Abstract
Background
Renal Doppler US is used to evaluate suspected vascular causes of hypertension in children, despite mostly unknown diagnostic performance characteristics.
Objective
To evaluate renal Doppler US for detecting vascular causes of hypertension in children with high clinical suspicion of aortic or renal artery narrowing.
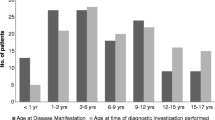
Materials and methods
We identified pediatric renal Doppler US examinations performed for hypertension between January 1995 and June 2010 at our institution. We excluded children without follow-up angiography (CT-, MR-, or catheter-based). Two pediatric radiologists reviewed imaging studies and documented relevant findings. Intrarenal spectral Doppler resistive index measurement <0.5 or tardus parvus waveform constituted a positive examination.
Results
Thirty-five boys and 13 girls underwent renal Doppler US and confirmatory imaging (mean age = 9.0 years). Nineteen US examinations were truly negative, two were falsely negative, 18 were truly positive (16 involved narrowing of the aorta or main renal artery) and nine were falsely positive. Sonography had a sensitivity and specificity of 90% and 68%, respectively, for detecting a vascular cause of hypertension.
Conclusion
Renal Doppler sonography reliably detects renin-mediated hypertension caused by aortic or main renal artery narrowing in children. More studies are needed to determine its ability to detect intrarenal and accessory renal artery stenoses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitsnefes MM (2006) Hypertension in children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am 53:493–512
Wyszynska T, Cichocka E, Wieteska-Klimczak A et al (1992) A single pediatric center experience with 1,025 children with hypertension. Acta Paediatr 81:244–246
Gomes RS, Quirino IG, Pereira RM et al (2011) Primary versus secondary hypertension in children followed up at an outpatient tertiary unit. Pediatr Nephrol 26:441–447
Kim HJ, Son JS, Kim KS (2011) A case of renal artery stenosis in a child confirmed by multidetector computed tomographic angiography. Pediatr Cardiol 32:702–703
Tullus K, Brennan E, Hamilton G et al (2008) Renovascular hypertension in children. Lancet 371:1453–1463
Srinivasan A, Krishnamurthy G, Fontalvo-Herazo L et al (2010) Angioplasty for renal artery stenosis in pediatric patients: an 11-year retrospective experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:1672–1680
Srinivasan A, Krishnamurthy G, Fontalvo-Herazo L et al (2011) Spectrum of renal findings in pediatric fibromuscular dysplasia and neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatr Radiol 41:308–316
Stanley JC, Criado E, Upchurch GR Jr et al (2006) Pediatric renovascular hypertension: 132 primary and 30 secondary operations in 97 children. J Vasc Surg 44:1219–1228
Devaney K, Kapur SP, Patterson K et al (1991) Pediatric renal artery dysplasia: a morphologic study. Pediatr Pathol 11:609–621
Vo NJ, Hammelman BD, Racadio JM et al (2006) Anatomic distribution of renal artery stenosis in children: implications for imaging. Pediatr Radiol 36:1032–1036
Tullus K, Roebuck DJ, McLaren CA et al (2010) Imaging in the evaluation of renovascular disease. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1049–1056
Soulez G, Olivia VL, Turpin S et al (2000) Imaging of renovascular hypertension: respective values of renal scintigraphy, renal Doppler US, and MR angiography. Radiographics 20:1355–1368
Castelli PK, Dillman JR, Smith EA et al (2013) Imaging of renin-mediated hypertension in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 200:W661–W672
Coley BD (2004) Pediatric applications of abdominal vascular Doppler: part II. Pediatr Radiol 34:772–786
Roth CG, Spottswood SE, Chan JC et al (2003) Evaluation of the hypertensive infant: a rational approach to diagnosis. Radiol Clin North Am 41:931–944
Garel L, Dubois J, Robitaille P et al (1995) Renovascular hypertension in children: curability predicted with negative intrarenal Doppler US results. Radiology 195:401–405
Desberg AL, Paushter DM, Lammert GK et al (1990) Renal artery stenosis: evaluation with color Doppler flow imaging. Radiology 177:749–753
Baxter GM, Aitchison F, Sheppard D et al (1996) Colour Doppler ultrasound in renal artery stenosis: intrarenal waveform analysis. Br J Radiol 69:810–815
Postma CT, van Aalen J, de Boo T et al (1992) Doppler ultrasound scanning in the detection of renal artery stenosis in hypertensive patients. Br J Radiol 65:857–860
Li JC, Wang L, Jiang YX et al (2006) Evaluation of renal artery stenosis with velocity parameters of Doppler sonography. J Ultrasound Med 25:735–742
Stavros AT, Parker SH, Yakes WF et al (1992) Segmental stenosis of the renal artery: pattern recognition of tardus and parvus abnormalities with duplex sonography. Radiology 184:487–492
Eklof H, Ahlstrom H, Magnusson A et al (2006) A prospective comparison of duplex ultrasonography, captopril renography, MRA, and CTA in assessing renal artery stenosis. Acta Radiol 47:764–774
Rountas C, Vlychou M, Vassiou K et al (2007) Imaging modalities for renal artery stenosis in suspected renovascular hypertension: prospective intraindividual comparison of color Doppler US, CT angiography, GD-enhanced MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. Ren Fail 29:295–302
Brun P, Kchouk H, Mouchet B et al (1997) Value of Doppler ultrasound for the diagnosis of renal artery stenosis in children. Pediatr Nephrol 11:27–30
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castelli, P.K., Dillman, J.R., Kershaw, D.B. et al. Renal sonography with Doppler for detecting suspected pediatric renin-mediated hypertension – is it adequate?. Pediatr Radiol 44, 42–49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2785-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2785-z