Abstract
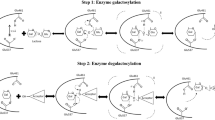
It has been a long time since the first α-agarase was discovered. However, only two α-agarases have been cloned and partially characterized so far and the study of α-agarases has lagged far behind that of β-agarases. Here, we report an α-agarase, AgaD, cloned from marine bacterium Thalassomonas sp. LD5. Its cDNA consists of 4401 bp, encoding a protein of 1466 amino acids. Based on amino acid similarity, AgaD is classified into glycoside hydrolase (GH) family GH96. The recombinant enzyme gave a molecular weight of about 180 kDa on SDS-PAGE and 360 kDa on Native-PAGE indicating it acted as a dimer. However, the recombinant enzyme is labile and easy to be fractured into series of small active fragments, of which the smallest one is about 70 kDa, matching the size of catalytic module. The enzyme has maximal activity at 35 °C and pH 7.4, and shows a strong dependence on the presence of calcium ions. AgaD degrades agarose to yield agarotetraose as the predominate end product. However, the hydrolysates are rapidly degraded to odd-numbered oligosaccharides under strong alkaline condition. The spectra of ESI-MS and 1H-NMR proved that the main hydrolysate agarotetraose is degraded into neoagarotriose, bearing the sequence of G-A-G (G, d-galactose; A, 3,6-anhydro-α-l-galactose). Unlike the alkaline condition, the hydrolysates are further hydrolyzed into smaller degree polymerization (DP) of agaro-oligosaccharides (AOS) in dilute strong acid. Therefore, this study provides more insights into the properties for both the α-agarases and the AOS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Hachem M, Karlsson EN, Simpson PJ, Linse S, Sellers P, Williamson MP, Jamieson SJ, Gilbert HJ, Bolam DN, Holst O (2002) Calcium binding and thermostability of carbohydrate binding module CBM4-2 of Xyn10A from Rhodothermus marinus. Biochemistry 41(18):5720–5729. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi012094a
Araki C (1959) Seaweed polysaccharides. In: Wolfrom ML (ed) Carbohydrate chemistry of substances of biological interest Pergamon press, London, pp 15–30
Ariga O, Inoue T, Kubo H, Minami K, Nakamura M, Iwai M, Moriyama H, Yanagisawa M, Nakasaki K (2012) Cloning of agarase gene from non-marine agarolytic bacterium Cellvibrio sp. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22(9):1237–1244
Chi WJ, Chang YK, Hong SK (2012) Agar degradation by microorganisms and agar-degrading enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(4):917–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4023-2
Chi WJ, Lee CR, Dugerjonjuu S, Park JS, Kang DK, Hong SK (2015) Biochemical characterization of a novel iron-dependent GH16 beta-agarase, AgaH92, from an agarolytic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. H9. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv035
Flament D, Barbeyron T, Jam M, Potin P, Czjzek M, Kloareg B, Michel G (2007) Alpha-agarases define a new family of glycoside hydrolases, distinct from beta-agarase families. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(14):4691–4694. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00496-07
Ghosh A, Luis AS, Bras JL, Pathaw N, Chrungoo NK, Fontes CM, Goyal A (2013) Deciphering ligand specificity of a Clostridium thermocellum family 35 carbohydrate binding module (CtCBM35) for gluco- and galacto- substituted mannans and its calcium induced stability. PLoS One 8(12):e80415. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080415
Han W, Cheng Y, Wang D, Wang S, Liu H, Gu J, Wu Z, Li F (2016) Biochemical characteristics and substrate degradation pattern of a novel exo-type beta-agarase from the polysaccharide-degrading marine bacterium Flammeovirga sp. strain MY04. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(16):4944–4954. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00393-16
Hatada Y, Ohta Y, Horikoshi K (2006) Hyperproduction and application of alpha-agarase to enzymatic enhancement of antioxidant activity of porphyran. J Agric Food Chem 54(26):9895–9900. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0613684
Henshaw J, Horne-Bitschy A, van Bueren AL, Money VA, Bolam DN, Czjzek M, Ekborg NA, Weiner RM, Hutcheson SW, Davies GJ, Boraston AB, Gilbert HJ (2006) Family 6 carbohydrate binding modules in beta-agarases display exquisite selectivity for the non-reducing termini of agarose chains. J Biol Chem 281(25):17099–17107. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600702200
Hsu PH, Wei CH, Lu WJ, Shen F, Pan CL, Lin HT (2015) Extracellular production of a novel endo-beta-agarase AgaA from Pseudomonas vesicularis MA103 that cleaves agarose into neoagarotetraose and neoagarohexaose. Int J Mol Sci 16(3):5590–5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16035590
Jung S, Lee CR, Chi WJ, Bae CH, Hong SK (2017) Biochemical characterization of a novel cold-adapted GH39 beta-agarase, AgaJ9, from an agar-degrading marine bacterium Gayadomonas joobiniege G7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(5):1965–1974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7951-4
Kazlowski B, Pan CL, Ko YT (2008) Separation and quantification of neoagaro- and agaro-oligosaccharide products generated from agarose digestion by beta-agarase and HCl in liquid chromatography systems. Carbohydr Res 343(14):2443–2450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2008.06.019
Lee CH, Kim HT, Yun EJ, Lee AR, Kim SR, Kim JH, Choi IG, Kim KH (2014) A novel agarolytic beta-galactosidase acts on agarooligosaccharides for complete hydrolysis of agarose into monomers. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(19):5965–5973. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01577-14
Li J, Han F, Lu X, Fu X, Ma C, Chu Y, Yu W (2007) A simple method of preparing diverse neoagaro-oligosaccharides with beta-agarase. Carbohydr Res 342(8):1030–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2007.02.008
Li G, Sun M, Wu J, Ye M, Ge X, Wei W, Li H, Hu F (2015) Identification and biochemical characterization of a novel endo-type beta-agarase AgaW from Cohnella sp. strain LGH. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(23):10019–10029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6869-6
Liu D, Xing P-C, Yu W-G, Lu X-Z (2013) Cloning of an new agarase gene using site-finding PCR. Progress Mod Biomed 18(1):6
Ma C, Lu X, Shi C, Li J, Gu Y, Ma Y, Chu Y, Han F, Gong Q, Yu W (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel beta-agarase, AgaB, from marine Pseudoalteromonas sp. CY24. J Biol Chem 282(6):3747–3754. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M607888200
Miller RL, Guimond SE, Shivkumar M, Blocksidge J, Austin JA, Leary JA, Turnbull JE (2016) Heparin isomeric oligosaccharide separation using volatile salt strong anion exchange chromatography. Anal Chem 88(23):11542–11550. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02801
Montanier CY, Correia MA, Flint JE, Zhu Y, Basle A, McKee LS, Prates JA, Polizzi SJ, Coutinho PM, Lewis RJ, Henrissat B, Fontes CM, Gilbert HJ (2011) A novel, noncatalytic carbohydrate-binding module displays specificity for galactose-containing polysaccharides through calcium-mediated oligomerization. J Biol Chem 286(25):22499–22509. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.217372
Ohta Y, Hatada Y, Miyazaki M, Nogi Y, Ito S, Horikoshi K (2005) Purification and characterization of a novel alpha-agarase from a Thalassomonas sp. Curr Microbiol 50(4):212–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4435-z
Potin P, Richard C, Rochas C, Kloareg B (1993) Purification and characterization of the alpha-agarase from Alteromonas agarlyticus (Cataldi) comb. nov., strain GJ1B. Eur J Biochem/FEBS 214(2):599–607. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17959.x
Rebuffet E, Groisillier A, Thompson A, Jeudy A, Barbeyron T, Czjzek M, Michel G (2011) Discovery and structural characterization of a novel glycosidase family of marine origin. Environ Microbiol 13(5):1253–1270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02426.x
Rochas C, Potin P, Kloareg B (1994) NMR spectroscopic investigation of agarose oligomers produced by an alpha-agarase. Carbohydr Res 253:69–77
Rozycka M, Wojtas M, Jakob M, Stigloher C, Grzeszkowiak M, Mazur M, Ozyhar A (2014) Intrinsically disordered and pliable Starmaker-like protein from medaka (Oryzias latipes) controls the formation of calcium carbonate crystals. PLoS One 9(12):e114308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114308
Xie W, Lin B, Zhou Z, Lu G, Lun J, Xia C, Li S, Hu Z (2013) Characterization of a novel beta-agarase from an agar-degrading bacterium Catenovulum sp. X3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(11):4907–4915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4385-5
Yang B, Yu G, Zhao X, Jiao G, Ren S, Chai W (2009) Mechanism of mild acid hydrolysis of galactan polysaccharides with highly ordered disaccharide repeats leading to a complete series of exclusively odd-numbered oligosaccharides. FEBS J 276(7):2125–2137. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06947.x
Yun EJ, Yu S, Kim KH (2017) Current knowledge on agarolytic enzymes and the industrial potential of agar-derived sugars. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(14):5581–5589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8383-5
Zhu H, Wu Z, Gadi MR, Wang S, Guo Y, Edmunds G, Guan W, Fang J (2017) Cation exchange assisted binding-elution strategy for enzymatic synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27(18):4285–4287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.08.041
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41376144), NSFC-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Centers (U1606403), Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Shandong Province (2014GGH215002), and the National High-tech R&D Program of China (2014AA093504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 402 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Xu, J., Liu, D. et al. Characterization of an α-agarase from Thalassomonas sp. LD5 and its hydrolysate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 2203–2212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8762-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8762-6