Abstract
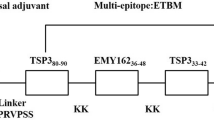
Alveolar echinococcosis is a zoonotic disease caused by the infection of the larval stage Echinococcus multilocularis with worldwide distribution especially in the northwest China. It is important to develop a well-tolerated immunoprophylaxis against E. multilocularis for alveolar echinococcosis control. In this study, a prokaryotic expression system for recombinant immunogen LTB-EMY162 was established, and the immunological features, sensitized lymphocyte, IL-4/IFN-γ secreted, prophylactic effect, and therapeutic effect were also evaluated. Arctic Express (DE3) system, Ni2+-charged and molecular sieve chromatography were used to obtain a high-purity 29 kDa protein. The ELISA and lymphocyte proliferation assay showed that LTB-EMY162 induced high-titer specific IgG against EMY162 and E. multilocularis protoscoleces protein in BALB/c mice and promoted sensitized T lymphocyte cell proliferation, and LTB-EMY162 stimulated Th cell to secrete IL-4 and IFN-γ and induced a Th1/Th2 mixed type immunological response. We also found that LTB-EMY162 significantly inhibited the cysts formation by challenging with 1000 E. multilocularis protoscoleces. The growth of protoscoleces and cysts were also significantly decreased by treating with LTB-EMY162 in 1000 protoscoleces intraperitoneal injection therapeutic mice model. In conclusion, we have constructed a subunit vaccine LTB-EMY162 which has prevention and therapeutic effect against E. multilocularis infection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batçık OE, A Ö KO, Ekşi MŞ, Bilge T (2016) Cerebral alveolar echinococcosis concomitant with liver and lung lesions in a young adult patient: case report and literature review. Turkiye Parazitol Derg:169–171
Boubaker G, Hemphill A, Huber CO, Spiliotis M, Babba H, Gottstein B (2015) Prevention and immunotherapy of secondary murine alveolar echinococcosis employing recombinant EmP29 antigen. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9(6):e0003795. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003795
Capron M, Capron A, Torpier G, Bazin H, Bout D, Joseph M (1978) Eosinophil-dependent cytotoxicity in rat schistosomiasis. Involvement of IgG2a antibody and role of mast cells. Eur J Immunol 8(2):127–133. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830080211
Clements DA, Gilbert GL (1990) Immunisation for the prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b infections: a review. Aust NZ J Med 20(6):828–834. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-5994.1990.tb00435.x
Dang Z, Yagi K, Oku Y, Kouguchi H, Kajino K, Watanabe J, Matsumoto J, Nakao R, Wakaguri H, Toyoda A (2009) Evaluation of Echinococcus multilocularis tetraspanins as vaccine candidates against primary alveolar echinococcosis. Vaccine 27(52):7339–7345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.09.045
Emery I, Liance M, Leclerc C (1997) Secondary Echinococcus multilocularis infection in A/J mice: delayed metacestode development is associated with Th1 cytokine production. Parasite Immunol 19(11):493–503
Giraudoux P, Raoul F, Afonso E, Ziadinov I, Yang Y, Li LI, Tiaoying LI, Quéré J, Feng X, Wang Q (2013) Transmission ecosystems of Echinococcus multilocularis in China and Central Asia. Parasitology 140(13 (control of cestode zoonoses in Asia: role of basic and applied science)):1655–1666
Gottstein B, Müller N, Jr SJC, Vogel M, Tanner I, Seebeck T (1990) Humoral and cellular immune response in mice and dogs induced by a recombinant Echinococcus multilocularis antigen produced by a Salmonella typhimurium vaccine strain. Parasite Immunol 12(2):163–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00945.x
Guo L, Yin R, Liu K, Lv X, Li Y, Duan X, Chu Y, Xi T, Xing Y (2014) Immunological features and efficacy of a multi-epitope vaccine CTB-UE against H. pylori in BALB/c mice model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(8):3495–3507
Hemphill A, Muller J (2009) Alveolar and cystic echinococcosis: towards novel chemotherapeutical treatment options. J Helminthol 83(2):99–111. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X0928936X
Ishizuka EK, Ferreira MJ, Grund LZ, Coutinho EMM, Komegae EN, Cassado AA, Bortoluci KR, Lopes-Ferreira M, Lima C (2012) Role of interplay between IL-4 and IFN-γ in the in regulating M1 macrophage polarization induced by Nattectin. Int Immunopharmacol 14(4):513–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2012.08.009
Joliat GR, Melloul E, Petermann D, Demartines N, Gillet M, Uldry E, Halkic N (2015) Outcomes after liver resection for hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: a single-center cohort study. World J Surg 39(10):2529
Kamishima T, Harabayashi T, Ishikawa S, Kubota KC, Nonomura K, Omatsu T, Onodera Y, Shirato H, Terae S (2009) Alveolar hydatid disease of the adrenal gland: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Jpn J Radiol 27(5):225–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-009-0326-3
Katoh Y, Kouguchi H, Matsumoto J, Goto A, Suzuki T, Oku Y, Yagi K (2008) Characterization of em Y162 encoding an immunogenic protein cloned from an adult worm-specific cDNA library of Echinococcus multilocularis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780(1):1–6
Khusmith S, Panitchakorn J, Krudsood S, Wilairatana P, Looareesuwan S (2001) IgE elevation and anti-plasmodium falciparum IgE antibodies: association of high level with malaria resistance. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 32(4):696–701
King CL, Ottesen EA, Nutman TB (1990) Cytokine regulation of antigen-driven immunoglobulin production in filarial parasite infections in humans. J Clin Investig 85(6):1810–1815. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI114639
Kizaki T, Kobayashi S, Ogasawara K, Day NK, Good RA, Onoé K (1991) Immune suppression induced by protoscoleces of Echinococcus multilocularis in mice. Evidence for the presence of CD8dull suppressor cells in spleens of mice intraperitoneally infected with E. multilocularis. J Immunol 147(5):1659
Klaver AC, Patrias LM, Coffey MP, Finke JM, Loeffler DA (2010) Measurement of anti-Abeta1-42 antibodies in intravenous immunoglobulin with indirect ELISA: the problem of nonspecific binding. J Neurosci Methods 187(2):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.01.018
Kouguchi H, Matsumoto J, Katoh Y, Oku Y, Suzuki T, Yagi K (2007) The vaccination potential of EMY162 antigen against Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363(4):915–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.09.023
Kouguchi H, Matsumoto J, Nakao R, Yamano K, Oku Y, Yagi K (2013) Characterization of a surface glycoprotein from Echinococcus multilocularis and its mucosal vaccine potential in dogs. PLoS One 8(7):e69821. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069821
Le G, Li X, Feng T, He Y, Xing Y, Deng X, Tao X (2012) Immunological features and the ability of inhibitory effects on enzymatic activity of an epitope vaccine composed of cholera toxin B subunit and B cell epitope from Helicobacter pylori urease a subunit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(5):1937–1945
Moro P, Schantz PM (2009) Echinococcosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis 13(2):125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2008.03.037
Nail LC, Reimundes ER, Galluzzo CW, Dan L, Ibrahim YL, Lobrinus JA, Chappuis F (2017) Disseminated alveolar echinococcosis resembling metastatic malignancy: a case report. J Med Case Rep 11(1):113. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-017-1279-2
Nunnari G, Pinzone MR, Gruttadauria S, Celesia BM, Madeddu G, Malaguarnera G, Pavone P, Cappellani A, Cacopardo B (2012) Hepatic echinococcosis: clinical and therapeutic aspects. World J Gastroenterol 18(13):1448–1458. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1448
Ricardblum S, Bressonhadni S, Vuitton DA, Ville G, Grimaud JA (1992) Hydroxypyridinium collagen cross-links in human liver fibrosis: study of alveolar echinococcosis. Hepatology 15(4):599–602
Sá-Nunes A, Faccioli L, Sforcin J (2003) Propolis: lymphocyte proliferation and IFN-γ production. J Ethnopharmacol 87(1):93–97
Siles-Lucas M, Merli M, Mackenstedt U, Gottstein B (2003) The Echinococcus multilocularis 14-3-3 protein protects mice against primary but not secondary alveolar echinococcosis. Vaccine 21(5–6):431–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00517-0
Torgerson PR, Keller K, Magnotta M, Ragland N (2010) The global burden of alveolar echinococcosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4(6):e722. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000722
Turcanu V, Hirst TR, Williams NA (2002) Modulation of human monocytes by Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B-subunit; altered cytokine production and its functional consequences. Immunology 106(3):316–325. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01429.x
Verweij WR, De HL, Holtrop M, Agsteribbe E, Brands R, van Scharrenburg GJ, Wilschut J (1998) Mucosal immunoadjuvant activity of recombinant Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and its B subunit: induction of systemic IgG and secretory IgA responses in mice by intranasal immunization with influenza virus surface antigen. Vaccine 16(20):2069–2076. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(98)00076-0
Vuitton DA (2003) The ambiguous role of immunity in echinococcosis: protection of the host or of the parasite? Acta Trop 85(2):119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-706X(02)00230-9
Wang J, Zhang C, Wei X, Oleg B, Lv G, Lu X, Georges M, Vuitton DA, Hao W, Lin R (2013) TGF-βand TGF-β/Smad signaling in the interactions between Echinococcus multilocularis and its hosts. PLoS One 8(2):e55379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055379
Wang H, Zhang F, Ma X, Ma H, Zhu Y, Liu X, Zhu M, Wen H, Ding J (2014) Prokaryotic expression and identification of B- and T-cell combined epitopes of Em95 antigen of Echinococcus multilocularis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(8):5117–5122
Yang YR, Vuitton DA, Jones MK, Craig PS, Mcmanus DP (2005) Brain metastasis of alveolar echinococcosis in a hyperendemic focus of Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 99(12):937–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.04.020
Acknowledgments
We thank all of the staffs for their helpful suggestions and advice during this project. We would like to thank the editor for the helpful comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81360300, Tang F; No. 32571231, Ge RL), the Province Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai (No. 2015-ZJ-745), the 123Talent Project of Qinghai University, the Key Project of Qinghai Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission (No. 2016-wjzd-04), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB518200, L-RG), and the Science and technology project of Qinghai Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Bureau (NMSY-2017-09). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All experiments were conducted with adherence to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and the protocol was approved by the Animal Ethical and Experimental Committee of Qinghai University (QHDX-2014-07). This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Yang, Q., Guo, L. et al. Immunological features and efficacy of the recombinant subunit vaccine LTB-EMY162 against Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 2143–2154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8771-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8771-5