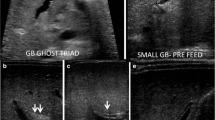
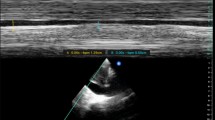
Abstract
Umbilical catheters are commonly used in the neonatal period for blood sampling or for administering medication or parenteral nutrition. The position of the catheter is usually confirmed with radiography. However, many complications associated with the use of umbilical catheters, such as liver collections from extravasation or vascular thrombosis, are not apparent on radiographs but can be easily diagnosed with ultrasound. This pictorial review illustrates the sonographic findings of complications that should be excluded in the sick neonate with an indwelling catheter.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
British Association of Perinatal Medicine (2015) Use of central venous catheters in neonates. A framework for practice. https://www.bapm.org/resources/use-central-venous-catheters-neonates-framework-practice. Accessed 2 July 2018
Ades A, Sable C, Cummings A et al (2003) Echocardiographic evaluation of umbilical venous catheter placement. J Perinatol 23:24–28
de Almeida MM, de Sousa Tavares WG, Furtado MMAA et al (2016) Neonatal atrial flutter after insertion of an intracardiac umbilical venous catheter. Rev Paul Pediatr 34:132–135
Schlesinger AE, Braveman RM, DiPietro M (2003) Neonates and umbilical venous catheters: normal appearance, anomalous positions, complications, and potential aid to diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1147–1153
Grizelj R, Vukovic J, Bojanic K et al (2014) Severe liver injury while using umbilical venous catheter: case series and literature review. Am J Perinatol 31:965–974
Franta J, Harabor A, Soraisham AS (2017) Ultrasound assessment of umbilical venous catheter migration in preterm infants: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 102:F251–F255
Greenberg M, Movahed H, Peterson B et al (1995) Placement of umbilical venous catheters with use of bedside real-time ultrasonography. J Pediatr 126:633–635
Michel F, Brevaut-Malaty V, Pasquali R et al (2012) Comparison of ultrasound and X-ray in determining the position of umbilical venous catheters. Resuscitation 83:705–709
Barrington KJ (1999) Umbilical artery catheters in the newborn: effects of position of the catheter tip. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD000505 http://cochranelibrary-wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD000505/abstract;jsessionid=C1201DF1153EE5E151492FD2AF758FEF.f02t01. Accessed 2 July 2018
Mobrohisky ST, Levine RL, Blumhagen JD et al (1978) Low positioning of umbilical artery catheters increases associated complications in newborn infants. N Engl J Med 299:561–564
Munoz ME, Escriba R, Martinez-Bermejo A et al (1993) Flaccid paraplegia as complication of umbilical artery catheterization. Pediatr Neurol 9:401–403
Carey BE, Zellinger TC (1989) Hypoglycaemia due to high positioning of umbilical artery catheters. J Perinatol 9:407–410
Cumming WA, Buechfield DJ (1994) Accidental catheterization of internal iliac artery branches: a serious complication of umbilical artery catheterisation. J Perinatol 14:304–309
Eifinger F, Fuchs Z, Koerber F et al (2018) Investigation of umbilical venous vessel anatomy and diameters as a guideline for catheter placement in newborns. Clin Anat 31:269–274
Hermansen MC, Hermansen MG (2005) Intravascular catheter complications in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clin Perinatol 32:141–156
Ramasethu J (2008) Complications of vascular catheters in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clin Perinatol 35:199–222
Deeg KH, Wölfel D, Rupprecht T (1992) Diagnosis of neonatal aortic thrombosis by colour coded Doppler sonography. Pediatr Radiol 22:62–63
Seibert JJ, Northington FJ, Miers JF et al (1991) Aortic thrombosis after umbilical artery catheterization in neonates: prevalence of complications on long-term follow-up. AJR Am J Roentgenol 156:567–569
Ergaz Z, Simanovsky N, Rozovsky K et al (2012) Clinical outcome of umbilical artery catheter-related thrombosis — a cohort study. J Perinatol 32:933–940
Boo NY, Wong NC, Zulkifli SS et al (1999) Risk factors associated with umbilical vascular catheter-associated thrombosis in newborn infants. J Paediatr Child Health 35:460–465
Marks SD, Masscotte P, Steele BT et al (2005) Neonatal renal venous thrombosis: clinical outcomes and prevalence of prothrombotic disorders. J Pediatr 146:811–816
Winyard PJD, Bharucha T, De Bruyn R et al (2006) Perinatal renal venous thrombosis: presenting renal lengths predicts outcome. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 91:F273–F278
Hibbert J, Howlett DC, Greenwood KL et al (1997) The ultrasound appearances of neonatal renal vein thrombosis. Br J Radiol 70:1191–1194
Lau KK, Stoffman JM, Williams S et al (2007) Neonatal renal vein thrombosis: review of the English-language literature between 1992 and 2006. Pediatrics 120:e1278–e1284
Orazi C, Fariella G, Malena S et al (1993) Renal vein thrombosis and adrenal haemorrhage in the newborn: ultrasound evaluation of 4 cases. J Clin Ultrasound 21:163–169
Kraft JK, Brandao LR, Navarro OM (2011) Sonography of renal vein thrombosis in neonates and infants: can we predict outcome? Pediatr Radiol 41:299–307
Williams S, Chan AKC (2011) Neonatal portal vein thrombosis: diagnosis and management. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 16:329–339
Schwartz DS, Gettner PA, Konstantino MM et al (1997) Umbilical venous catheterization and the risk of portal vein thrombosis. J Pediatr 131:760–762
Sakha SH, Rafeey M, Tarzamani MK (2007) Portal vein thrombosis after umbilical vein catheterization. Indian J Gastroenterol 26:283–284
Kim JH, Lee YS, Lee SK et al (2001) Does umbilical vein catheterisation lead to portal venous thrombosis? Prospective US evaluation in 100 neonates. Radiology 219:645–650
Morag I, Shah PS, Epelman M et al (2011) Childhood outcomes of neonates diagnosed with portal vein thrombosis. J Paediatr Child Health 47:356–360
Oski FA, Allen DM, Diamond LK (1963) Portal hypertension — a complication of umbilical vein catheterization. Pediatrics 31:297–302
Sequin J, Fletcher MA, Landers S et al (1994) Umbilical venous catheterization: audit by the study group for complications of perinatal care. Am J Perinatol 11:67–70
Coley BD, Sequin J, Codero L et al (1998) Neonatal total parenteral nutrition ascites from liver erosion by umbilical vein catheters. Pediatr Radiol 28:923–927
Lim-Dunham JE, Vade A, Capitano HN et al (2007) Characteristic sonographic findings of hepatic erosion by umbilical vein catheters. J Ultrasound Med 26:661–666
Levkoff AH, Macpherson RI (1990) Intrahepatic encystment of umbilical vein catheter infusate. Pediatr Radiol 20:360–361
Pignotti MS, Monciotti F, Frati P, Fineschi V (2017) Hepatic laceration due to umbilical venous catheter malpositioning. Pediatr Neonatol 58:386–387
Yigiter M, Arda IS, Hiçsönmez A (2008) Hepatic laceration because of malpositioning of the umbilical vein catheter: case report and literature review. J Pediatr Surg 43:E39–E41
Carvajal-Barrios GA, Corrales-Cobos IF, Cuenca-Arias MC et al (2014) Absceso hepático asociado con cateterización umbilical en un neonato [Liver abscess secondary to umbilical catheterization in a newborn]. Infectio 18:158–161
Hagerott HE, Kulkarni S, Restrepo R et al (2014) Clinico-radiologic features and treatment of hepatic lesions caused by inadvertent infusion of parenteral nutrition in liver parenchyma due to malposition of umbilical vein catheters. Pediatr Radiol 44:810–815
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvam, S., Humphrey, T., Woodley, H. et al. Sonographic features of umbilical catheter-related complications. Pediatr Radiol 48, 1964–1970 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4214-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4214-9