Abstract
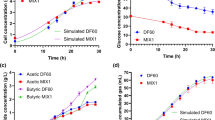
A new hydrogen-producing bacterium was isolated from the intestine of wild carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) of the Tarim River Basin. The isolate was identified as Klebsiella sp. based on 16S rDNA gene sequencing and examination of physiological and biochemical characteristics. The isolated strain, Klebsiella sp. WL1316, could effectively produce a high yield of hydrogen by using cotton stalk hydrolysate as substrate. The optimum fermentation conditions for hydrogen production were determined as follows: an initial sugar concentration of 40 g/L, a fermentation temperature of 37 °C and an initial pH value of 8.0. The scaled-up fermentation process was conducted in a 5-L fermenter using these parameters. Higher productivities with maximum daily hydrogen production of 937.0 ± 41.0 mL L−1 day−1, cumulative hydrogen production of 2908.5 ± 47.4 mL L−1, viable cell count of (20.2 ± 0.6) × 108 CFU mL−1 and hydrogen yield of 1.44 ± 0.08 mol mol−1sugarconsumed were obtained. The cumulative hydrogen production was predicted by the modified Gompertz equation with R2 of 0.997, and values of R m and P were 44.8 mL L−1 h−1 and 3057.6 mL L−1, respectively. These results indicated that the strain Klebsiella sp. WL1316 resulted in a high hydrogen production rate (HPR) and good hydrogen production potential. Moreover, this strain exhibited higher values of maximum hydrogen yield and HPR than the reported pure cultures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akutsu Y, Li YY, Harada H, Yu HQ (2009) Effects of temperature and substrate concentration on biological hydrogen production from starch. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:2558–2566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.01.048
Arreola-Vargas J, Celis LB, Buitrón G, Razo-Flores E, Alatriste-Mondragón F (2013) Hydrogen production from acid and enzymatic oat straw hydrolysates in an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor: performance and microbial population analysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:13884–13894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.08.065
Arreola-Vargas J, Razo-Flores E, Celis LB, Alatriste-Mondragón F (2015) Sequential hydrolysis of oat straw and hydrogen production from hydrolysates: role of hydrolysates constituents. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:10756–10765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.05.200
Arriaga S, Rosas I, Alatriste-Mondragón F, Razo-Flores E (2011) Continuous production of hydrogen from oat straw hydrolysate in a biotrickling filter. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:3442–3449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.12.019
Asadi N, Zilouei H (2017) Optimization of organosolv pretreatment of rice straw for enhanced biohydrogen production using Enterobacter aerogenes. Bioresour Technol 227:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.073
Chookaew T, O-Thong S, Prasertsan P (2012) Fermentative production of hydrogen and soluble metabolites from crude glycerol of biodiesel plant by the newly isolated thermotolerant Klebsiella pneumoniae TR17. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:13314–13322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.06.022
Chookaew T, O-Thong S, Prasertsan P (2014) Biohydrogen production from crude glycerol by immobilized Klebsiella sp. TR17 in a UASB reactor and bacterial quantification under non-sterile conditions. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:9580–9587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.04.083
Doetsch RN (1981) Determinative methods of light microscopy. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 21–23
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Identification manual of systematic bacteriology. Science press, Beijing, pp 267–294
Fang HHP, Liu H (2002) Effect of pH on hydrogen production from glucose by mixed culture. Bioresour Technol 82:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00110-9
Gonzales RR, Sivagurunathan P, Parthiban A, Kim SH (2016) Optimization of substrate concentration of dilute acid hydrolyzate of lignocellulosic biomass in batch hydrogen production. Int Biodeter Biodegr 113:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.016
Hallenbeck PC, Abohashesh M, Ghosh D (2012) Strategies for improving biological hydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 110:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.103
Kongjan P, Angelidaki I (2010) Extreme thermophilic biohydrogen production from wheat straw hydrolysate using mixed culture fermentation: effect of reactor configuration. Bioresour Technol 101:7789–7796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.024
Kumar K, Roy S, Das D (2013) Continuous mode of carbon dioxide sequestration by C. sorokiniana and subsequent use of its biomass for hydrogen production by E. cloacae IIT-BT 08. Bioresour Technol 145:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.137
Liu F, Fang BS (2007) Optimization of bio-hydrogen production from biodiesel wastes by Klebsiella pneumonia. Biotechnol J 2:374–380. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.200600102
Liu DW, Zeng RJ, Angelidaki I (2008) Enrichment and adaptation of extreme-thermophilic (70 °C) hydrogen producing bacteria to organic household solid waste by repeated batch cultivation. Int J Hydrog Energy 33:19317–19322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.08.014
Liu CM, Wu SY, Chu CY, Chou YP (2014) Biohydrogen production from rice straw hydrolyzate in a continuously external circulating bioreactor. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:19317–19322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.05.175
Long C, Cui J, Liu Z, Liu Y, Long M, Hu Z (2010) Statistical optimization of fermentative hydrogen production from xylose by newly isolated Enterobacter sp. CN1. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:6657–6664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.04.094
Lopez-Hidalgo AM, Sánchez A, León-Rodríguez AD (2017) Simultaneous production of bioethanol and biohydrogen by Escherichia coli WDHL using wheat straw hydrolysate as substrate. Fuel 188:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.022
Maintinguer SI, Fernandes BS, Duarte ICS, Saavedra NK, Adorno MAT, Varesche MBA (2011) Fermentative hydrogen production with xylose by Clostridium and Klebsiella species in anaerobic batch reactors. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:13508–13517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.07.095
Nath K, Kumar A, Das D (2006) Effect of some environmental parameters on fermentative hydrogen production by Enterobacter cloacae DM11. Can J Microbiol 52:525–532. https://doi.org/10.1139/w06-005
Nissilä ME, Lay CH, Puhakka JA (2014) Dark fermentative hydrogen production from lignocellulosic hydrolyzate—a review. Biomass Bioenergy 67:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.04.035
Niu K, Zhang X, Tan WS, Zhu ML (2010) Characteristics of fermentative hydrogen production with Klebsiella pneumoniae ECU-15 isolated from anaerobic sewage sludge. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.10.071
Özgür E, Peksel B (2013) Biohydrogen production from barley straw hydrolysate through sequential dark and photofermentation. J Clean Prod 52:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.02.035
Pan CM, Fan YT, Zhao P, Hou HW (2008) Fermentative hydrogen production by the newly isolated Clostridium beijerinckii Fanp3. Int J Hydrog Energy 33:5383–5391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.05.037
Reddy K, Nasr M, Kumari S, Kumar S, Gupta SK, Enitan AM, Bux F (2017) Biohydrogen production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate: effects of pH, S/X, Fe2+, and magnetite nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:8790–8804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8560-1
Ren N, Cao G, Wang A, Lee DJ, Guo W, Zhu Y (2008) Dark fermentation of xylose and glucose mix using isolated Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum W16. Int J Hydrog Energy 33:6124–6132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.07.107
Roy S, Vishnuvardhan M, Das D (2014) Improvement of hydrogen production by newly isolated Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum IIT BT-ST1. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:7541–7552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.06.128
Shiyan SP, Krishnaveni M (2013) Hydrogen production by Pseudomonas stutzeri JX442762 isolated from thermal soil at Mettur power station, Salem district, Tamil Nadu, India. J Pharm Res 6:112–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jopr.2012.11.024
Taguchi F, Chang JD, Mizukami N, Saito-taki T, Hasegawa K, Morimoto M (1993) Isolation of a hydrogen-producing bacterium, Clostridium beijerinckii strain AM21B, from termites. Can J Microbiol 39:726–730. https://doi.org/10.1139/m93-105
Valdez-Vazquez I, Ríos-Leal E, Esparza-García F, Cecchi F, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2005) Semi-continuous solid substrate anaerobic reactors for H2 production from organic waste: mesophilic versus thermophilic regime. Int J Hydrog Energy 30:1383–1391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2004.09.016
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA (1991) Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74:3583–3597. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(91)78551-2
Wang J, Wan W (2009) Factors influencing fermentative hydrogen production: a review. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:799–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.11.015
Wu JH, Lin CY, Choi E, Yun Z (2004) Biohydrogen production by mesophilic fermentation of food waste water. Water Sci Technol 49:223–228
Wu KJ, Saratale GD, Lo YC, Chen WM, Tseng ZJ, Chang MC, Tsai BC, Su A, Chang JS (2008) Simultaneous production of 2,3-butanediol, ethanol and hydrogen with a Klebsiella sp. strain isolated from sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 99:7966–7970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.062
Wu KJ, Lin YH, Lo YC, Chen YC, Chen WM, Chang JS (2011) Converting glycerol into hydrogen, ethanol, and diols with a Klebsiella sp. HE1 strain via anaerobic fermentation. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 42:20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2010.04.005
Wu XB, Huang GF, Bai LP, Long MN, Chen QX (2014) Enhanced hydrogen production from xylose and bamboo stalk hydrolysate by overexpression of xylulokinase and xylose isomerase in Klebsiella oxytoca HP1. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:221–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.10.078
Zhang K, Ren NQ, Cao GL, Wang AJ (2011a) Biohydrogen production behavior of moderately thermophile Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum W16 under different gas-phase conditions. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:14041–14048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.04.056
Zhang Q, Li Y, Li J, Ma C (2011b) Dilute acid hydrolysis of cotton stalks and ethanol production from hydrolytic liquids. Proceedings 2011 International Conference on Materials for Renewable Energy & Environment (ICMREE 2011) 1: 459–463. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMREE.2011.5930852
Zhang Q, Li YB, Xia LM (2014a) An oleaginous endophyte Bacillus subtilis HB1310 isolated from thin-shelled walnut and its utilization of cotton stalk hydrolysate for lipid production. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:152–165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-014-0152-4
Zhang Q, Li Y, Xia L, Liu Z, Pu Y (2014b) Enhanced xylitol production from statistically optimized fermentation of cotton stalk hydrolysate by immobilized Candida tropicalis. Chem Biochem Eng Q 28:13–19. https://doi.org/10.15255/CABEQ.2013.1888
Zhang K, Ren NQ, Wang AJ (2015) Fermentative hydrogen production from corn stover hydrolyzate by two typical seed sludges: effect of temperature. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:3838–3848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.01.120
Zhu H, Stadnyk A, Béland M, Seto P (2008) Co-production of hydrogen and methane from potato waste using a twostage anaerobic digestion process. Bioresour Technol 99:5078–5084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.083
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (21406150, 21476017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The protocol of the present study was given approval by the Tarim University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. And the procedures of harvest samples followed the Guidelines on Ethical Treatment of Experimental Animals enacted by the Ministry of Science and Technology, China.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 167 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, Q., Deng, L. et al. Biohydrogen production from fermentation of cotton stalk hydrolysate by Klebsiella sp. WL1316 newly isolated from wild carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) of the Tarim River basin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 4231–4242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8882-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8882-z