Abstract
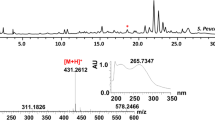
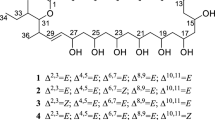
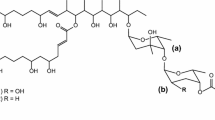
Clethramycin (1) and mediomycin A (2) belong to the linear polyene polyketide (LPP) family of antibiotics that exhibit potent antifungal activity. Structural similarities exist between 1 and 2, except that 2 contains an amino moiety substituted for the guanidino moiety. Herein, the draft genome sequence of Streptomyces mediocidicus ATCC23936, a strain which produces both 1 and 2, was obtained through de novo sequencing. Bioinformatic analysis of the genome revealed a clethramycin (cle) gene cluster that contained 25 open reading frames (orfs). However, amidinohydrolase for 2 formation was not found in the cle gene cluster. Further genomic analysis revealed an amidinohydrolase MedX, which can hydrolyse the guanidino form (1) into the amino form (2) via heterologous co-expression of the cle cluster in Streptomyces lividans or by in vitro catalysis. These results also suggest the feasibility of engineering novel LPPs for drug discovery by manipulating the biosynthetic machinery of S. mediocidicus.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banskota AH, Mcalpine JD, Ibrahim A, Aouidate M, Piraee M, Alarco AM, Farnet CM, Zazopoulos E (2006) Genomic analyses lead to novel secondary metabolites. Part 3. ECO-0501, a novel antibacterial of a new class. J Antibiot 59(9):533–542. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2006.74
Cai P, Kong F, Fink P, Ruppen ME, Williamson RT, Keiko T (2007) Polyene antibiotics from Streptomyces mediocidicus. J Nat Prod 70(2):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1021/np060542f
Chandra A, Nair MG (1995) Azalomycin F complex from Streptomyces hygroscopicus, MSU/MN-4-75B. J Antibiot 48(8):896–898. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.48.896
Chen S, Wu Q, Shen Q, Wang H (2015) Progress in understanding the genetic information and biosynthetic pathways behind Amycolatopsis antibiotics, with implications for the continued discovery of novel drugs. Chembiochem 17:119–128
Dowling DP, Di CL, Gennadios HA, Christianson DW (2008) Evolution of the arginase fold and functional diversity. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(13):2039–2055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-7554-z
Elkins JM, Clifton IJ, Hernández H, Doan LX, Robinson CV, Schofield CJ, Hewitson KS (2002) Oligomeric structure of proclavaminic acid amidino hydrolase: evolution of a hydrolytic enzyme in clavulanic acid biosynthesis. Biochem J 366(2):423–434. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20020125
Frank J, Dékány G, Pelczer I, ApSimon JW (1987) The composition of primycin. Tetrahedron Lett 28(24):2759–2762. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(00)96202-6
Furumai T, Yamakawa T, Yoshida R, Igarashi Y (2003) Clethramycin, a new inhibitor of pollen tube growth with antifungal activity from Streptomyces hygroscopicus TP-A0623. I. Screening, taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological properties. J Antibiot 56(8):700–704. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.56.700
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(4):1541–1546. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0337542100
Hong H, Samborskyy M, Lindner F, Leadlay PF (2016) An amidinohydrolase provides the missing link in the biosynthesis of amino marginolactone antibiotics. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 55(3):1118–1123. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201509300
Hornung A, Bertazzo M, Dziarnowski A, Schneider K, Welzel K, Wohlert SE, Holzenkämpfer M, Nicholson GJ, Bechthold A, Süssmuth RD (2007) A genomic screening approach to the structure-guided identification of drug candidates from natural sources. Chembiochem 8(7):757–766. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200600375
Igarashi Y, Iwashita T, Fujita T, Naoki H, Yamakawa T, Yoshida R, Furuma T (2003) Clethramycin, a new inhibitor of pollen tube growth with antifungal activity from Streptomyces hygroscopicus TP-A0623. II. Physico-chemical properties and structure determination. J Antibiot 56(8):705–708. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.56.705
Kusserow K, Tam G (2017) Complete genome sequence of Actinomadura parvosata subsp. kistnae, a rich source of novel natural product (bio-)chemistry. J Genomics 5:75–76. https://doi.org/10.7150/jgen.19673
Lee SJ, Kim DJ, Kim HS, Lee BI, Yoon HJ, Yoon JY, Kim KH, Jang JY, Im HN, An DR (2011) Crystal structures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa guanidinobutyrase and guanidinopropionase, members of the ureohydrolase superfamily. J Struct Biol 175(3):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2011.05.002
Liu W, Min M, Xue Y, Nan L, Wang S, Chen Y (2013a) The C-terminal extended serine residue is absolutely required in nosiheptide maturation. Chembiochem 14(5):573–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201200681
Liu W, Xue Y, Ma M, Wang S, Liu N, Chen Y (2013b) Multiple oxidative routes towards the maturation of nosiheptide. Chembiochem 14(13):1544–1547. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201300427
Mcalpine JB, Bachmann BO, Piraee M, Tremblay S, Alarco AM, Zazopoulos E, Farnet CM (2005) Microbial genomics as a guide to drug discovery and structural elucidation: ECO-02301, a novel antifungal agent, as an example. J Nat Prod 68(4):493–496. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0401664
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, USA
Park HB, Perez CE, Barber KW, Rinehart J, Crawford JM (2017) Genome mining unearths a hybrid nonribosomal peptide synthetase-like-pteridine synthase biosynthetic gene cluster. elife 6:e25229
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Sbaraini N, Andreis FC, Thompson CE, Guedes RLM, Junges Â, Campos T, Staats CC, Vainstein MH, Vasconcelos ATRD, Schrank A (2017) Genome-wide analysis of secondary metabolite gene clusters in ophiostoma ulmi and ophiostoma novo-ulmi reveals a fujikurin-like gene cluster with a putative role in infection. Front Microbiol 8:1063. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01063
Stephan H, Kempter C, Metzger JW, Jung G, Potterat O, Pfefferle C, Fiedler H (1996) Kanchanamycins, new polyol macrolide antibiotics produced by Streptomyces olivaceus Tü 4018. J Antibiot 49(8):765–769. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.49.765
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1596–1599. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm092
Zhang L, Hashimoto T, Qin B, Hashimoto J, Kozone I, Kawahara T, Okada M, Awakawa T, Ito T, Asakawa Y, Ueki M, Takahashi S, Osada H, Wakimoto T, Ikeda H, Shin-Ya K, Abe I (2017) Characterization of giant modular PKSs provides insight into genetic mechanism for structural diversification of aminopolyol polyketides. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56(7):1740–1745. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201611371
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Mei Ge, Shanghai Laiyi Center for Biopharmaceuticals R & D, for providing S. mediocidicus ATCC23936.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Tianjin science and technology plan projects (no. 16YFZCSY01000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 489 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Xu, S., Jiang, F. et al. Genomic-driven discovery of an amidinohydrolase involved in the biosynthesis of mediomycin A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 2225–2234 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8729-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8729-z