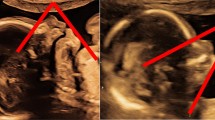
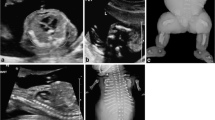
Abstract
Background
Prenatal ultrasonographic (US) diagnosis of cloacal exstrophy (CE) is challenging.
Objective
To define the fetal MRI findings in CE.
Materials and methods
We performed a retrospective review of eight patients with CE. Imaging was performed between 22 weeks and 36 weeks of gestation with US in four and MRI in eight fetuses. Abdominal wall, gastrointestinal/genitourinary, and spine and limb abnormalities detected were compared with postnatal evaluation.
Results
US failed to display CE in one of the four fetuses. Fetal MRI confirmed CE in all eight fetuses by demonstrating absence of a normal bladder and lack of meconium-filled rectum/colon, associated with protuberant pelvic contour and omphalocele. These findings correlated postnatally with CE, atretic hindgut and omphalocele. One fetus had imaging before rupture of the cloacal membrane, showing a protruding pelvic cyst. Absent bladder was noted in the remaining seven fetuses. Confirmed skin-covered spinal defects were noted in seven fetuses, low conus/tethered cord in one and clubfoot in three. Six fetuses had renal anomalies, two had hydrocolpos and one had ambiguous genitalia.
Conclusion
Fetal MRI provides a confident diagnosis of CE when a normal bladder is not identified, there is a protuberant abdominopelvic contour and there is absence of meconium-filled rectum and colon. Genitourinary and spinal malformations are common associations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hendren WH (1996) Urogenital sinus and cloacal malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg 5:72–79
Carey JC, Greenbaum B, Hall BD (1978) The OEIS complex (omphalocele, exstrophy, imperforate anus, spinal defects). Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 14:253–263
Martinez-Frias ML, Bermejo E, Rodriguez-Pinilla E et al (2001) Exstrophy of the cloaca and exstrophy of the bladder: two different expressions of a primary developmental field defect. Am J Med Genet 99:261–269
Ebert AK, Reutter H, Ludwig M et al (2009) The exstrophy-epispadias complex. Orphanet J Rare Dis 4:23
Bohring A (2002) OEIS complex, VATER, and the ongoing difficulties in terminology and delineation. Am J Med Genet 107:72–76
Carey JC (2001) Exstrophy of the cloaca and the OEIS complex: one and the same. Am J Med Genet 99:270
Austin PF, Homsy YL, Gearhart JP et al (1998) The prenatal diagnosis of cloacal exstrophy. J Urol 160:1179–1181
Wu JL, Fang KH, Yeh GP et al (2004) Using color Doppler sonography to identify the perivesical umbilical arteries: a useful method in the prenatal diagnosis of omphalocele-exstrophy-imperforate anus-spinal defects complex. J Ultrasound Med 23:1211–1215
Gobbi D, Fascetti Leon F, Tregnaghi A et al (2008) Early prenatal diagnosis of cloacal exstrophy with fetal magnetic resonance imaging. Fetal Diagn Ther 24:437–439
Caire JT, Ramus RM, Magee KP et al (2003) MRI of fetal genitourinary anomalies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:1381–1385
Chauvin NA, Epelman M, Victoria T et al (2012) Complex genitourinary abnormalities on fetal MRI: imaging findings and approach to diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:W222–W231
Chen CP, Chang TY, Liu YP et al (2008) Prenatal 3-dimensional sonographic and MRI findings in omphalocele-exstrophy-imperforate anus-spinal defects complex. J Clin Ultrasound 36:308–311
Chen CP (2007) Syndromes and disorders associated with omphalocele (II): OEIS complex and Pentalogy of Cantrell. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 46:103–110
Phillips TM (2011) Spectrum of cloacal exstrophy. Semin Pediatr Surg 20:113–118
Pinette MG, Pan YQ, Pinette SG et al (1996) Prenatal diagnosis of fetal bladder and cloacal exstrophy by ultrasound. A report of three cases. J Reprod Med 41:132–134
Gearhart JP, Ben-Chaim J, Jeffs RD et al (1995) Criteria for the prenatal diagnosis of classic bladder exstrophy. Obstet Gynecol 85:961–964
Yiee J, Wilcox D (2008) Abnormalities of the fetal bladder. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 13:164–170
Wilcox DT, Chitty LS (2001) Non-visualisations of the fetal bladder: aetiology and management. Prenat Diagn 21:977–983
Langer JC, Brennan B, Lappalainen RE et al (1992) Cloacal exstrophy: prenatal diagnosis before rupture of the cloacal membrane. J Pediatr Surg 27:1352–1355
Emanuel PG, Garcia GI, Angtuaco TL (1995) Prenatal detection of anterior abdominal wall defects with US. Radiographics 15:517–530
Chen CP (2008) Syndromes, disorders and maternal risk factors associated with neural tube defects (III). Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 47:131–140
Carr MC, Benacerraf BR, Mandell J (1994) Prenatal diagnosis of an XY fetus with aphallia and cloacal exstrophy variant. J Ultrasound Med 13:323–325
Soffer SZ, Rosen NG, Hong AR et al (2000) Cloacal exstrophy: a unified management plan. J Pediatr Surg 35:932–937
Marvin T (2007) Cloacal exstrophy: a case study. Neonatal Netw 26:21–30
Tiblad E, Wilson RD, Carr M et al (2008) OEIS sequence – a rare congenital anomaly with prenatal evaluation and postnatal outcome in six cases. Prenat Diagn 28:141–147
Hamada H, Takano K, Shiina H et al (1999) New ultrasonographic criterion for the prenatal diagnosis of cloacal exstrophy: elephant trunk-like image. J Urol 162:2123–2124
Richards DS, Langham MR Jr, Mahaffey SM (1992) The prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of cloacal exstrophy. J Ultrasound Med 11:507–510
Keppler-Noreuil K, Gorton S, Foo F et al (2007) Prenatal ascertainment of OEIS complex/cloacal exstrophy – 15 new cases and literature review. Am J Med Genet A 143A:2122–2128
Kutzner DK, Wilson WG, Hogge WA (1988) OEIS complex (cloacal exstrophy): prenatal diagnosis in the second trimester. Prenat Diagn 8:247–253
Hyun SJ (2006) Cloacal exstrophy. Neonatal Netw 25:101–115
Saguintaah M, Couture A, Veyrac C et al (2002) MRI of the fetal gastrointestinal tract. Pediatr Radiol 32:395–404
Brugger PC, Prayer D (2006) Fetal abdominal magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol 57:278–293
Hsieh K, O’Loughlin MT, Ferrer FA (2005) Bladder exstrophy and phenotypic gender determination on fetal magnetic resonance imaging. Urology 65:998–999
Calvo-Garcia MA, Kline-Fath BM, Levitt MA et al (2011) Fetal MRI clues to diagnose cloacal malformations. Pediatr Radiol 41:1117–1128
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calvo-Garcia, M.A., Kline-Fath, B.M., Rubio, E.I. et al. Fetal MRI of cloacal exstrophy. Pediatr Radiol 43, 593–604 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2571-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2571-3