Abstract
Background
Data regarding transsplenic portal venous access for diagnostic imaging and endovascular intervention in children are limited, possibly due to concerns regarding high bleeding risks and resultant underutilization.
Objective
To investigate the safety and utility of transsplenic splenoportography and portal venous interventions in children.
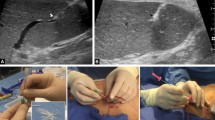
Materials and methods
A retrospective review was performed of all pediatric patients undergoing percutaneous transsplenic portal venous access and intervention at two large tertiary pediatric institutions between January 2012 and April 2017 was performed. Parameters assessed included procedural indications, procedural and relevant prior imaging, technical details of the procedures, laboratory values and clinical follow-up.
Results
Transsplenic portal venous access was achieved in all patients. Diagnostic transsplenic splenoportography was performed in 22 patients and was 100% successful at providing the desired anatomical and functional information. Four transsplenic portal venous interventions were performed with 100% success: meso-Rex shunt angioplasty, snare targeted transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation through cavernous transformation, pharmacomechanical thrombectomy for acute thrombosis, and transplant portal vein angioplasty. Intraperitoneal bleeding occurred in 2/26 (7.7%) and one case required transfusion (3.8%). No cases of hemorrhage were observed when transsplenic access size was 4 Fr or smaller.
Conclusion
Transsplenic splenoportography in children is safe and effective when noninvasive imaging methods have yielded incomplete information. Additionally, a transsplenic approach has advantages for complex portal interventions. Bleeding risks are proportional to tract access size and may be mitigated by tract embolization.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosch J, Dotter CT (1971) Extrahepatic portal obstruction in childhood and its angiographic diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 112:143–149
Foster JH, Conkle DM, Crane JM, Bruko H (1974) Splenoportography: an assessment of its value and risk. Ann Surg 179:773
Caridi JG, Hawkins IF Jr, Cho K et al (2003) CO2 splenoportography: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1375–1378
Liang HL, Yang CF, Pan HB et al (1997) Percutaneous transsplenic catheterization of the portal venous system. Acta Radiol 38:292–295
Zhu K, Meng X, Zhou B et al (2013) Percutaneous transsplenic portal vein catheterization: technical procedures, safety, and clinical applications. J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:518–527
Gong GQ, Wang XL, Wang JH et al (2001) Percutaneous transsplenic embolization of esophageal and gastrio-fundal varices in 18 patients. World J Gastroenterol 7:880
Tuite DJ, Rehman J, Davies MH et al (2007) Percutaneous transsplenic access in the management of bleeding varices from chronic portal vein thrombosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:1571–1575
Chu HH, Kim HC, Jae HJ et al (2012) Percutaneous transsplenic access to the portal vein for management of vascular complication in patients with chronic liver disease. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 35:1388–1395
Habib A, Desai K, Hickey R et al (2015) Portal vein recanalization–transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt using the transsplenic approach to achieve transplant candidacy in patients with chronic portal vein thrombosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26:499–506
Rasinska G, Wermenski K, Rajszys P (1987) Percutaneous transsplenic embolization of esophageal varices in a 5-year-old child. Acta Radiol 28:299–301
Bertram H, Pfister ED, Becker T, Schoof S (2010) Transsplenic endovascular therapy of portal vein stenosis and subsequent complete portal vein thrombosis in a 2-year-old child. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:1760–1764
Chick JFB, Jo A, Dasika N et al (2017) Transsplenic endovascular recanalization and stenting of a completely occluded portal vein with jejunal variceal embolization in a pediatric liver transplant recipient. Pediatr Radiol 47:1012–1015
Pimpalwar S, Chinnadurai P, Hernandez A et al (2017) Trans-splenic access for portal venous interventions in children: do benefits outweigh risks? Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 41:87–95
Lungren MP, Lindquester WS, Seidel FG et al (2016) Ultrasound-guided liver biopsy with gelatin sponge pledget tract embolization in infants weighing less than 10 kg. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 63:e147–e151
Omary RA, Bettmann MA, Cardella JF et al (2003) Quality improvement guidelines for the reporting and archiving of interventional radiology procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:S293–S295
Uller W, Müller-Wille R, Grothues D et al (2014) Gelfoam for closure of large percutaneous transhepatic and transsplenic puncture tracts in pediatric patients. Röfo 186:693–697
Robbins KA, Keet CA (2015) Intraoperative anaphylaxis likely due to Gelfoam in a pediatric patient undergoing liver biopsy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 114:531–533
Dollinger M, Goessmann H, Mueller-Wille R (2014) Percutaneous transhepatic and transsplenic portal vein access: embolization of the puncture tract using amplatzer vascular plugs. Röfo 186:142–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monroe, E.J., Speir, E.J., Hawkins, C.M. et al. Transsplenic splenoportography and portal venous interventions in pediatric patients. Pediatr Radiol 48, 1441–1450 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4157-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4157-1