Abstract
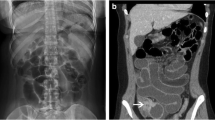
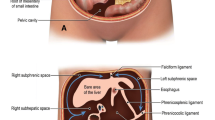
The complex and sometimes controversial subject of malrotation and midgut volvulus is reviewed commencing with the 19th-century Bohemian anatomist, Václav Treitz, who described the suspensory muscle anchoring of the duodenal-jejunal junction in the left upper quadrant, and continuing with William Ladd, the 20th-century American “father of pediatric surgery” who pioneered the surgical treatment of midgut volvulus. In this review, we present the interesting history of malrotation and discuss the current radiologic and surgical controversies surrounding its diagnosis and treatment. In the symptomatic patient with malrotation and possible midgut volvulus, prompt diagnosis is critical. The clinical examination and plain film are often confusing, and delayed diagnosis can lead to significant morbidity and death. Despite recent intense interest in the position of the mesenteric vessels on US and CT scans, the upper gastrointestinal series remains the fastest and most accurate method of demonstrating duodenal obstruction, the position of the ligament of Treitz, and, if the contrast agent is followed distally, cecal malposition. Controversy exists over the management of asymptomatic patients with malrotation in whom the diagnosis is made incidentally during evaluation for nonspecific complaints, prior to reflux surgery, and in those with heterotaxy syndromes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford WC (1963) Wenzel Treitz: the man and his “ligament”. Surgery 53:556–562
Fox RS, Fox CG, Graham WP (1985) Václav Treitz (1819-1872): Czechoslovakian pathoanatomist and patriot. World J Surg 9:361–366
Ladd WE (1936) Surgical disease of the alimentary tract in infants. N Engl J Med 215:705–708
Randolph J (1985) The first of the best. J Pediatr Surg 20:580–591
Nance ML (2001) The Halifax disaster of 1917 and the birth of North American pediatric surgery. J Pediatr Surg 36:405–408
Xydas S, Widmann WD, Hardy MA (1986) William E. Ladd: father of pediatric surgery. Prog Pediatr Surg 20:52–59
Sizemore AW, Rabbani KZ, Ladd A et al (2008) Diagnostic performance of the upper gastrointestinal series in the evaluation of children with clinically suspected malrotation. Pediatr Radiol 38:518–528
Long FR, Kramer SS, Markowitz RI et al (1996) Intestinal malrotation in children: tutorial on radiographic diagnosis in difficult cases. Radiology 198:775–780
Long FR, Kramer SS, Markowitz RI et al (1996) Radiographic patterns of intestinal malrotation in children. Radiographics 16:547–556
Strouse PJ (2004) Disorders of intestinal rotation and fixation (“malrotation”). Pediatr Radiol 34:837–851
Applegate KE, Anderson JM, Klatte E (2006) Intestinal malrotation in children: a problem-solving approach to the upper gastrointestinal series. Radiographics 26:1485–1500
Houston CS, Wittenborg MH (1965) Roentgen evaluation of anomalies of rotation and fixation of the bowel in children. Radiology 84:1–17
Berdon WE, Baker DH, Bull S et al (1970) Midgut malrotation and volvulus. Which films are most helpful? Radiology 96:375–383
Weinberger E, Winters WD, Rosenbaum DM et al (1992) Sonographic diagnosis of intestinal malrotation in infants: importance of the relative positions of the superior mesenteric vein and artery. AJR 159:825–828
Nichols DM, Li DK (1983) Superior mesenteric vein rotation: a CT sign of midgut malrotation. AJR 141:707–708
Shatzkes D, Gordon DH, Haller JO et al (1990) Malrotation of the bowel: malalignment of the superior mesenteric artery-vein complex shown by CT and MR. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:93–95
Pracros JP, Sann L, Genin G et al (1992) Ultrasound diagnosis of midgut volvulus: the “whirlpool” sign. Pediatr Radiol 22:18–20
Leonidas JC, Magid N, Soberman N et al (1991) Midgut volvulus in infants: diagnosis with US. Radiology 179:491–493
Hayden CK Jr, Boulden TF, Swischuk LE et al (1984) Sonographic demonstration of duodenal obstruction with midgut volvulus. AJR 143:9–10
Chang J, Bruechner M, Touloukian RJ (1993) Intestinal rotation and fixation abnormalities in heterotaxia: early detection and management. J Pediatr Surg 28:1281–1284
Ferdman B, States L, Gaynor JW et al (2007) Abnormalities of intestinal rotation in patients with congenital heart disease and the heterotaxy syndrome. Congenit Heart Dis 2:12–18
Ditchfied MR, Hutson JM (1998) Intestinal rotational abnormalities in polysplenia and asplenia syndromes. Pediatr Radiol 28:303–306
Malek MM, Burd RS (2006) The optimal management of malrotation diagnosed after infancy: a decision analysis. Am J Surg 191:45–51
Choi M, Borenstein SH, Homberger L et al (2005) Heterotaxia syndrome: the role of screening for intestinal rotation abnormalities. Arch Dis Child 90:813–815
Warner BW (1997) Malrotation. In: Oldham KT, Colombani PM, Foglia RP (eds) Surgery of infants and children: scientific principles and practice. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 1229–1240
Bill A, Grauman D (1966) Rationale and technique for stabilization of the mesentery in cases of nonrotation of the midgut. J Pediatr Surg 1:127–136
Millar AJ, Rode H, Cywes S (2003) Malrotation and volvulus in infancy and childhood. Semin Pediatr Surg 12:229–236
Katz ME, Siegel MJ, Shackelford GD et al (1987) The position and mobility of the duodenum in children. AJR 148:947–951
McVay MR, Kokosha ER, Jackson RJ et al (2007) The changing spectrum of intestinal malrotation: diagnosis and management. Am J Surg 194:714–719
Dilley AV, Pereira J, Shi ECP et al (2000) The radiologist says malrotation: does the surgeon operate? Pediatr Surg Int 16:45–49
Orzech N, Navarro OM, Langer JC (2006) Is ultrasonography a good screening test for intestinal malrotation? J Pediatr Surg 41:1005–1009
Zerin JM, DiPietro MA (1992) Superior mesenteric vascular anatomy at US in patients with surgically proved malrotation of the midgut. Radiology 183:693–694
Dufour D, Delaet MH, Dassonviille M et al (1992) Midgut malrotation, the reliability of sonographic diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol 22:21–23
Ashley LM, Allen S, Teele RL (2001) A normal sonogram does not exclude malrotation. Pediatr Radiol 31:354–356
Addendum
A physiologic explanation of “distal small bowel obstructive pattern” can be found in Kassner EG, Kottmeier PK (1975) Absence and retention of small bowel gas in infants with midgut volvulus: mechanisms and significance. Pediatr Radiol 4:28–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lampl, B., Levin, T.L., Berdon, W.E. et al. Malrotation and midgut volvulus: a historical review and current controversies in diagnosis and management. Pediatr Radiol 39, 359–366 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-009-1168-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-009-1168-y