Abstract
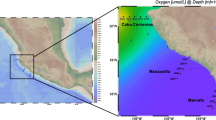
A central goal in marine microecology is to understand the ecological factors shaping spatiotemporal microbial patterns and the underlying processes. We hypothesized that abiotic and/or biotic interactions are probably more important for explaining the distribution patterns of marine bacterioplankton than environmental filtering. In this study, surface seawater samples were collected about 7000 miles from the Mediterranean Sea, transecting the North Atlantic Ocean, to the Brazilian marginal sea. In bacterial biosphere, SAR11, SAR86, Rhodobacteraceae, and Rhodospiriaceae were predominant in the Mediterranean Sea; Prochlorococcus was more frequent in Atlantic Ocean; whereas in the Brazilian coastal sea, the main bacterial members were Synechococcus and SAR11. With respect to archaea, Euryarchaeota were predominant in the Atlantic Ocean and Thaumarchaeota in the Mediterranean Sea. With respect to the eukaryotes, Syndiniales, Spumellaria, Cryomonadida, and Chlorodendrales were predominant in the open ocean, while diatoms and microzooplankton were dominant in the coastal sea. Distinct clusters of prokaryotes and eukaryotes displayed clear spatial heterogeneity. Among the environmental parameters measured, temperature and salinity were key factors controlling bacterial and archaeal community structure, respectively, whereas N/P/Si contributed to eukaryotic variation. The relative contribution of environmental parameters to the microbial distribution pattern was 45.2%. Interaction analysis showed that Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, and Flavobacteriia were the keystone taxa within the positive-correlation network, while Thermoplasmata was the main contributor in the negative-correlation network. Our study demonstrated that microbial communities are co-governed by environmental filtering and biotic interactions, which are the main deterministic driving factors modulating the spatiotemporal patterns of marine plankton synergistically at the regional or global levels.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azam F, Malfatti F (2007) Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nat Rev Microbiol. 5(10):782–791
Signori CN, Thomas F, Enrich-Prast A, Pollery RC, Sievert SM (2014) Microbial diversity and community structure across environmental gradients in Bransfield Strait, Western Antarctic Peninsula. Front. Microbiol. 5:647
Chapin 3rd FS, Zavaleta ES, Eviner VT, Naylor RL, Vitousek PM, Reynolds HL, Hooper DU, Lavorel S, Sala OE, Hobbie SE, Mack MC, Díaz S (2000) Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 405(6783):234–242
Fuhrman JA (2009) Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature 459(7244):193–199
Fuhrman JA, Cram JA, Needham DM (2015) Marine microbial community dynamics and their ecological interpretation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 13(3):133–146
Gilbert JA, Field D, Swift P, Newbold L, Oliver A, Smyth T, Somerfield PJ, Huse S, Joint I (2009) The seasonal structure of microbial communities in the Western English Channel. Environ. Microbiol. 11(12):3132–3139
Hahnke RL, Probian C, Fuchs BM, Harder J (2013) Variations in pelagic bacterial communities in the North Atlantic Ocean coincide with water bodies. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 71:131–140
Bazin P, Jouenne F, Deton-Cabanillas AF, Perez-Ruzafa A, Veron B (2014) Complex patterns in phytoplankton and microeukaryote diversity along the estuarine continuum. Hydrobiologia 726:155–178
Suh SS, Park M, Hwang J, Lee S, Chung Y, Lee TK (2014) Distinct patterns of marine bacterial communities in the South and North Pacific Oceans. J. Microbiol. 52(10):834–841
Liu J, Fu B, Yang H, Zhao M, He B, Zhang XH (2015) Phylogenetic shifts of bacterioplankton community composition along the Pearl Estuary: the potential impact of hypoxia and nutrients. Front. Microbiol. 6:64
Techtmann SM, Fortney JL, Ayers KA, Joyner DC, Linley TD, Pfiffner SM, Hazen TC (2015) The unique chemistry of eastern Mediterranean water masses selects for distinct microbial communities by depth. PLoS One 10:e0120605
Tinta T, Vojvoda J, Mozetič P, Talaber I, Vodopivec M, Malfatti F, Turk V (2015) Bacterial community shift is induced by dynamic environmental parameters in a changing coastal ecosystem (northern Adriatic, northeastern Mediterranean Sea)—a 2-year time-series study. Environ. Microbiol. 17(10):3581–3596
Eggleston EM, Hewson I (2016) Abundance of two Pelagibacter ubique bacteriophage genotypes along a latitudinal transect in the North and South Atlantic Oceans. Front. Microbiol. 7:1534
Zheng X, Dai X, Huang L (2016) Spatial variations of prokaryotic communities in surface water from India Ocean to Chinese marginal seas and their underlining environmental determinants. Front Mar Sci. 3:17
Li WK (2002) Macroecological patterns of phytoplankton in the northwestern North Atlantic Ocean. Nature 419(6903):154–157
Giovannoni SJ, Vergin KL (2012) Seasonality in ocean microbial communities. Science 335(6069):671–676
Rusch DB, Halpern AL, Sutton G, Heidelberg KB, Williamson S, Yooseph S, Wu D, Eisen JA, Hoffman JM, Remington K, Beeson K, Tran B, Smith H, Baden-Tillson H, Stewart C, Thorpe J, Freeman J, Andrews-Pfannkoch C, Venter JE, Li K, Kravitz S, Heidelberg JF, Utterback T, Rogers YH, Falcón LI, Souza V, Bonilla-Rosso G, Eguiarte LE, Karl DM, Sathyendranath S, Platt T, Bermingham E, Gallardo V, Tamayo-Castillo G, Ferrari MR, Strausberg RL, Nealson K, Friedman R, Frazier M, Venter JC (2007) The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling expedition: northwest Atlantic through eastern tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 5(3):e77
Armbrust EV, Palumbi SR (2015) Marine biology. Uncovering hidden worlds of ocean biodiversity. Science 348(6237):865–867
Pesant S, Not F, Picheral M, Kandels-Lewis S, Le Bescot N, Gorsky G, Iudicone D, Karsenti E, Speich S, Troublé R, Dimier C, Searson S, Tara Oceans Consortium Coordinators (2015) Open science resources for the discovery and analysis of Tara Oceans data. Sci Data. 2:150023
Irigoien X, Huisman J, Harris RP (2004) Global biodiversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton. Nature 429(6994):863–867
Finlay BJ (2002) Global dispersal of free-living microbial eukaryote species. Science 296(5570):1061–1063
Sunagawa S, Coelho LP, Chaffron S, Kultima JR, Labadie K, Salazar G, Djahanschiri B, Zeller G, Mende DR, Alberti A, Cornejo-Castillo FM, Costea PI, Cruaud C, d'Ovidio F, Engelen S, Ferrera I, Gasol JM, Guidi L, Hildebrand F, Kokoszka F, Lepoivre C, Lima-Mendez G, Poulain J, Poulos BT, Royo-Llonch M, Sarmento H, Vieira-Silva S, Dimier C, Picheral M, Searson S, Kandels-Lewis S, Tara Oceans coordinators, Bowler C, de Vargas C, Gorsky G, Grimsley N, Hingamp P, Iudicone D, Jaillon O, Not F, Ogata H, Pesant S, Speich S, Stemmann L, Sullivan MB, Weissenbach J, Wincker P, Karsenti E, Raes J, Acinas SG, Bork P (2015) Ocean plankton. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 348(6237):1261359
Faust K, Raes J (2012) Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nat Rev Microbiol. 10(8):538–550
Zhang Z, Geng J, Tang X, Fan H, Xu J, Wen X, Ma ZS, Shi P (2014) Spatial heterogeneity and co-occurrence patterns of human mucosal-associated intestinal microbiota. ISME J. 8(4):881–993
Chaffron S, Rehrauer H, Pernthaler J, von Mering C (2010) A global network of coexisting microbes from environmental and whole-genome sequence data. Genome Res. 20(7):947–959
Medail F, Quezel P (1996) Hot-spots analysis for conservation of plant biodiversity in the Mediterranean basin. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 84:112–127
Peel MC, Finlayson BL, McMahon TA (2007) Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Dis. 4:439–473
Henry LG, McManus JF, Curry WB, Roberts NL, Piotrowski AM, Keigwin LD (2016) North Atlantic ocean circulation and abrupt climate change during the last glaciation. Science 353(6298):470–474
Xue W, Tobino T, Nakajima F, Yamamoto K (2015) Seawater-driven forward osmosis for enriching nitrogen and phosphorous in treated municipal wastewater: effect of membrane properties and feed solution chemistry. Water Res. 69:120–130
Gordon LI, Jennings Jr JC, Ross AA, Krest JM (1992) A suggested protocol for continuous flow automated analysis of seawater nutrients. WHPO, Methods Manual
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 27(30)
Porter KG, Feig YS (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25:943–948
Fierer N, Hamady M, Lauber CL, Knight R (2008) The influence of sex, handedness, and washing on the diversity of hand surface bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105:17994–17999
Bates ST, Berg-Lyons D, Caporaso JG, Walters WA, Knight R, Fierer N (2011) Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J. 5:908–917
Liu Z, Lozupone C, Hamady M, Bushman FD, Knight R (2007) Short pyrosequencing reads suffice for accurate microbial community analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:e120
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75(23):7537–7541
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7:335–336
Quince C, Lanzen A, Curtis TP, Davenport RJ, Hall N, Read LF, Sloan WT (2009) Accurate determination of microbial diversity from 454 pyrosequencing data. Nat. Methods 6:639–641
Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2010) Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ. Microbiol. 12:1889–1898
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200
Huse SM, Huber JA, Morrison HG, Sogin ML, Welch DM (2007) Accuracy and quality of massively parallel DNA pyrosequencing. Genome Biol. 8(7):R143
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 10(10):996–998
Faust K, Sathirapongsasuti JF, Izard J, Segata N, Gevers D, Raes J, Huttenhower C (2012) Microbial co-occurrence relationships in the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 8(7):e1002606
Yang S, Wen X, Shi Y, Liebner S, Jin H, Perfumo A (2016) Hydrocarbon degraders establish at the costs of microbial richness, abundance and keystone taxa after crude oil contamination in permafrost environments. Sci. Rep. 6:37473
Lima-Mendez G, Faust K, Henry N, Decelle J, Colin S, Carcillo F, Chaffron S, Ignacio-Espinosa JC, Roux S, Vincent F, Bittner L, Darzi Y, Wang J, Audic S, Berline L, Bontempi G, Cabello AM, Coppola L, Cornejo-Castillo FM, d’Ovidio F, De Meester L, Ferrera I, Garet-Delmas MJ, Guidi L, Lara E, Pesant S, Royo-Llonch M, Salazar G, Sánchez P, Sebastian M, Souffreau C, Dimier C, Picheral M, Searson S, Kandels-Lewis S, Tara Oceans coordinators, Gorsky G, Not F, Ogata H, Speich S, Stemmann L, Weissenbach J, Wincker P, Acinas SG, Sunagawa S, Bork P, Sullivan MB, Karsenti E, Bowler C, de Vargas C, Raes J (2015) Ocean plankton. Determinants of community structure in the global plankton interactome. Science 348(6237):1262073(1)–1262073(9)
Yambartsev A, Perlin MA, Kovchegov Y, Shulzhenko N, Mine KL, Dong X, Morgun A (2016) Unexpected links reflect the noise in networks. Biol. Direct 11(1):52
Parks DH, Tyson GW, Hugenholtz P, Beiko RG (2014) STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 30(21):3123–3124
Clarke K, Gorley R (2006) PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth, UK. Companion web site table w5: available at www.raselab.org/companion/ocean_interactone/tables/w5.xlsx
Polson SW (2007) Comparative analysis of microbial community structure associated with Acroporid corals during a disease outbreak in the Florida Reef Tract. PhD Thesis, Molecular and Cellular Biology and Pathobiology Program, Marine Biomedicine and Environmental Sciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC
Zinger L, Amaral-Zettler LA, Fuhrman JA, Horner-Devine MC, Huse SM, Welch DB, Martiny JB, Sogin M, Boetius A, Ramette A (2011) Global patterns of bacterial beta-diversity in seafloor and seawater ecosystems. PLoS One 6(9):e24570
Louca S, Parfrey LW, Doebeli M (2016) Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 353(6305):1272–1277
Livermore JA, Jones SE (2015) Local-global overlap in diversity informs mechanisms of bacterial biogeography. ISME J. 9(11):2413–2422
Ottesen EA, Young CR, Eppley JM, Ryan JP, Chavez FP, Scholin CA, DeLong EF (2013) Pattern and synchrony of gene expression among sympatric marine microbial populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(6):E488–E497
Aylward FO, Eppley JM, Smith JM, Chavez FP, Scholin CA, DeLong EF (2015) Microbial community transcriptional networks are conserved in three domains at ocean basin scales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112(17):5443–5448
Fuhrman JA, Liang X, Noble RT (2005) Rapid detection of enter viruses in small volumes of natural waters by real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71:4523–4530
Keuter S, Rahav E, Herut B, Rinkevich B (2015) Distribution patterns of bacterioplankton in the oligotrophic south-eastern Mediterranean Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 91(8):fiv070
Thingstad TF, Krom MD, Mantoura RF, Flaten GA, Groom S, Herut B, Kress N, Law CS, Pasternak A, Pitta P, Psarra S, Rassoulzadegan F, Tanaka T, Tselepides A, Wassmann P, Woodward EM, Riser CW, Zodiatis G, Zohary T (2005) Nature of phosphorus limitation in the ultraoligotrophic eastern Mediterranean. Science 309(5737):1068–1071
Salter I, Galand PE, Fagervold SK, Lebaron P, Obernostere I, Oliver MJ, Suzuki MT, Tricoire C (2015) Seasonal dynamics of active SAR11 ecotypes in the oligotrophic Northwest Mediterranean Sea. ISME J. 9(2):347–360
Mapelli F, Varela MM, Barbato M, Alvariño R, Fusi M, Alvarez M, Merlino G, Daffonchio D, Borin S (2013) Biogeography of planktonic bacterial communities across the whole Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Sci. 9:585–595
Swan BK, Tupper B, Sczyrba A, Lauro FM, Martinez-Garcia M, González JM, Luo H, Wright JJ, Landry ZC, Hanson NW, Thompson BP, Poulton NJ, Schwientek P, Acinas SG, Giovannoni SJ, Moran MA, Hallam SJ, Cavicchioli R, Woyke T, Stepanauskas R (2013) Prevalent genome streamlining and latitudinal divergence of planktonic bacteria in the surface ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110:11463–11468
Giovannoni SJ, Cameron TJ, Temperton B (2014) Implications of streamlining theory for microbial ecology. ISME J. 8:1553–1565
Ghai R, Mizuno CM, Picazo A, Camacho A, Rodriguez-Valera F (2013) Metagenomics uncovers a new group of low GC and ultra-small marine Actinobacteria. Sci. Rep. 3:2471
Scott JJ, Breier JA, Luther III GW, Emerson D (2015) Microbial iron mats at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and evidence that Zetaproteobacteria may be restricted to iron-oxidizing marine systems. PLoS One 10(3):e0119284
Muck S, Griessler T, Köstner N, Klimiuk A, Winter C, Herndl GJ (2014) Fracture zones in the Mid Atlantic Ridge lead to alterations in prokaryotic and viral parameters in deep-water masses. Front. Microbiol. 5:264
Mendonça A, Arístegui J, Vilas JC, Montero MF, Ojeda A, Espino M, Martins A (2012) Is there a seamount effect on microbial community structure and biomass? The case study of Seine and Sedlo seamounts (northeast Atlantic). PLoS One 7(1):e29526
Carrero-Colón M, Nakatsu CH, Konopka A (2006) Effect of nutrient periodicity on microbial community dynamics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72(5):3175–3183
Partensky F, Blanchot J, Vaulot D, in Marine Cyanobacteria Vol. 19 (eds Charpy, L. & Larkum, A. W. D.) 457–475 (Institute Océanographique, 1999)
Jeffries TC, Schmitz Fontes ML, Harrison DP, Van-Dongen-Vogels V, Eyre BD, Ralph PJ, Seymour JR (2016) Bacterioplankton dynamics within a large anthropogenically impacted urban estuary. Front. Microbiol. 6:1438
Steele JA, Countway PD, Xia L, Vigil PD, Beman JM, Kim DY, Chow CE, Sachdeva R, Jones AC, Schwalbach MS, Rose JM, Hewson I, Patel A, Sun F, Caron DA, Fuhrman JA (2011) Marine bacterial, archaeal and protistan association networks reveal ecological linkages. ISME J. 5(9):1414–1425
Forti F, Boechi L, Bikiel D, Martí MA, Nardini M, Bolognesi M, Viappiani C, Estrin D, Luque FJ (2011) Ligand migration in Methanosarcina acetivorans protoglobin: effects of ligand binding and dimeric assembly. J. Phys. Chem. B 115(46):13771–13780
Marg BL, Schweimer K, Sticht H, Oesterhelt D (2005) A two-alpha-helix extra domain mediates the halophilic character of a plant-type ferredoxin from halophilic archaea. Biochemistry 44(1):29–39
Kim JG, Park SJ, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Schouten S, Rijpstra WI, Jung MY, Kim SJ, Gwak JH, Hong H, Si OJ, Lee S, Madsen EL, Rhee SK (2016) Hydrogen peroxide detoxification is a key mechanism for growth of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113(28):7888–7893
Yu S, Yao P, Liu J, Zhao B, Zhang G, Zhao M, Yu Z, Zhang XH (2016) Diversity, abundance, and niche differentiation of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in mud deposits of the Eastern China marginal seas. Front. Microbiol. 7:137
Zhou L, Wang S, Zou Y, Xia C, Zhu G (2015) Species, abundance and function of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in inland waters across China. Sci. Rep. 5:15969
Reigstad LJ, Richter A, Daims H, Urich T, Schwark L, Schleper C (2008) Nitrification in terrestrial hot springs of Iceland and Kamchatka. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 64:167–174
Santoro AE, Casciotti KL, Francis CA (2010) Activity, abundance and diversity of nitrifying archaea and bacteria in the central California current. Environ. Microbiol. 12:1989–2006
Liu Y, Whitman WB (2008) Metabolic, phylogenetic, and ecological diversity of the methanogenic archaea. Annu N Y Acad Sci. 1125:171–189
Ferry JG (2010) How to make a living by exhaling methane. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 64:453–473
Purdy KJ, Cresswell-Maynard TD, Nedwell DB, McGenity TJ, Grant WD, Timmis KN, Embley TM (2004) Isolation of haloarchaea that grow at low salinities. Environ. Microbiol. 6(6):591–595
Lohner ST, Deutzmann JS, Logan BE, Leigh J, Spormann AM (2014) Hydrogenase-independent uptake and metabolism of electrons by the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis. ISME J. 8(8):1673–1681
Ozuolmez D, Na H, Lever MA, Kjeldsen KU, Jørgensen BB, Plugge CM (2015) Methanogenic archaea and sulfate reducing bacteria co-cultured on acetate: teamwork or coexistence? Front. Microbiol. 6:492
Zhu F, Massana R, Not F, Dominique M, Vaulot D (2005) Mapping of picoeukaryotes in marine ecosystems with quantitative PCR of the 18S rRNA gene. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 52:79–92
Garcia VMT, Garcia CAE, Mata MM, Pollery RC, Piola AR, Signorini SR, McClain CR, Iglesias-Rodriguez MD (2008) Environmental factors controlling the phytoplankton blooms at the Patagonia shelf-break in spring. Deep Sea Res A. 55:1150–1166
Carreto JI, Montoya NG, Benavides HR, Guerrero R, Carignan MO (2003) Characterization of spring phytoplankton communities in the Río de La Plata maritime front using pigment signatures and cell microscopy. Mar. Biol. 143:1013–1027
Kengwoung-Keumo JJ (2016) Competition between a nonallelopathic phytoplankton and an allelopathic phytoplankton species under predation. Math. Biosci. Eng. 13(4):787–812
Hamm CE, Merkel R, Springer O, Jurkojc P, Maier C, Prechtel K, Smetacek V (2003) Architecture and material properties of diatom shells provide effective mechanical protection. Nature 421:841–843
Keeling PJ, Burki F, Wilcox HM, Allam B, Allen EE, Amaral-Zettler LA, Armbrust EV, Archibald JM, Bharti AK, Bell CJ, Beszteri B, Bidle KD, Cameron CT, Campbell L, Caron DA, Cattolico RA, Collier JL, Coyne K, Davy SK, Deschamps P, Dyhrman ST, Edvardsen B, Gates RD, Gobler CJ, Greenwood SJ, Guida SM, Jacobi JL, Jakobsen KS, James ER, Jenkins B, John U, Johnson MD, Juhl AR, Kamp A, Katz LA, Kiene R, Kudryavtsev A, Leander BS, Lin S, Lovejoy C, Lynn D, Marchetti A, McManus G, Nedelcu AM, Menden-Deuer S, Miceli C, Mock T, Montresor M, Moran MA, Murray S, Nadathur G, Nagai S, Ngam PB, Palenik B, Pawlowski J, Petroni G, Piganeau G, Posewitz MC, Rengefors K, Romano G, Rumpho ME, Rynearson T, Schilling KB, Schroeder DC, Simpson AG, Slamovits CH, Smith DR, Smith GJ, Smith SR, Sosik HM, Stief P, Theriot E, Twary SN, Umale PE, Vaulot D, Wawrik B, Wheeler GL, Wilson WH, Xu Y, Zingone A, Worden AZ (2014) The marine microbial eukaryote transcriptome sequencing project (MMETSP): illuminating the functional diversity of eukaryotic life in the oceans through transcriptome sequencing. PLoS Biol. 12(6):e1001889
Poggiale JC, Baklouti M, Queguiner B, Kooijman SALM (2010) How far details are important in ecosystem modelling: the case of multi-limiting nutrients in phytoplankton-zooplankton interactions. Phil Trans R Soc B. 365:3495–3507
Milici M, Tomasch J, Wos-Oxley ML, Decelle J, Jáuregui R, Wang H, Deng ZL, Plumeier I, Giebel HA, Badewien TH, Wurst M, Pieper DH, Simon M, Wagner-Döbler I (2016) Bacterioplankton biogeography of the Atlantic Ocean: a case study of the distance-decay relationship. Front. Microbiol. 7:590
Dumbrell AJ, Nelson M, Helgason T, Dytham C, Fitter AH (2010) Relative roles of niche and neutral processes in structuring a soil microbial community. ISME J. 4(3):337–345
Pontarp M, Canback B, Tunlid A, Lundberg P (2012) Phylogenetic analysis suggests that habitat filtering is structuring marine bacterial communities across the globe. Microb. Ecol. 64:8–17
Ulrich W, Hajdamowicz I, Zalewski M, Stańska M, Ciurzycki W, Tykarski P (2009) Species assortment or habitat filtering: a case study of spider communities on lake islands. Ecol. Res. 25:375–381
Maire V, Gross N, Börger L, Proulx R, Wirth C, da Silveira Pontes L, Soussana JF, Louault F (2012) Habitat filtering and niche differentiation jointly explain species relative abundance within grassland communities along fertility and disturbance gradients. New Phytol. 196:497–509
Macalady JL, Dattagupta S, Schaperdoth I, Jones DS, Druschel GK, Eastman D (2008) Niche differentiation among sulfur-oxidizing bacterial populations in cave waters. ISME J. 2:590–601
Brown MV, Lauro FM, DeMaere MZ, Muir L, Wilkins D, Thomas T, Riddle MJ, Fuhrman JA, Andrews-Pfannkoch C, Hoffman JM, McQuaid JB, Allen A, Rintoul SR, Cavicchioli R (2012) Global biogeography of SAR11 marine bacteria. Mol. Syst. Biol. 8:595
Lewin A, Wentzel A, Valla S (2013) Metagenomics of microbial life in extreme temperature environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 24(3):516–525
Walsh EA, Smith DC, Sogin ML, DHondt S (2015) Bacterial and archaeal biogeography of the deep chlorophyll maximum in the South Pacific Gyre. Aquat Microbiol Ecol. 75:1–13
Auguet JC, Barberan A, Casamayor EO (2010) Global ecological patterns in uncultured archaea. ISME J. 4(2):182–190
Wang J, Yang D, Zhang Y, Shen J, van der Gast C, Hahn MW, Wu Q (2011) Do patterns of bacterial diversity along salinity gradients differ from those observed for macroorganisms? PLoS One 6(11):e27597
O’Malley MA (2008) Everything is everywhere: but the environment selects: ubiquitous distribution and ecological determinism in microbial biogeography. Stud. Hist. Phil. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 39(3):314–325
Rohwer F, Thurber RV (2009) Viruses manipulate the marine environment. Nature 459:207–212
Worden AZ, Follows MJ, Giovannoni SJ, Wilken S, Zimmerman AE, Keeling PJ (2015) Rethinking the marine carbon cycle: factoring in the multifarious lifestyles of microbes. Science 347(6223):1257594
Lupatini M, Suleiman AKA, Jacques RJS, Antoniolli ZI, de Siqueira Ferreira A, Kuramae EE, Roesch LFW (2014) Network topology reveals high connectance levels and few key microbial genera within soils. Front Environ Sci. 2:10
Zhou J, Deng Y, Luo F, He Z, Tu Q, Zhi X (2010) Functional molecular ecological networks. MBio 1:1592–1601
Shi S, Nuccio EE, Shi ZJ, He Z, Zhou J, Firestone MK (2016) The interconnected rhizosphere: high network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 19:926–936
Zheng YM, Cao P, Fu B, Hughes JM, He J (2013) Ecological drivers of biogeographic patterns of soil archaeal community. PLoS One 8(5):e63375
Jamieson RE, Rogers AD, Billett DS, Smale DA, Pearce DA (2012) Patterns of marine bacterioplankton biodiversity in the surface waters of the Scotia Arc, Southern Ocean. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 80(2):452–468
Coutinho FH, Meirelles PM, Moreira AP, Paranhos RP, Dutilh BE, Thompson FL (2015) Niche distribution and influence of environmental parameters in marine microbial communities: a systematic review. Peer J. 3:e1008
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41476092), S&T Projects of Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (KQJSCX20160226190419, JCYJ20170412171959157, JCYJ20150529164918736), Marine Fishery Science and Technology and Industry Development of Guangdong Province (A201603D05), as well as the HIT Scientific Research Innovation Fund (No. HIT.NSRIF.201702).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2912 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Song, X., Zhang, CY. et al. Distribution Patterns of Microbial Community Structure Along a 7000-Mile Latitudinal Transect from the Mediterranean Sea Across the Atlantic Ocean to the Brazilian Coastal Sea. Microb Ecol 76, 592–609 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1150-z