Abstract
Background
The 320-row multidetector computed tomography (CT) scanner has multiple scan modes, including volumetric modes.
Objective
To compare the image quality and radiation dose of 320-row CT in three acquisition modes — helical, one-shot volume, and wide-volume scan — at pediatric brain imaging.
Materials and methods
Fifty-seven children underwent unenhanced brain CT using one of three scan modes (helical scan, n=21; one-shot volume scan, n=17; wide-volume scan, n=19). For qualitative analysis, two reviewers evaluated overall image quality and image noise using a 5-point grading system. For quantitative analysis, signal-to-noise ratio, image noise and posterior fossa artifact index were calculated. To measure the radiation dose, adjusted CT dose index per unit volume (CTDIadj) and dose length product (DLP) were compared.
Results
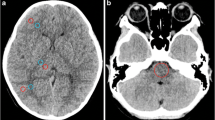
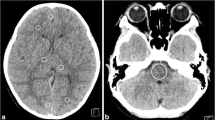
Qualitatively, the wide-volume scan showed significantly less image noise than the helical scan (P=0.009), and less streak artifact than the one-shot volume scan (P=0.001). The helical mode showed significantly lower signal-to-noise ratio, with a higher image noise level compared with the one-shot volume and wide-volume modes (all P<0.05). The CTDIadj and DLP were significantly lower in the one-shot volume and wide-volume modes compared with those in the helical scan mode (all P<0.05).
Conclusion
For pediatric unenhanced brain CT, both the wide-volume and one-shot volume scans reduced radiation dose compared to the helical scan mode, while the wide-volume scan mode showed fewer streak artifacts in the skull vertex and posterior fossa than the one-shot volume scan.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kroft LJ, Roelofs JJ, Geleijns J (2010) Scan time and patient dose for thoracic imaging in neonates and small children using axial volumetric 320-detector row CT compared to helical 64-, 32-, and 16-detector row CT acquisitions. Pediatr Radiol 40:294–300
Podberesky DJ, Angel E, Yoshizumi TT et al (2013) Comparison of radiation dose estimates and scan performance in pediatric high-resolution thoracic CT for volumetric 320-detector row, helical 64-detector row, and noncontiguous axial scan acquisitions. Acad Radiol 20:1152–1161
Sorantin E, Riccabona M, Stucklschweiger G et al (2013) Experience with volumetric (320 rows) pediatric CT. Eur J Radiol 82:1091–1097
Joemai RMS (2011) Ultra helical scanning - fast acquisition of CT images. VISIONS 17:3
Johnston JH, Podberesky DJ, Yoshizumi TT et al (2013) Comparison of radiation dose estimates, image noise, and scan duration in pediatric body imaging for volumetric and helical modes on 320-detector CT and helical mode on 64-detector CT. Pediatr Radiol 43:1117–1127
Ryu YJ, Kim WS, Choi YH et al (2015) Pediatric chest CT: wide-volume and helical scan modes in 320-MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 205:1315–1321
No authors listed (2007) The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP 37:1–332
Cristy M (1981) Active bone marrow distribution as a function of age in humans. Phys Med Biol 26:389–400
Udayasankar UK, Braithwaite K, Arvaniti M et al (2008) Low-dose nonenhanced head CT protocol for follow-up evaluation of children with ventriculoperitoneal shunt: reduction of radiation and effect on image quality. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:802–806
Rozeik C, Kotterer O, Preiss J et al (1991) Cranial CT artifacts and gantry angulation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 15:381–386
Mullins ME, Lev MH, Bove P et al (2004) Comparison of image quality between conventional and low-dose nonenhanced head CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:533–538
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Siebert E, Bohner G, Dewey M et al (2009) 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation. Br J Radiol 82:561–570
Mori S, Endo M, Obata T et al (2006) Properties of the prototype 256-row (cone beam) CT scanner. Eur Radiol 16:2100–2108
Mori S, Endo M, Nishizawa K et al (2006) Comparison of patient doses in 256-slice CT and 16-slice CT scanners. Br J Radiol 79:56–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, S.K., Choi, Y.H., Cheon, JE. et al. Unenhanced 320-row multidetector computed tomography of the brain in children: comparison of image quality and radiation dose among wide-volume, one-shot volume, and helical scan modes. Pediatr Radiol 48, 594–601 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-4060-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-4060-1