Abstract
Background
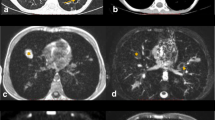
Maximum intensity projection (MIP) images might be useful in helping to differentiate small pulmonary nodules from adjacent vessels on thoracic multidetector CT (MDCT).
Objective
The aim was to evaluate the benefits of axial MIP images over axial source images for the paediatric chest in an interobserver variability study.
Materials and methods
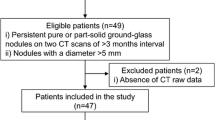
We included 46 children with extra-pulmonary solid organ malignancy who had undergone thoracic MDCT. Three radiologists independently read 2-mm axial and 10-mm MIP image datasets, recording the number of nodules, size and location, overall time taken and confidence.
Results
There were 83 nodules (249 total reads among three readers) in 46 children (mean age 10.4 ± 4.98 years, range 0.3–15.9 years; 24 boys). Consensus read was used as the reference standard. Overall, three readers recorded significantly more nodules on MIP images (228 vs. 174; P < 0.05), improving sensitivity from 67% to 77.5% (P < 0.05) but with lower positive predictive value (96% vs. 85%, P < 0.005). MIP images took significantly less time to read (71.6 ± 43.7 s vs. 92.9 ± 48.7 s; P < 0.005) but did not improve confidence levels.
Conclusion
Using 10-mm axial MIP images for nodule detection in the paediatric chest enhances diagnostic performance, improving sensitivity and reducing reading time when compared with conventional axial thin-slice images. Axial MIP and axial source images are complementary in thoracic nodule detection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankier A, McMahon H, Naidich D (2012) Pulmonary nodules. Radiol Select 1:7–9. http://www2.rsna.org/timssnet/radiologyselect/PulmonaryNodules.cfm. Accessed June 2012
Rubin GD, Lyo JK, Paik DS et al (2005) Pulmonary nodules on multi-detector row CT scans: performance comparison of radiologists and computer-aided detection. Radiology 234:274–283
Peloschek P, Sailer J, Weber M et al (2007) Pulmonary nodules: sensitivity of maximum intensity projection versus that of volume rendering of 3D multidetector CT data. Radiology 243:561–569
Punwani S, Zhang J, Davies W et al (2008) Paediatric CT: the effects of increasing image noise on pulmonary nodule detection. Pediatr Radiol 38:192–201
Li X, Samei E, Barnhart HX et al (2011) Lung nodule detection in pediatric chest CT: quantitative relationship between image quality and radiologist performance. Med Phys 38:2609–2618
Fischbach F, Knollmann F, Griesshaber V et al (2003) Detection of pulmonary nodules by multislice computed tomography: improved detection rate with reduced slice thickness. Eur Radiol 13:2378–2383
Paranjpe DV, Bergin CJ (1994) Spiral CT of the lungs: optimal technique and resolution compared with conventional CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:561–567
Gruden JF, Ouanounou S, Tigges S et al (2002) Incremental benefit of maximum-intensity-projection images on observer detection of small pulmonary nodules revealed by multidetector CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:149–157
Valencia R, Denecke T, Lehmkuhl L et al (2006) Value of axial and coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP) images in the detection of pulmonary nodules by multislice spiral CT: comparison with axial 1-mm and 5-mm slices. Eur Radiol 16:325–332
Jankowski A, Martinelli T, Timsit JF et al (2007) Pulmonary nodule detection on MDCT images: evaluation of diagnostic performance using thin axial images, maximum intensity projections, and computer-assisted detection. Eur Radiol 17:3148–3156
Diederich S, Lentschig MG, Overbeck TR et al (2001) Detection of pulmonary nodules at spiral CT: comparison of maximum intensity projection sliding slabs and single-image reporting. Eur Radiol 11:1345–1350
Kawel N, Seifer B, Luetolf M et al (2009) Effect of slab thickness on the CT detection of pulmonary nodules: use of sliding thin-slab maximum intensity projection and volume rendering. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:1324–1329
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
McCarville MB, Lederman HM, Kaufman RA et al (2006) Distinguishing benign from malignant pulmonary nodules with helical chest CT in children with malignant solid tumors. Radiology 239:514–520
Smets AM, van Tinteren H, Bergeron C et al (2012) The contribution of chest CT-scan at diagnosic in children with unilateral Wilms’ tumour. Results of the SIOP 2001 study. Eur J Cancer 48:1060–1065
Coakley F, Cohen MD, Johnson MS et al (1998) Maximum intensity projection images in the detection of simulated pulmonary nodules by spiral CT. Br J Radiol 71:135–140
Silva CT, Amaral JG, Moineddin R et al (2010) CT characteristics of lung nodules present at diagnosis of extrapulmonary malignancy in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:772–778
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Addenbrooke’s Charitable Trust and the NIHR comprehensive Biomedical Research Centre award to Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust in partnership with the University of Cambridge. Preliminary data from 11 children in this study were presented in oral format at RSNA 2011 (Abstract ID 11009689)
Funding
None
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilburn-Toppin, F., Arthurs, O.J., Tasker, A.D. et al. Detection of pulmonary nodules at paediatric CT: maximum intensity projections and axial source images are complementary. Pediatr Radiol 43, 820–826 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2597-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2597-6