational tests (START). Bioinformatics 17(12):1230–1231
Kaur J, Lee S, Park Y-S, Sharma A (2017) RAPD analysis of Leuconostoc mesenteroides strains associated with vegetables and food products from Korea. LWT - Food Sci Technol 77:383–388
Konstantinidis KT, Ramette A, Tiedje JM (2006) Towards a more robust assessment of intra-species diversity using fewer genetic markers. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7286–7293
Korber B (2000) HIV signature and sequence variation analysis. In: Rodrigo AG, Learn GH (eds) Computational analysis of HIV molecular sequences. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 55–72
Kot W, Neve H, Heller KJ, Vogensen FK (2014) Bacteriophages of Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, and Weissella. Front Microbiol 5:186
Kryazhimskiy S, Plotkin JB (2008) The population genetics of d N /d S . PLoS Genet 4:e1000304
Kunene NF, Geornaras I, Von Holy A, Hastings JW (2000) Characterization and determination of origin of lactic acid bacteria from a sorghum-based fermented weaning food by analysis of soluble proteins and amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(3):1084–1092
de Las Rivas B, Marcobal A, Munoz R (2006) Development of a multilocus sequence typing method for analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Microbiology 152:85–93
Lee HM, Lee Y (2008) A differential medium for lactic acid-producing bacteria in a mixed culture. Lett Appl Microbiol 46(6):676–681
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSPv5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphisms data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Maiden MC, Bygraves JA, Feil E, Morelli G, Russell JE, Urwin R, Zhang Q, Zhou J, Zurth K, Caugant DA, Feavers IM, Achtman M, Spratt BG (1998) Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(6):3140–3145
Meslier V, Loux V, Renault P (2012) Genome sequence of Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides strain 4882, isolated from a diary starter culture. J Bacteriol 194:696–712
Nieto-Arribas P, Sesena S, Poveda JM, Palop L, Cabezas L (2010) Genotypic and technological characterization of Leuconostoc isolates to be used as adjunct starters in Manchego cheese manufacture. Food Microbiol 27:85–93
Oh PL, Benson AK, Peterson DA, Patil PB, Moriyama EN, Roos S, Walter J (2010) Diversification of the gut symbiont Lactobacillus reuteri as a result of host-driven evolution. ISME J 4(3):377–387
Passerini D, Beltramo C, Coddeville M, Quentin Y, Ritzenthaler P, Daveran-Mingot M-L, Bourgeois PL (2010) Genes but not genomes reveal bacterial domestication of Lactococcus Lactis. PLoS One 5(12):e15306
Pérez G, Cardell E, Zárate V (2002) Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis for differentiation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides subspecies isolated from Tenerife cheese. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:82–85
Picozzi C, Bonacina G, Vigentini I, Foschino R (2010) Genetic diversity in Italian Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis strains assessed by multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analyses. Microbiology 156:2035–2045
Rahman A, Cailliez-Grimal C, Bontemps C, Payot S, Chaillou S, Revol-Junelles A-M, Borgesa F (2014) High genetic diversity among strains of the unindustrialized lactic acid bacterium Carnobacterium maltaromaticum in dairy products as revealed by multilocus sequence typing. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(13):3920–3929
Sabat AG, Budimir AJ, Nashev D, Sá-Leão R, van Dijl J, Laurent F, Grundmann H, Friedrich AW (2013) Overview of molecular typing methods for outbreak detection and epidemiological surveillance. Euro Surveill 18(4):20380
Sánchez JI, Martínez B, Rodríguez A (2005) Rational selection of Leuconostoc strains for mixed starters based on the physiological biodiversity found in raw milk fermentations. Int J Food Microbiol 105:377–387
Song Y, Sun Z, Guo C, Wu Y, Liu W, Yu J, Menghe B, Yang R, Zhang H (2016) Genetic diversity and population structure of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subspecies bulgaricus isolated from naturally fermented dairy foods. Sci Reports 6:22704
Steele J, Broadbent J, Kok J (2013) Perspective on the contribution of lactic acid bacteria to cheese flavor development. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(2):135–141
Tanganurat W, Quinquis B, Leelawatcharamas V, Bolotin A (2009) Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Thai fermented fruits and vegetables. J Basic Microbiol 49:377–385
Tanigawa K, Watanabe K (2011) Multilocus sequence typing reveals a novel sub speciation of Lactobacillus delbrueckii. Microbiology 157:727–738
Unemo M, Dillon J-AR (2011) Review and international recommendation of methods for typing Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates and their implications for improved knowledge of gonococcal epidemiology, treatment and biology. Clinic Microbiol Rev 24(3):447–458
Urwin R, Maiden MC (2003) Multi-locus sequence typing: a tool for global epidemiology. Trends Microbiol 11(10):479–487
Vihavainen EJ, Björkroth KJ (2009) Diversity of Leuconostoc gasicomitatum associated with meat spoilage. Int J Food Microbiol 136(1):32–36
Wassie M, Wassie T (2016) Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from raw cow milk. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci 3(8):44–49
Weng PL, Ramli R, Shamsudin MN, Cheah YK, Hamat RA (2013) High genetic diversity of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis clinical isolates by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and multilocus sequence typing from a hospital in Malaysia. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–6
Zhang ZG, Ye ZQ, Yu L, Shi P (2011) Phylogenomic reconstruction of lactic acid bacteria: an update. BMC Evol Biol 11(1):1–12
Zhang W, Liu W, Song Y, Xu H, Menghe B, Zhang H, Sun Z (2015) Multilocus sequence typing of a dairy-associated Leuconostoc mesenteroides population reveals clonal structure with intragenic homologous recombination. J Dairy Sci 98:1–10
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through the High Value-added Food Technology Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (grant number: 314073-03-2-HD040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Kaur, J., Lee, S. et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Leuconostoc mesenteroides from Korean vegetables and food products by multilocus sequence typing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 4853–4861 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8942-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8942-4