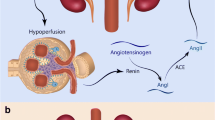
Abstract
The incidence of primary (i.e. essential) hypertension in children and adolescents is increasing; however, secondary hypertension, with an identifiable cause, remains relatively common and might be treatable or even curable. Renovascular hypertension is an uncommon but important secondary cause of hypertension in the pediatric population that can be associated with substantial morbidity. In this article we discuss renin-mediated causes of hypertension in children and related complications, review renal Doppler ultrasound techniques for the evaluation of renin-mediated hypertension (including both direct and indirect assessments), and briefly appraise the literature pertaining to renal Doppler ultrasound and the assessment of pediatric hypertension. Finally, we describe a proposed role for renal Doppler ultrasound in the workup of suspected renin-mediated hypertension in children and adolescents.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gomes RS, Quirino IG, Pereira RM et al (2011) Primary versus secondary hypertension in children followed up at an outpatient tertiary unit. Pediatr Nephrol 26:441–447
Falkner B (2010) Hypertension in children and adolescents: epidemiology and natural history. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1219–1224
Gupta-Malhotra M, Banker A, Shete S et al (2015) Essential hypertension vs. secondary hypertension among children. Am J Hypertens 28:73–80
Tullus K, Brennan E, Hamilton G et al (2008) Renovascular hypertension in children. Lancet 371:1453–1463
Welch WJ (2000) The pathophysiology of renin release in renovascular hypertension. Semin Nephrol 20:394–401
Burnei G, Burnei A, Hodorogea D et al (2009) Diagnosis and complications of renovascular hypertension in children: literature data and clinical observations. J Med Life 2:18–28
Bianchi E, Savasta S, Torcetta F et al (1989) Thalamic hemorrhage in a 4-year-old child induced by nephro-vascular hypertension. Pediatr Radiol 19:513–515
Stanley JC, Fry WJ (1981) Pediatric renal artery occlusive disease and renovascular hypertension. Etiology, diagnosis, and operative treatment. Arch Surg 116:669–676
Stanley JC, Criado E, Upchurch GR Jr et al (2006) Pediatric renovascular hypertension: 132 primary and 30 secondary operations in 97 children. J Vasc Surg 44:1219–1228
Green R, Gu X, Kline-Rogers E et al (2016) Differences between the pediatric and adult presentation of fibromuscular dysplasia: results from the US registry. Pediatr Nephrol 31:641–650
Vo NJ, Hammelman BD, Racadio JM et al (2006) Anatomic distribution of renal artery stenosis in children: implications for imaging. Pediatr Radiol 36:1032–1036
Trautmann A, Roebuck DJ, McLaren CA et al (2016) Non-invasive imaging cannot replace formal angiography in the diagnosis of renovascular hypertension. Pediatr Nephrol 32:495–502
American College of Radiology (2013) ACR–AIUM–SPR–SRU practice parameter for the performance of native renal artery duplex sonography. http://www.acr.org/~/media/70460ec59008432aa63c0ee9a4960498.pdf. Accessed 2 November 2016
Li JC, Wang L, Jiang YX et al (2006) Evaluation of renal artery stenosis with velocity parameters of Doppler sonography. J Ultrasound Med 25:735–742
Castelli PK, Dillman JR, Kershaw DB et al (2014) Renal sonography with Doppler for detecting suspected pediatric renin-mediated hypertension — is it adequate? Pediatr Radiol 44:42–49
Ozbek SS, Aytaç SK, Erden MI et al (1993) Intrarenal Doppler findings of upstream renal artery stenosis: a preliminary report. Ultrasound Med Biol 19:3–12
Miralles M, Cairols M, Cotillas J et al (1996) Value of Doppler parameters in the diagnosis of renal artery stenosis. J Vasc Surg 23:428–435
Riehl J, Fritz A, Sieberth HG (1997) The use of duplex sonography in the diagnosis of renal artery stenosis. Eur J Med Res 2:14–22
Stavros AT, Parker SH, Yakes WF et al (1992) Segmental stenosis of the renal artery: pattern recognition of tardus and parvus abnormalities with duplex sonography. Radiology 184:487–492
House MK, Dowling RJ, King P et al (1999) Using Doppler sonography to reveal renal artery stenosis: an evaluation of optimal imaging parameters. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:761–765
Granata A, Fiorini F, Andrulli S et al (2009) Doppler ultrasound and renal artery stenosis: an overview. J Ultrasound 12:133–143
Li JC, Jiang YX, Zhang SY et al (2008) Evaluation of renal artery stenosis with hemodynamic parameters of Doppler sonography. J Vasc Surg 48:323–328
Stein MW, Koenigsberg M, Grigoropoulos J et al (2002) Aortic coarctation diagnosed in a hypertensive child undergoing Doppler sonography for suspected renal artery stenosis. Pediatr Radiol 32:384–386
Chhadia S, Cohn RA, Vural G et al (2013) Renal Doppler evaluation in the child with hypertension: a reasonable screening discriminator? Pediatr Radiol 43:1549–1556
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no financial interests, investigational or off-label uses to disclose. Dr. Dillman has unrelated ultrasound research funding from Toshiba America Medical Systems and Siemens Healthineers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dillman, J.R., Smith, E.A. & Coley, B.D. Ultrasound imaging of renin-mediated hypertension. Pediatr Radiol 47, 1116–1124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-3840-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-3840-y