Abstract
Background
Image-guided percutaneous microwave ablation has been used to treat adult osteoid osteomas but has not been thoroughly evaluated in the pediatric population.
Objective
To evaluate the technical feasibility and clinical efficacy of microwave ablation to treat osteoid osteomas in pediatric patients.
Materials and methods
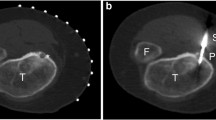
The electronic medical record and imaging archive were reviewed for 24 consecutive patients who had undergone microwave ablation of osteoid osteomas between January 1, 2015, and May 31, 2018, at a single tertiary care pediatric hospital. All patients were diagnosed by clinical and imaging criteria, and referred by a pediatric orthopedic surgeon after failing conservative management with pain medication. The average age of the patients was 13.3 years (range: 3–18 years), and the average size of the osteoid osteoma nidus was 8.8 mm (range: 5–22 mm). Technical success was defined as placement of the microwave antenna at the distal margin of the lesion nidus and achievement of the target ablation temperature. Clinical findings were assessed pre- and post-ablation and clinical success was defined as complete relief of pain without pain medication at 1-month follow-up. The number and severity of complications were also documented.
Results
Clinical success was achieved in 100% of patients (24/24), with all reporting complete cessation of pain medication use 1 week after treatment and 0/10 pain at 1 month. There were 4 minor complications (17%) including access site numbness and a minor soft-tissue infection. There were no major complications.
Conclusion
Microwave ablation is a technically feasible and clinically effective treatment for pediatric osteoid osteomas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boscainos PJ, Cousins GR, Kulshreshtha R et al (2013) Osteoid osteoma. Orthopedics 36:792–800
Zhang Y, Rosenberg AE (2017) Bone-forming tumors. Surg Pathol Clin 10:513–535
Hakim DN, Pelly T, Kulendran M, Caris JA (2015) Benign tumours of the bone: A review. J Bone Oncol 4:37–41
Natali GL, Paolantonio G, Fruhwirth R et al (2016) Paediatric musculoskeletal interventional radiology. Br J Radiol 89:20150369
Laurence N, Epelman M, Markowitz RI et al (2012) Osteoid osteomas: a pain in the night diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol 42:1490–1501
Ghanem I (2006) The management of osteoid osteoma: updates and controversies. Curr Opin Pediatr 18:36–41
Miyazaki M, Arai Y, Myoui A et al (2016) Phase I/II multi-institutional study of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for painful osteoid osteoma (JIVROSG-0704). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39:1464–1470
Donkol RH, Al-Nammi A, Moghazi K (2008) Efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in children. Pediatr Radiol 38:180–185
Lubner MG, Brace CL, Hinshaw JL, Lee FT Jr (2010) Microwave tumor ablation: mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:S192–S203
Prud'homme C, Nueffer J-P, Runge M et al (2017) Prospective pilot study of CT-guided microwave ablation in the treatment of osteoid osteomas. Skeletal Radiol 46:315–323
Kostrzewa M, Diezler P, Michaely H et al (2014) Microwave ablation of osteoid osteomas using dynamic MR imaging for early treatment assessment: preliminary experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol 25:106–111
Basile A, Failla G, Reforgiato A et al (2014) The use of microwaves ablation in the treatment of epiphyseal osteoid osteomas. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37:737–742
Lee EH, Shafi M, Hui JH (2006) Osteoid osteoma: a current review. J Pediatr Orthop 26:695–700
Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF, Lewis CA (2003) Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14(9 Pt 2):S199–S202
Brown SD, vanSonnenberg E (2007) Issues in imaging-guided tumor ablation in children versus adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:626–632
Whitmore MJ, Hawkins CM, Prologo JD et al (2016) Cryoablation of osteoid osteoma in the pediatric and adolescent population. J Vasc Interv Radiol 27:232–237
Earhart J, Wellman D, Donaldson J et al (2013) Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of osteoid osteoma: results and complications. Pediatr Radiol 43:814–819
Perry BC, Monroe EJ, McKay T et al (2017) Pediatric percutaneous osteoid osteoma ablation: cone-beam CT with fluoroscopic overlay versus conventional CT guidance. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40:1593–1599
de Baere T, Deschamps F (2014) New tumor ablation techniques for cancer treatment (microwave, electroporation). Diagn Interv Imaging 95:677–682
Abbas G, Schuchert MJ, Pennathur A et al (2007) Ablative treatments for lung tumors: radiofrequency ablation, stereotactic radiosurgery, and microwave ablation. Thorac Surg Clin 17:261–271
Moser T, Buy X, Goyault G et al (2008) Image-guided ablation of bone tumors: thermal ablation. J Radiol 89:461–471
Montana MC, Evers AS (2017) Anesthetic neurotoxicity: new findings and future directions. J Pediatr 181:279–285
Ing C, DiMaggio C, Whitehouse A et al (2012) Long-term differences in language and cognitive function after childhood exposure to anesthesia. Pediatrics 130:e476–e485
Schramm W, Yang D, Haemmerich D (2006) Contribution of direct heating, thermal conduction and perfusion during radiofrequency and microwave ablation. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 1:5013–5016
Wright AS, Sampson LA, Warner TF et al (2005) Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology 236:132–139
Krokidis M, Ahmed I (2013) Overview of thermal ablation devices: Radiofrequency Ablation. In: Clark T, Sabharwal T (eds) Interventional radiology techniques in ablation, 1st edn. Springer-Verlag London, London, pp 5–11
Lanza E, Thouvenin Y, Viala P et al (2014) Osteoid osteoma treated by percutaneous thermal ablation: when do we fail? A systematic review and guidelines for future reporting. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37:1530–1539
Trembly BS, Douple EB, Ryan TP, Hoopes PJ (1994) Effect of phase modulation on the temperature distribution of a microwave hyperthermia antenna array, in vivo. Int J Hyperth 10:691–705
Shields DW, Sohrabi S, Crane EO et al (2017) Radiofrequency ablation for osteoid osteoma - Recurrence rates and predictive factors. Surgeon 16:156–162
Iyer RS, Chapman T, Chew FS (2012) Pediatric bone imaging: diagnostic imaging of osteoid osteoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198:1039–1052
Towbin R, Kaye R, Meza MP et al (1995) Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous excision using a CT-guided coaxial technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol 164:945–949
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rinzler, E.S., Shivaram, G.M., Shaw, D.W. et al. Microwave ablation of osteoid osteoma: initial experience and efficacy. Pediatr Radiol 49, 566–570 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4327-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4327-1