Abstract
Background
Phalangeal microgeodic syndrome is an uncommon benign self-limiting condition that often occurs during cold weather. The etiology and the pathogenesis of the disease remain unclear.
Objective
To report a series of children with phalangeal microgeodic syndrome.
Materials and methods
Twenty children with phalangeal microgeodic syndrome were retrospectively identified at our hospital after 2007. The clinical data, radiologic manifestation and pathologic appearance were analyzed.
Results
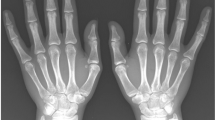
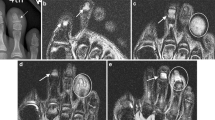
The average age was 10.3 years (range: 6.5–14.6 years). Twelve patients were boys. Twenty-five phalanges were affected radiographically (23 middle phalanges [92%] and 2 proximal phalanges [8%]). On radiographs, there were multiple small phalangeal lacunae in all cases. Metaphyseal rarefaction was seen in 15 phalanges, and metaphyseal transverse lucent bands were found in 7 phalanges. Epiphyseal rarefaction was seen in three phalanges. On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), diffuse signal abnormalities of affected phalanges were observed in all cases. Multiple other phalanges and metacarpals also showed marrow edema in three cases.
Conclusion
Phalangeal microgeodes may represent bone absorption and destruction in response to exaggerated peripheral circulatory impairment following chilblain, and mainly occur in bone growth spurts.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maroteaux P (1970) 5 cases of microgeodic disease of phalanges of unknown etiology in infants. Ann Radiol (Paris) 13:229–236
Fujita A, Sugimoto H, Kikkawa I et al (1999) Phalangeal microgeodic syndrome: findings on MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:711–712
Kaibara N, Masuda S, Katsuki I et al (1981) Phalangeal microgeodic syndrome in childhood: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr 136:41–46
Brijs S, Brijs A (1992) Microgeodic phalangeal syndrome in an infant. Pediatr Radiol 22:80–81
Kashiwa K, Yagi M, Futani H et al (2008) Microgeodic disease affecting the toes in athletes: a report of 2 cases. Am J Sports Med 36:1190–1192
Sato K, Sugiura H, Aoki M (1995) Transient phalangeal osteolysis (microgeodic disease). Report of a case involving the foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:1888–1890
MacCarthy J, O'Brien N (1976) Phalangeal microgeodic syndrome of infancy. Arch Dis Child 51:472–474
Viseux V, Chaby G, Esquenet P et al (2003) Phalangeal microgeodic syndrome and pine processionary caterpillar. Eur J Dermatol 13:497–499
Lee RK, Griffith JF, Read JW et al (2013) Phalangeal microgeodic disease: report of two cases and review of imaging. Skelet Radiol 42:451–455
Lagier R (1975) Foreign body induced osteolytic phalangeal remodelling in an infant. Röfo 123:181–183
Radhakrishnan R, Emery KH, Merrow AC (2017) Diffuse phalangeal signal abnormality on magnetic resonance imaging: phalangeal microgeodic disease. Pediatr Radiol 47:313–320
Crouch C, Smith WL (1990) Long term sequelae of frostbite. Pediatr Radiol 20:365–366
Van Ackere T, Eykens A, Wouters C, Toelen J (2013) The phalangeal microgeodic syndrome in childhood: awareness leads to diagnosis. Eur J Pediatr 172:763–767
Yamamoto T, Kurosaka M, Mizuno K, Fujii M (2001) Phalangeal microgeodic syndrome: MR appearance. Skelet Radiol 30:170–172
Sweet EM, Smith MG (1979) "Winter fingers". Bone infarction in Scottish children as a manifestation of cold injury. Ann Radiol (Paris) 22:71–75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YZ., Ma, XH., Yang, XH. et al. Phalangeal microgeodic syndrome in childhood. Pediatr Radiol 48, 1108–1112 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4137-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4137-5