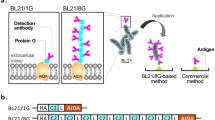
Abstract
A functional fusion protein, which consists of an antibody and an enzyme that can be used in enzyme immunoassays, has been constructed. However, a quantitative comparison of the characteristics of fusion proteins and chemical conjugates of the parents, which are functionally produced in a uniform microbial system, has not been adequately achieved. In this study, a fusion protein between the ZZ protein and Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase (AP) and the parental ZZ protein and AP for chemical conjugate was functionally produced in the same bacterial system. A detailed examination of the ZZ–AP fusion protein and the effect of the ZZ–AP chemical conjugate on IgG affinity and enzymatic activity were performed. Compared with the parents, the equilibrium dissociation constant of ZZ–AP conjugate decreased by 32 % and catalytic activity decreased by 24 %, whereas the ZZ–AP fusion retained full parental activities and exhibited an approximately tenfold higher sensitivity than that of ZZ–AP conjugate in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Thus, ZZ–AP fusion is a promising immunoreagent for IgG detection and a potential biolinker between antibodies and reporter enzymes (i.e., IgG–ZZ–AP fusion complex) in immunoassays.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angkawidjaja C, Kuwahara K, Omori K, Koga Y, Takano K, Kanaya S (2006) Extracellular secretion of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase with a C-terminal tag by type I secretion system: purification and biochemical characterization. Protein Eng Des Sel 19:337–343. doi:10.1093/protein/gzl017
Chattopadhaya S, Abu Bakar FB, Yao SQ (2009) Expanding the chemical biologist’s tool kit: chemical labelling strategies and its applications. Curr Med Chem 16:4527–4543. doi:10.2174/092986709789760706
Chowdhury PS, Kushwaha A, Abrol S, Chaudhary VK (1994) An expression system for secretion and purification of a genetically engineered thermostable chimera of protein A and alkaline phosphatase. Protein Expr Purif 5:89–95
Grigorenko V, Andreeva I, Börchers T, Spener F, Egorov A (2001) A genetically engineered fusion protein with horseradish peroxidase as a marker enzyme for use in competitive immunoassays. Anal Chem 73:1134–1139. doi:10.1021/ac000684t
Huang B, Liu FF, Dong XY, Sun Y (2012) Molecular mechanism of the effects of salt and pH on the affinity between protein A and human immunoglobulin G1 revealed by molecular simulations. J Phys Chem B 116:424–433. doi:10.1021/jp205770p
Iijima M, Kadoya H, Hatahira S, Hiramatsu S, Jung G, Martin A, Quinn J, Jung J, Jeong SY, Choi EK, Arakawa T, Hinako F, Kusunoki M, Yoshimoto N, Niimi T, Tanizawa K, Kuroda S (2011) Nanocapsules incorporating IgG Fc-binding domain derived from Staphylococcus aureus protein A for displaying IgGs on immunosensor chips. Biomaterials 32:1455–1464. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.057
Jansson B, Uhlen M, Nygren PA (1998) All individual domains of staphylococcal protein A show Fab binding. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 20:69–78. doi:10.1016/S0928-824
Jendeberg L, Tashiro M, Tejero R, Lyons BA, Uhlén M, Montelione GT, Nilsson B (1996) The mechanism of binding staphylococcal protein A to immunoglobin G does not involve helix unwinding. Biochemistry 35:22–31. doi:10.1021/bi9512814
Kerschbaumer RJ, Hirschl S, Schwager C, Ibl M, Himmler G (1996) pDAP2: a vector for construction of alkaline phosphatase fusion-proteins. Immunotechnology 2:145–150
Kerschbaumer RJ, Hirschl S, Kaufmann A, Ibl M, Koenig R, Himmler G (1997) Single-chain Fv fusion proteins suitable as coating and detecting reagents in a double antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Biochem 249:219–227. doi:10.1006/abio.1997.2171
Lequin RM (2005) Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Chem 51:2415–2418. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2005.051532
Liu X, Wang H, Liang Y, Yang J, Zhang H, Lei H, Shen Y, Sun Y (2010) Production and characterization of a single-chain Fv antibody-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein specific for clenbuterol. Mol Biotechnol 45:56–64. doi:10.1007/s12033-010-9240-2
Nilsson B, Moks T, Jansson B, Abrahmsen L, Elmblad A, Holmgren E, Henrichson C, Jones TA, Uhlen M (1987) A synthetic IgG-binding domain based on staphylococcal protein A. Protein Eng 1:107–113. doi:10.1093/protein/1.2.107
Porstmann T, Kiessig ST (1992) Enzyme-immunoassay techniques: an overview. J Immunol Methods 150:5–21
Rau D, Kramer K, Hock B (2002) Single-chain Fv antibody-alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins produced by one-step cloning as rapid detection tools for ELISA. J Immunoassay Immunochem 23:129–143. doi:10.1081/IAS-120003657
Rönnmark J, Kampf C, Asplund A, Höidén-Guthenberg I, Wester K, Pontén F, Uhlén M, Nygren PA (2003) Affibody-β-galactosidase immunoconjugates produced as soluble fusion proteins in the Escherichia coli cytosol. J Immunol Methods 281:149–160. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2003.06.001
Sasajima Y, Iwasaki R, Tsumoto K, Kumagai I, Ihara M, Ueda H (2010) Expression of antibody variable region-human alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins in mammalian cells. J Immunol Methods 361:57–63. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2010.07.012
Stec B, Holtz KM, Kantrowitz ER (2000) A revised mechanism for the alkaline phosphatase reaction involving three metal ions. J Mol Biol 299:1303–1311. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3799
Swain MD, Anderson GP, Serrano-González J, Liu JL, Zabetakis D, Goldman ER (2011) Immunodiagnostic reagents using llama single domain antibody-alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins. Anal Biochem 417:188–194. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2011.06.012
Tang J, Liang S, Zhang J, Gao Z, Zhang S (2009) pGreen-S: a clone vector bearing absence of enhanced green fluorescent protein for screening recombinants. Anal Biochem 388:173–174. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2009.02.007
Wang CL, Huang M, Wesson CA, Birdsell DC, Trumble WR (1994) A single Fc binding domain–alkaline phosphatase gene fusion expresses a protein with both IgG binding ability and alkaline phosphatase enzymatic activity. Protein Eng 7:715–722. doi:10.1093/protein/7.5.715
Wang SH, Zhang JB, Zhang ZP, Zhou YF, Yang RF, Chen J, Guo YC, You F, Zhang XE (2006) Construction of single chain variable fragment (ScFv) and BiscFv-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein for detection of Bacillus anthracis. Anal Chem 78:997–1004. doi:10.1021/ac0512352
Wisdom GB (1988) Antibody-enzyme conjugate formation. Methods Mol Biol 3:373–382. doi:10.1385/0-89603-126-8:373
Wisdom GB (2005) Conjugation of antibodies to alkaline phosphatase. Methods Mol Biol 295:123–126. doi:10.1385/1-59259-873-0:123
Zhang XM, Kobatake E, Kobayashi K, Yanagida Y, Aizawa M (2000) Genetically fused protein A-luciferase for immunological blotting analyses. Anal Biochem 282:65–69. doi:10.1006/abio.2000.4584
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following funds: Science & Technology Brainstorm Project of Shandong Province (2008GG10002022); National population and family planning commission of China (C1–90) and National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (81101363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, JB., Yang, HM., Liang, SJ. et al. Comparative characterization of recombinant ZZ protein–alkaline phosphatase and its application in enzyme immunoassays. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 153–158 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4303-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4303-x