Abstract
Background
Normal intrauterine conditions are essential to normal brain growth and development; premature birth and growth restriction can interrupt brain maturation. Maturation processes can be studied using diffusion tensor imaging.
Objective
The aim of this study was to use tract-based spatial statistics to assess the effect that early postnatal growth from birth to 40 gestational weeks has on brain white matter maturation.
Materials and methods
A total of 36 preterm infants were accepted in the study. Postnatal growth was assessed by weight, length and head circumference. Birth weight z-score and gestational age were used as confounding covariates.
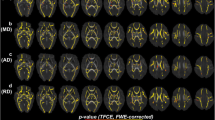
Results
Head circumference catch-up growth was associated with less mature diffusion parameters (P < 0.05). No significant associations were observed between weight or length growth and diffusion parameters.
Conclusion
Growth-restricted infants seem to have delayed brain maturation that is not fully compensated at term, despite catch-up growth.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volpe JJ (2000) Overview: normal and abnormal human brain development. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 6:1–5
Bonifacio SL, Glass HC, Chau V et al (2010) Extreme premature birth is not associated with impaired development of brain microstructure. J Pediatr 157:726–732
Ment LR, Hirtz D, Huppi PS (2009) Imaging biomarkers of outcome in the developing preterm brain. Lancet Neurol 8:1042–1055
Morsing E, Asard M, Ley D et al (2011) Cognitive function after intrauterine growth restriction and very preterm birth. Pediatrics 127:E874–E882
Guellec I, Lapillonne A, Renolleau S et al (2011) Neurologic outcomes at school age in very preterm infants born with severe or mild growth restriction. Pediatrics 127:E883–E891
Maunu J, Kirjavainen J, Korja R et al (2006) Relation of prematurity and brain injury to crying behavior in infancy. Pediatrics 118:E57–E65
Leppanen M, Ekholm E, Palo P et al (2010) Abnormal antenatal Doppler velocimetry and cognitive outcome in very-low-birth-weight infants at 2 years of age. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 36:178–185
Ehrenkranz RA, Dusick AM, Vohr BR et al (2006) Growth in the neonatal intensive care unit influences neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 117:1253–1261
Belfort MB, Rifas-Shiman SL, Sullivan T et al (2011) Infant growth before and after term: effects on neurodevelopment in preterm infants. Pediatrics 128:E899–E906
Franz AR, Pohlandt F, Bode H et al (2009) Intrauterine, early neonatal, and postdischarge growth and neurodevelopmental outcome at 5.4 years in extremely preterm infants after intensive neonatal nutritional support. Pediatrics 123:E101–E109
Cooke RW (2006) Are there critical periods for brain growth in children born preterm? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 91:F17–F20
Anjari M, Srinivasan L, Allsop JM et al (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging with tract-based spatial statistics reveals local white matter abnormalities in preterm infants. NeuroImage 35:1021–1027
Lepomaki VK, Paavilainen TP, Hurme SA et al (2012) Fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity parameters of the brain white matter tracts in preterm infants: reproducibility of region-of-interest measurements. Pediatr Radiol 42:175–182
Lepomaki V, Paavilainen T, Matomaki J et al (2012) Effect of antenatal growth and prematurity on brain white matter: diffusion tensor study. Pediatr Radiol 42:692–698
Pannek K, Guzzetta A, Colditz PB et al (2012) Diffusion MRI of the neonate brain: acquisition, processing and analysis techniques. Pediatr Radiol 42:1169–1182
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Neil J, Miller J, Mukherjee P et al (2002) Diffusion tensor imaging of normal and injured developing human brain—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:543–552
Mori S, Zhang JY (2006) Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its applications to basic neuroscience research. Neuron 51:527–539
Mukherjee P, Miller JH, Shimony JS et al (2002) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging of gray and white matter development during normal human brain maturation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1445–1456
Berman JI, Mukherjee P, Partridge SC et al (2005) Quantitative diffusion tensor MRI fiber tractography of sensorimotor white matter development in premature infants. NeuroImage 27:862–871
Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D et al (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging assessment of brain white matter maturation during the first postnatal year. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:476–486
Saksena S, Husain N, Malik GK et al (2008) Comparative evaluation of the cerebral and cerebellar white matter development in pediatric age group using quantitative diffusion tensor imaging. Cerebellum 7:392–400
Van Kooij BJ, de Vries LS, Ball G et al (2012) Neonatal tract-based spatial statistics findings and outcome in preterm infants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:188–194
Partridge SC, Mukherjee P, Henry RG et al (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns. NeuroImage 22:1302–1314
Suzuki Y, Matsuzawa H, Kwee IL et al (2003) Absolute eigenvalue diffusion tensor analysis for human brain maturation. NMR Biomed 16:257–260
Thompson DK, Inder TE, Faggian N et al (2011) Characterization of the corpus callosum in very preterm and full-term infants utilizing MRI. NeuroImage 55:479–490
Lepomäki V, Matomaki J, Lapinleimu H et al (2013) Effect of antenatal growth on brain white matter maturation in preterm infants at term using tract-based spatial statistics. Pediatr Radiol 43:80–85
Pihkala J, Hakala T, Voutilainen P et al (1989) Characteristic of recent fetal growth curves in Finland. Duodecim 105:1540–1546
Sorva R, Tolppanen EM, Perheentupa J (1990) Variation of growth in length and weight of children.1. Years 1 and 2. Acta Paediatr Scand 79:490–497
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW et al (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage 23:S208–S219
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17:143–155
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage 31:1487–1505
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage 44:83–98
Lundgren EM, Cnattingius S, Jonsson B et al (2001) Intellectual and psychological performance in males born small for gestational age with and without catch-up growth. Pediatr Res 50:91–96
Maunu J, Ekholm E, Parkkola R et al (2007) Antenatal Doppler measurements and early brain injury in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 150:51–56
Lundgren EM, Tuvemo T (2008) Effects of being born small for gestational age on long-term intellectual performance. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 22:477–488
Mallard C, Loeliger M, Copolov D et al (2000) Reduced number of neurons in the hippocampus and the cerebellum in the postnatal guinea-pig following intrauterine growth-restriction. Neuroscience 100:327–333
Frisk V, Amsel R, Whyte HEA (2002) The importance of head growth patterns in predicting the cognitive abilities and literacy skills of small-for-gestational-age children. Dev Neuropsychol 22:565–593
Ramenghi LA, Martinelli A, De Carli A et al (2011) Cerebral maturation in IUGR and appropriate for gestational age preterm babies. Reprod Sci 18:469–475
Hudspeth WJ, Pribram KH (1990) Stages of brain and cognitive maturation. J Educ Psychol 82:881–884
Ozdemir OM, Ergin H, Sahiner T (2009) Electrophysiological assessment of the brain function in term SGA infants. Brain Res 1270:33–38
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepomäki, V., Leppänen, M., Matomäki, J. et al. Preterm infants’ early growth and brain white matter maturation at term age. Pediatr Radiol 43, 1357–1364 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2699-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-013-2699-9