Abstract
Background
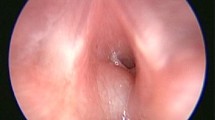
Subglottic haemangioma causes progressive and life-threatening stridor, typically manifesting at age 2–3 months. Standard diagnosis is by laryngoscopy. Larynx sonography is rarely used but allows assessment of the presence and extension of a mass that impinges on the subglottic airway. The additional use of colour Doppler enables demonstration of the vascular nature of such masses.
Objective
To compare US and endoscopic findings in infants with subglottic haemangioma and to evaluate accuracy of US and colour Doppler imaging in this diagnosis.
Materials and methods
We report eight infants with subglottic haemangioma seen in our institution over the last decade. They presented with laryngeal stridor and were all investigated with both US and endoscopy. Six infants underwent colour Doppler sonography.
Results
US and endoscopic findings showed excellent anatomical correlation in lateral subglottic haemangioma. Colour Doppler imaging was deemed helpful in four infants.
Conclusion
Larynx sonography with complementary colour Doppler imaging was non-invasive and helpful in the diagnosis of subglottic haemangioma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silverman RA (1991) Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Pediatr Clin North Am 38:811–834
Denoyelle F (1996) Angiome sous-glottique et trachéal du nourrisson. In: Garabédian EN, Bobin S, Monteil JP, Triglia JM (eds) ORL de l’enfant: pathologie de l’oreille. Flammarion, Paris, pp 205–208
Altman KW, Wetmore RF, Marsh RR (1999) Congenital airway abnormalities in patients requiring hospitalization. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:525–528
Narcy P, Bobin S, Contencin P et al (1984) Laryngeal anomalies in newborn infants. Apropos of 687 cases. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 101:363–373
Fan HC, Hung CH, Juan CJ et al (2000) Subglottic hemangioma associated with cutaneous and cerebellar hemangiomas detected by MRI: report of one case. Acta Paediatr Taiwan 41:214–217
Buzenet C, Hamel-Teillac D, Acar P et al (2000) Facial hemangioma associated with arterial anomalies, coarctation of the aorta, and eye abnormalities: PHACES syndrome. Ann Dermatol Venereol 127:292–295
Choa DI, Smith MC, Evans JN et al (1986) Subglottic haemangioma in children. J Laryngol Otol 100:447–454
Royal SA (2000) Pediatric laryngeal granular cell tumor. Pediatr Radiol 30:869–870
Riding K (1992) Subglottic hemangioma: a practical approach. J Otolaryngol 21:419–421
Mancuso RF (1996) Stridor in neonates. Pediatr Clin North Am 43:1339–1356
Garel C (2002) Ultrasonography of the larynx. In: King SJ, Boothroyd AE (eds) Pediatric ENT radiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 345–350
Garel C, Hassan M, Legrand I et al (1991) Laryngeal ultrasonography in infants and children: pathological findings. Pediatr Radiol 21:164–167
Agada FO, Bell J, Knight L (2006) Subglottic cysts in children: a 10-year review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70:1485–1488
Chetty A, Mischler E, Gregg D (1997) Diagnosis of subglottic hemangioma by chest CT. Pediatr Pulmonol 23:464–467
Liu P, Daneman A (1984) Computed tomography of intrinsic laryngeal and tracheal abnormalities in children. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8:662–669
Triglia JM, Nazarian B, Sudre-Levillain I et al (2002) Virtual laryngotracheal endoscopy based on geometric surface modeling using spiral computed tomography data. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 111:36–43
Frey EE, Smith WL, Grandgeorge S et al (1987) Chronic airway obstruction in children: evaluation with cine-CT. AJR 148:347–352
Nozawa K, Aihara T, Takano H (1995) MR imaging of a subglottic hemangioma. Pediatr Radiol 25:235–236
Leaute-Labreze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T et al (2008) Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med 358:2649–2651
Jephson CG, Manunza F, Syed S et al (2009) Successful treatment of isolated subglottic haemangioma with propranolol alone. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1821–1823
Denoyelle F, Leboulanger N, Enjolras O et al (2009) Role of Propranolol in the therapeutic strategy of infantile laryngotracheal hemangioma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1168–1172
Buckmiller L, Dyamenahalli U, Richter GT (2009) Propranolol for airway hemangiomas: case report of novel treatment. Laryngoscope 119:2051–2054
Leboulanger N, Fayoux P, Teissier N et al (2010) Propranolol in the therapeutic strategy of infantile laryngotracheal hemangioma: a preliminary retrospective study of French experience. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:1254–1257
Peridis S, Pilgrim G, Athanasopoulos I et al (2011) A meta-analysis on the effectiveness of propranolol for the treatment of infantile airway hemangiomas. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:455–460
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mrs. Greifenberg and Mr. Müller (photo laboratory, St. Josef-Hospital, Bochum) for their great help in processing of the images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossler, L., Rothoeft, T., Teig, N. et al. Ultrasound and colour Doppler in infantile subglottic haemangioma. Pediatr Radiol 41, 1421–1428 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2213-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2213-1