Abstract
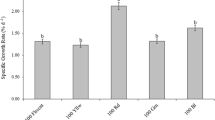
The effect of mixed light quality with red, blue, and green LED lamps on the growth of Arthrospira platensis was studied, so as to lay the theoretical and technical basis for establishing a photo-bioreactor lighting system for application in space. Meanwhile, indexes, like morphology, growth rate, photosynthetic pigment compositions, energy efficiency, and main nutritional components, were measured respectively. The results showed that the blue light combined with red light could decrease the tightness of filament, and the effect of green light was opposite. The combination of blue light or green light with red light induced the filaments to get shorter in length. The 8R2B treatment could promote the growth of Arthrospira platensis significantly, and its dry weight reached 1.36 g L−1, which was 25.93% higher than the control. What’s more, 8R2B treatment had the highest contents of carbohydrate and lipid, while 8R2G was rich in protein. 8R0.5G1.5B had the highest efficiency of biomass production, which was 161.53 mg L−1 kW−1 h−1. Therefore, the combination of red and blue light is more conducive to the growth of Arthrospira platensis, and a higher biomass production and energy utilization efficiency can be achieved simultaneously under the mixed light quality with the ratio of 8R0.5G1.5B.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carvalho AP, Silva SO, Baptista JM, Malcata FX (2011) Light requirements in microalgal photobioreactors: an overview of biophotonic aspects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1275–1288
Ciferri O (1983) Spirulina, the edible microorganism. Microbiol Rev 47:551
Das P, Lei W, Aziz SS, Obbard JP (2011) Enhanced algae growth in both phototrophic and mixotrophic culture under blue light. Bioresour Technol 102:3883–3887
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1980) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances—analytical chemistry (ACS publications). Spring 89:449–454
Fu W, Guðmundsson Ó, Paglia G, Herjólfsson G, Andrésson ÓS, Palsson BØ, Brynjólfsson S (2013) Enhancement of carotenoid biosynthesis in the green microalga Dunaliella salina with light-emitting diodes and adaptive laboratory evolution. Appl Microbiol Biot 97:2395–2403
Ganzer B, Messerschmid E (2009) Integration of an algal photobioreactor into an environmental control and life support system of a space station. Acta Astronaut 65:248–261
Gao K, Li P, Watanabe T, Walter HE (2010) Combine effects of ultraviolet radiation and temperature on morphology photosynthesis and DNA of Arthrospira (spirulina) platensis (cyanophyta). J Phycol 44:777–786
Guo S, Ai W, Fei J, Xu G, Zeng G, Shen Y (2015) Study on the kinetic characteristics of trace harmful gases for a two-person-30-day integrated CELSS test. Envion Sci Pollut 22:7020–7024
Hans P, Martins RST, Peter B, Buma AGJ, Osamu N, Breeman AM (2010) Effects of temperature on the photoreactivation of UVB-induced DNA damage in Palmaria palmata (Rhodophyta). J Phycol 36:334–341
Hohmann MF, Blankenship RE (2011) Evolution of photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:515
Iacute M, Dek JI, Iacute K, Žek M, Torzillo G (2004) Photosynthesis in microalgae. Blackwell Publishing Ltd 81:20–39
Itoh K, Nakamura K, Aoyama T, Kakimoto T, Murakami M, Takido T (2014) The influence of wavelength of light on cyanobacterial asymmetric reduction of ketone. Tetrahedron Lett 55:435–437
Jungandreas A, Costa BS, Jakob T, Bergen MV, Baumann S, Wilhelm C (2014) The acclimation of phaeodactylum tricornutum to blue and red light does not influence the photosynthetic light reaction but strongly disturbs the carbon allocation pattern. PLoS One 9:e99727
Keeling PJ (2013) The number, speed, and impact of plastid endosymbioses in eukaryotic evolution. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:583–607
Kim HH, Goins GD, Wheeler RM, Sager JC (2004) Green-light supplementation for enhanced lettuce growth under red- and blue-light-emitting diodes. Hortscience 39:1617–1622
Kim T, Lee Y, Han S, Hwang S (2013) The effects of wavelength and wavelength mixing ratios on microalgae growth and nitrogen, phosphorus removal using Scenedesmus sp. for wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 130:75–80
Kommareddy A, Anderson G (2004) Study of light requirements of a photobioreactor. North Central ASAE/CSAE Conference Presentation MB04-111, South Winnipeg, USA.
Leduy A, Therien N (1977) An improved method for optical density measurement of the semimicroscopic blue green alga Spirulina maxima. Bioresour Technol 19:1219–1224
Marchetti J, Bougaran G, Jauffrais T, Lefebvre S, Rouxel C, Saint-Jean B, Lukomska E, Robert R, Cadoret JP (2013) Effects of blue light on the biochemical composition and photosynthetic activity of Isochrysis sp. (T-iso). J Appl Phycol 25:109–119
Markou G (2014) Effect of various colors of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on the biomass vomposition of Arthrospira platensis cultivated in semi-continuous mode. Appl Biochem Biotech 172:2758–2768
Mattos ER, Singh M, Cabrera ML, Das KC (2015) Enhancement of biomass production in Scenedesmus bijuga high-density culture using weakly absorbed green light. Biomass Bioenergy 81:473–478
Matula E, Nabity J (2016) Feasibility of photobioreactor systems for use in multifunctional environmental control and life support system for spacecraft and habitat environments. 46th International Conference on Environmental Systems ICES-2016-147, Vienna, Austria.
Möglich A, Yang X, Ayers RA, Moffat K (2010) Structure and function of plant photoreceptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:21
Ogato T, Kifle D (2014) Morphological variability of Arthrospira (Spirulina ) fusiformis (Cyanophyta) in relation to environmental variables in the tropical soda lake Chitu, Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia 738:21–33
Olle M, ViršIle A (2013) The effects of light-emitting diode lighting on greenhouse plant growth and quality. Agr Food Sci 22:223–234
Ooms MD, Cao TD, Sargent EH, Sinton D (2016) Photon management for augmented photosynthesis. Nat Commun:12699
Pérezpazos J, Fernándezizquierdo P (2011) Synthesis of neutral lipids in Chlorella SP. under different light and carbonate conditions. CT F-Ciencia Tecn Fut 4:47–58
Ravelonandro PH, Ratianarivo DH, Joannis Cassan C, Isambert A, Raherimandimby M (2008) Influence of light quality and intensity in the cultivation of Spirulina platensis from Toliara (Madagascar) in a closed system. J Chem Technol Biot 83:842–848
Schulze PSC, Barreira LA, Pereira HGC, Perales JA, Varela JCS (2014) Light emitting diodes (LEDs) applied to microalgal production. Trends Biotechnol 32:422–430
Sedmak JJ, Grossberg SE (1977) A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem 79:544–552
Singh J, Gu S (2010) Commercialization potential of microalgae for biofuels production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:2596–2610
Tikhomirov AA, Ushakova SA, Kovaleva NP, Lamaze B, Lobo M, Lasseur C (2007) Biological life support systems for a Mars mission planetary base: problems and prospects. Adv Space Res 40:1741–1745
Ulijasz AT, Vierstra RD (2011) Phytochrome structure and photochemistry: recent advances toward a complete molecular picture. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:498
Vadiveloo A, Moheimani NR, Kosterink NR, Cosgrove JJ, Parlevliet D, Gonzalez-Garcia C, Lubián LM (2016) Photosynthetic performance of two Nannochloropsis spp. under different filtered light spectra. Algal Res 19:168–177
Venkataraman LV (1997) Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira): Physiology, Cell Biology and Biotechnologym, edited by Avigad Vonshak. J Appl Phycol 9:295–296
Vonshak A (1997) Spirulina platensis arthrospira: physiology, cell-biology and biotechnology. Q Rev Biol 3:353–354
Wang C, Fu C, Liu Y (2007) Effects of using light-emitting diodes on the cultivation of Spirulina platensis. Biochem Eng J 37:21–25
Wang SK, Stiles AR, Guo C, Liu CZ (2014) Microalgae cultivation in photobioreactors: an overview of light characteristics. Eng Life Sci 14:550–559
Wu H, Gao K, Villafañe VE, Watanabe T, Helbling EW (2005) Effects of solar UV radiation on morphology and photosynthesis of filamentous cyanobacterium Arthrospira platensis. Appl Environ Microb 71:5004
Yan C, Zheng Z (2014) Performance of mixed LED light wavelengths on biogas upgrade and biogas fluid removal by microalga Chlorella sp. Appl Energ 113:1008–1014
Zarrouk C (1966) Contribution a L'etude D'une Cianophycee: Influence de Divers Facteurs Physiques Et Chimiques Sur la Croissance Et la Photosynthese de Spirulina Maxima (Setch. Et Garndner) Geitler: Ph.D. Thesis. Université de Paris. France. 25–36.
Zhu XG, Long SP, Ort DR (2008) What is the maximum efficiency with which photosynthesis can convert solar energy into biomass? Curr Opin Biotech 19:153–159
Zöllner N, Kirsch K (1962) Über die quantitative Bestimmung von Lipoiden (allen bekannten Plasmalipoiden) gemeinsamen Sulphophosphovanillin-Reaktion. Res Exp Med 135:545–561
Funding
This research was supported by the Foundation of National Key Laboratory of Human Factors Engineering. Grant No. YFD160051805.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, R., Guo, S. Performance of the mixed LED light quality on the growth and energy efficiency of Arthrospira platensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 5245–5254 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8923-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8923-7