Abstract
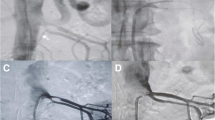
Twenty percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasties were performed on 16 children (mean age 8.7 years) with hypertension secondary to renal artery stenosis (RAS). The aetiologies were neurofibromatosis (n = 1), Williams syndrome (n = 2), Takayasu arteritis (n = 1) and fibromuscular dysplasia (n = 12). The stenosis was isolated proximal or distal in 13 cases and multiple in 3 cases. Angioplasty resulted in a complete cure without medical treatment in 9 cases. Angioplasty allowed a reduction of medical treatment in two single stenoses, but was ineffective in all cases of multiple stenoses. Our findings show that angioplasty of RAS in children is an effective treatment when the stenosis is isolated, with a 69 % success rate. It seems ineffective in case of multiple stenoses (three cases).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 July 1997 Accepted: 20 August 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Courtel, J., Soto, B., Niaudet, P. et al. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of renal artery stenosis in children. Pediatric Radiology 28, 59–63 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002470050294
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002470050294



