Abstract
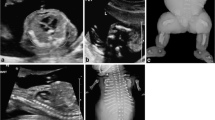
Skeletal dysplasias are a heterogeneous and complex group of conditions that affect bone growth and development and result in various anomalies in shape and size of the skeleton. Although US has proved reliable for the prenatal detection of skeletal abnormalities, the precise diagnosis of a dysplasia is often difficult to make before birth (especially in the absence of a familial history) due to their various phenotypic presentations, the variability in the time at which they manifest and often, the lack of precise molecular diagnosis. In addition to the accuracy of the antenatal diagnosis, it is very important to establish a prognosis. This is a clinically relevant issue as skeletal dysplasias may be associated with severe disability and may even be lethal. We will therefore describe the respective role of two-dimensional (2-D) US, three-dimensional (3-D) US and CT in the antenatal assessment of skeletal malformations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Working Group on Constitutional Diseases of Bone (1997) International nomenclature and classification of the osteochondrodysplasias. Am J Med Genet 79:376–382
Doray B, Favre R, Viville B et al (2000) Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of skeletal dysplasis. A report of 47 cases. Ann Genet 43:163–169
Garjian KV, Pretorius DH, Budorick NE et al (2000) Fetal skeletal dyplasia: three dimensional US—initial experience. Radiology 214:717–723
Krakow D, Williams J 3rd, Poehl M et al (2003) Use of three-dimensional ultrasound imaging in the diagnosis of prenatal onset skeletal dysplasias. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 21:467–472
Ruano R, Molho M, Roume J et al (2004) Prenatal diagnosis of fetal skeletal dysplasias by combining two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasound and intrauterine three-dimensional helical computer tomography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 24:134–140
Dighe M, Fligner C, Cheng E et al (2008) Fetal skeletal dysplasia: an approach to diagnosis with illustrative cases. Radiographics 28:1061–1077
Lachman RS (1994) Fetal imaging in the skeletal dysplasia: overview and experience. Pediatr Radiol 24:413–417
Nimrod C, Davies D, Iwanicki S et al (1986) Ultrasound prediction of pulmonary hypoplasia. Obstet Gynecol 68:495–498
Songster GS, Gray DI, Crane JP (1989) Prenatal prediction of lethal pulmonary hypoplasia using ultrasonic fetal chest circumference. Obstet Gynecol 73:261–266
Yoshimura S, Masukazi H, Gotoh H et al (1996) Ultrasonographic prediction of lethal pulmonary hypoplasia: comparison of eight different ultrasonographic parameters. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:477–483
Parilla BV, Leeth EA, Kambich MP et al (2003) Antenatal detection of skeletal dysplasias. J Ultrasound Med 22:255–258
Chen CP, Chern SR, Shih JC et al (2001) Prenatal diagnosis and genetic analysis of type I and type II thanatophoric dysplasia. Prenat Diagn 21:89–95
Viora E, Sciarrone A, Bastonero S et al (2002) Three-dimensional ultrasound evaluationof short-rib polydactyly syndrome type II in the second trimester: a case report. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 19:88–91
Hata T, Aoki S, Akiyama M et al (1998) Three-dimensional ultrasonographic assessment of fetal hands and feet. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 12:235–239
Plockinger-Ulm B, Ulm MR, Lee A et al (1996) Antenatal depiction of fetal digits with three-dimensional ultrasonography. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:571–574
Pretorius DH, Nelson TR (1995) Fetal face visualisation using three-dimensional ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 14:349–356
Steiner H, Spitzer D, Weiss-Wichert P et al (1995) Three dimensional ultrasound in prenatal diagnosis of skeletal dysplasia. Prenat Diagn 15:373–377
Miyazaki O, Nishimura G, Sago H et al (2007) Prenatal diagnosis of chondrodysplasia punctata tibia-metacarpal type using multidetector CT and three-dimensional reconstruction. Pediatr Radiol 37:1151–1154
Bonnefoy O, Delbosc JM, Maugey-Laulom B et al (2006) Prenatal diagnosis of hypochondroplasia: three-dimensional multislice computed tomography findings and molecular analysis. Fetal Diagn Ther 21:18–21
Cassart M, Massez A, Cos T et al (2007) Contribution of three-dimensional computed tomography in the assessment of skeletal dysplasia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 29:537–543
Breidt D, Bouquigny F, Clement JP et al (2003) Helical CT pelimetry: advantages of a low dose volume acquisition technique. J Radiol 84:1027–1030
Hurwitz LM, Yoshizumi T, Reiman RE et al (2006) Radiation dose to the fetus from MDCT during early gestation. AJR 186:871–876
Felmlee JP, Gray JE, Leetzow ML et al (1990) Estimated fetal radiation dose from multislice CT studies. AJR 154:185–190
Tsutsumi S, Sawai H, Nishimura G et al (2008) Prenatal diagnosis of thanatophoric dysplasia by 3-D helical computed tomography and genetic analysis. Fetal Diagn Ther 24:420–424
Ebina Y, Yamada H, Kato EH et al (2001) Prenatal diagnosis of agnathia-holoprosencephaly:three-dimensional imaging by helical computed tomography. Prenat Diagn 21:68–71