Abstract
Background
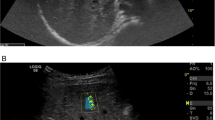
Two-dimensional (2-D) shear wave elastography is a new sonographic elastography method for noninvasive measurement of liver stiffness.
Objective
The aim of this study was to establish reference values of normal liver stiffness on 2-D shear wave elastography in children.
Materials and methods
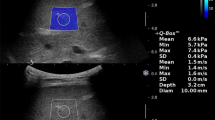
Two-dimensional shear wave elastography values were measured in 202 children with no liver disease from the neonatal period to puberty, who were divided into 4 age groups: newborns and infants, preschoolers, elementary school children and adolescents. We investigated the effects of age, depth of elastography measurement, transducer, number of measurements per child, liver size and Doppler parameters of hepatic blood flow on liver elasticity values.
Results
The mean normal liver elasticity value in the study population was: 4.29±0.59 kilopascals (kPa). In neonates and infants, mean liver elasticity value was 4.63 (± 0.6) kPa, in preschoolers and elementary school children, 4.05 (± 0.57) kPa and 4.15 (± 0.52) kPa, respectively, and in adolescents, 4.39 (± 0.55) kPa. Values in neonates and infants as well as adolescents were significantly higher than in preschoolers and elementary school children (Kruskal-Wallis, P<0.001; Mann-Whitney U tests, P<0.05). There was no significant association between liver elasticity values and size of the right lobe or Doppler parameters of hepatic blood flow. Different depths and the number of elastography measurements had no effect on liver elasticity values.
Conclusion
Two-dimensional shear wave elastography is achievable in a wide range of age in children. We established the reference values of normal liver stiffness on 2-D shear wave elastography in children.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belei O, Sporea I, Gradinaru-Tascau O et al (2016) Comparison of three ultrasound based elastographic techniques in children and adolescents with chronic diffuse liver diseases. Med Ultrason 18:145–150
Franchi-Abella S, Corno L, Gonzales E et al (2016) Feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of Supersonic shear-wave Elastography for the assessment of liver stiffness and liver fibrosis in children: a pilot study of 96 patients. Radiology 278:554–562
Tutar O, Beser OF, Adaletli I et al (2014) Shear wave elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 58:750–755
Dillman JR, Heider A, Bilhartz JL et al (2015) Ultrasound shear wave speed measurements correlate with liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 45:1480–1488
Behairy Bel-S, Sira MM, Zalata KR et al (2016) Transient elastography compared to liver biopsy and morphometry for predicting fibrosis in pediatric chronic liver disease: does etiology matter? World J Gastroenterol 22:4238–4249
de Ledinghen V, Le Bail B, Rebouissoux L et al (2007) Liver stiffness measurement in children using FibroScan: feasibility study and comparison with Fibrotest, aspartate transaminase to platelets ratio index, and liver biopsy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 45:443–450
Eiler J, Kleinholdermann U, Albers D et al (2012) Standard value of ultrasound elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) in healthy liver tissue of children and adolescents. Ultraschall Med 8:474–479
Noruegas MJ, Matos H, Goncalves I et al (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging in the assessment of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 42:201–204
Fitzpatrick E, Quaglia A, Vimalesvaran S et al (2013) Transient elastography is a useful noninvasive tool for the evaluation of fibrosis in paediatric chronic liver disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 56:72–76
Nobili V, Monti L, Alisi A et al (2011) Transient elastography for assessment of fibrosis in paediatric liver disease. Pediatr Radiol 41:1232–1238
Hanquinet S, Rougemont AL, Courvoisier D et al (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography for the noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 43:545–551
Tokuhara D, Cho Y, Shintaku H (2016) Transient Elastography-based liver stiffness age-dependently increases in children. PLoS One 11:e0166683
Goldschmidt I, Streckenbach C, Dingemann C et al (2013) Application and limitations of transient liver elastography in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 57:109–113
Engelmann G, Gebhardt C, Wenning D et al (2012) Feasibility study and control values of transient elastography in healthy children. Eur J Pediatr 171:353–360
Hanquinet S, Courvoisier D, Kanavaki A et al (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging—normal values of liver stiffness in healthy children. Pediatr Radiol 43:539–544
Matos H, Trindade A, Noruegas MJ (2014) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in Paediatric patients: normal liver values. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 59:684–688
Lee MJ, Kim MJ, Han KH, Yoon CS (2013) Age-related changes in liver, kidney and spleen stiffness in healthy children measured with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. Eur J Radiol 82:290–294
Shin HJ, Kim MJ, Kim HY et al (2016) Optimal acquisition number for hepatic shear wave velocity measurements in children. PLoS One 11:e0168758
Konus OL, Ozdemir A, Akkaya A et al (1998) Normal liver, spleen, and kidney dimensions in neonates, infants, and children: evaluation with sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171:1693–1698
de Bruyn R (2005) Pediatric ultrasound how, why and when. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone
Mueller S, Sandrin L (2010) Liver stiffness: a novel parameter for the diagnosis of liver disease. Hepat Med 2:49–67
Bende F, Sporea I, Șirli R et al (2017) Performance of 2D-SWE.GE for predicting different stages of liver fibrosis, using transient elastography as the reference method. Med Ultrason 19:143–149
Lee SM, Lee JM, Kang HJ et al (2017) Liver fibrosis staging with a new 2D-shear wave elastography using comb-push technique: applicability, reproducibility, and diagnostic performance. PLoS One 12:e0177264
Suh CH, Kim SY, Kim KW et al (2014) Determination of normal hepatic elasticity by using real-time shear-wave elastography. Radiology 271:895–900
GE Healthcare LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography Whitepaper recommendations. Available at: http://www3.gehealthcare.com
Bedossa P, Carrat F (2009) Liver biopsy: the best, not the gold standard. J Hepatol 50:1–3
Cohen MB, A-Kader HH, Lambers D, Heubi JE (1992) Complications of percutaneous liver biopsy in children. Gastroenterology 102:629–632
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galina, P., Alexopoulou, E., Zellos, A. et al. Performance of two--dimensional ultrasound shear wave elastography: reference values of normal liver stiffness in children. Pediatr Radiol 49, 91–98 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4244-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4244-3