Abstract
Background
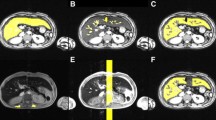
Serial surveillance of liver iron concentration (LIC) provides guidance for chelation therapy in patients with iron overload. The diagnosis of iron overload traditionally relies on core liver biopsy, which is limited by invasiveness, sampling error, cost and general poor acceptance by pediatric patients and parents. Thus noninvasive diagnostic methods such as MRI are highly attractive for quantification of liver iron concentration.
Objective
To compare two MRI-based methods for liver iron quantification in children.
Materials and methods
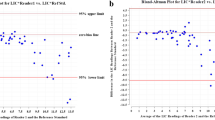
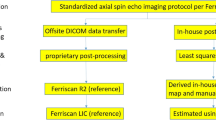
64 studies on 48 children and young adults (age range 4–21 years) were examined by gradient recalled echo (GRE) R2* and spin-echo R2 MRI at 1.5T to evaluate liver iron concentration. Scatter plots and Bland–Altman difference plots were generated to display and assess the relationship between the methods.
Results
With the protocols used in this investigation, Bland–Altman agreement between the methods is best when LIC is <20 mg/g dry tissue. Scatter plots show that all values with LIC <20 mg/g dry tissue fall within the 95% prediction limits.
Conclusion
Liver iron concentration as determined by the R2* and R2 MR methods is statistically comparable, with no statistical difference between these methods for LIC <20 mg/g.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lieu PT, Heiskala M, Peterson PA et al (2001) The roles of iron in health and disease. Mol Aspects Med 22:1–87
Towbin AJ, Serai SD, Podberesky DJ (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging of the pediatric liver: imaging of steatosis, iron deposition, and fibrosis. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 21:669–680
Brown K, Subramony C, May W et al (2009) Hepatic iron overload in children with sickle cell anemia on chronic transfusion therapy. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 31:309–312
Jensen PD, Jensen FT, Christensen T et al (2003) Relationship between hepatocellular injury and transfusional iron overload prior to and during iron chelation with desferrioxamine: a study in adult patients with acquired anemias. Blood 101:91–96
Perifanis V, Tziomalos K, Tsatra I et al (2005) Prevalence and severity of liver disease in patients with b thalassemia major. A single-institution fifteen-year experience. Haematologica 90:1136–1138
Crownover BK, Covey CJ (2013) Hereditary hemochromatosis. Am Fam Physician 87:183–190
Powell LW (2002) Diagnosis of hemochromatosis. Semin Gastrointest Dis 13:80–88
Brittenham GM, Badman DG (2003) Noninvasive measurement of iron: report of an NIDDK workshop. Blood 101:15–19
Mazza P, Giua R, De Marco S et al (1995) Iron overload in thalassemia: comparative analysis of magnetic resonance imaging, serum ferritin and iron content of the liver. Haematologica 80:398–404
Ware HM, Kwiatkowski JL (2013) Evaluation and treatment of transfusional iron overload in children. Pediatr Clin North Am 60:1393–1406
Zhou HB (2014) Hemobilia and other complications caused by percutaneous ultrasound-guided liver biopsy. World J Gastroenterol 20:3712–3715
Castera L, Pinzani M (2010) Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: does it take two to tango? Gut 59:861–866
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ et al (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97:2614–2618
Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A et al (2005) Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 128:1898–1906
Xanthakos SA, Podberesky DJ, Serai SD et al (2014) Use of magnetic resonance elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in children with chronic liver disease. J Pediatr 164:186–188
Serai SD, Towbin AJ, Podberesky DJ (2012) Pediatric liver MR elastography. Dig Dis Sci 57:2713–2719
Kim HK, Lindquist DM, Serai SD et al (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging of pediatric muscular disorders: recent advances and clinical applications. Radiol Clin North Am 51:721–742
Serai SD, Wallihan DB, Venkatesh SK et al (2014) Magnetic resonance elastography of the liver in patients status-post fontan procedure: feasibility and preliminary results. Congenit Heart Dis 9:7–14
Wallihan DB, Podberesky DJ, Marino BS et al (2013) Relationship of MR elastography determined liver stiffness with cardiac function after Fontan palliation. J Magn Reson Imaging J Magn Reson Imaging 40:1328–1335
Hankins JS, McCarville MB, Loeffler RB et al (2009) R2* magnetic resonance imaging of the liver in patients with iron overload. Blood 113:4853–4855
Hernando D, Levin YS, Sirlin CB et al (2014) Quantification of liver iron with MRI: State of the art and remaining challenges. J Magn Reson Imaging J Magn Reson Imaging 40:1003–1021
St. Pierre TG, Clark PR, Chua-anusorn W et al (2005) Noninvasive measurement and imaging of liver iron concentrations using proton magnetic resonance. Blood 105:855–861
Wood JC, Enriquez C, Ghugre N et al (2005) MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients. Blood 106:1460–1465
Cheng HL, Holowka S, Moineddin R et al (2012) Liver iron overload assessment by T *2 magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric patients: an accuracy and reproducibility study. Am J Hematol 87:435–437
St. Pierre TG, Clark PR, Chua-Anusorn W (2005) Measurement and mapping of liver iron concentrations using magnetic resonance imaging. Ann NY Acad Sci 1054:379–385
Bassett ML, Halliday JW, Powell LW (1986) Value of hepatic iron measurements in early hemochromatosis and determination of the critical iron level associated with fibrosis. Hepatology 6:24–29
Lambing A, Kachalsky E, Mueller ML (2012) The dangers of iron overload: bring in the iron police. J Am Acad Nurse Pract 24:175–183
Shander A, Sazama K (2010) Clinical consequences of iron overload from chronic red blood cell transfusions, its diagnosis, and its management by chelation therapy. Transfusion 50:1144–1155
Hoffbrand AV, Taher A, Cappellini MD (2012) How I treat transfusional iron overload. Blood 120:3657–3669
Wood JC (2014) Use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Monitor Iron Overload. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 28:747–764
Robson MD, Gatehouse PD, Bydder M et al (2003) Magnetic resonance: an introduction to ultrashort TE (UTE) imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27:825–846
Serai SD, Laor T, Dwek JR et al (2014) Feasibility of ultrashort TE (UTE) imaging of children at 1.5 T. Pediatr Radiol 44:103–108
Conflicts of interest
Dr. D. J. Podberesky receives travel reimbursement from Philips Healthcare and GE Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serai, S.D., Fleck, R.J., Quinn, C.T. et al. Retrospective comparison of gradient recalled echo R2* and spin-echo R2 magnetic resonance analysis methods for estimating liver iron content in children and adolescents. Pediatr Radiol 45, 1629–1634 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-015-3378-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-015-3378-9