Abstract
Background
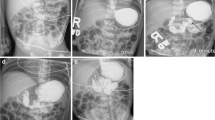
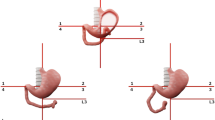
Malrotation is a congenital disorder of abnormal intestinal rotation and fixation that predisposes infants to potentially life-threatening midgut volvulus. Upper gastrointestinal tract (UGI) examination is sometimes equivocal and can lead to inaccurate diagnosis.
Objective
To determine the diagnostic performance of UGI examinations in children who subsequently underwent a Ladd procedure for suspected malrotation or volvulus.
Materials and methods
We reviewed all children up to 21 years old who had undergone both a UGI examination and a Ladd procedure for possible malrotation across 9 years. Children were excluded if they had not undergone either a UGI examination or a Ladd procedure and if congenital abdominal wall defects were present.
Results
Of 229 patients identified, 166 (59% male, median age 67 days) were included. Excluded were 47 without a UGI series, 12 with omphalocele or gastroschisis, 1 without verifiable operative data, 1 who had not undergone a Ladd procedure, and 2 older than 21 years. Of the 166 patients, 40% were neonates and 73% were <12 months old, and 31% presented with bilious vomiting and 15% with abdominal distention. Of 163 patients with surgically verified malrotation, 156 had a positive UGI examination, a sensitivity of 96%. There were two patients with a false-positive UGI examination and seven with false-negative examination. Jejunal position was normal in six of the seven with a false-negative examination and abnormal in the two with a false-positive examination. Of 38 patients with surgically verified volvulus, 30 showed volvulus on the UGI series. Five required bowel resection and three died.
Conclusion
Jejunal position can lead to inaccurate UGI series interpretation. Meticulous technique and periodic assessment of performance will help more accurately diagnose difficult or equivocal cases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torres A, Ziegler M (1993) Malrotation of the intestine. World J Surg 17:326–331
Strouse P (2004) Disorders of intestinal rotation and fixation (“malrotation”). Pediatr Radiol 34:837–851
Applegate KE, Anderson JM, Klatte EC (2006) Intestinal malrotation in children: a problem-solving approach to the upper gastrointestinal series. Radiographics 26:1485–1500
Orzech N, Navarro O, Langer J (2006) Is ultrasonography a good screening test for intestinal malrotation? J Pediatr Surg 41:1005–1009
Millar A, Rode H, Brown R et al (1987) The deadly vomit: malrotation and midgut volvulus. Pediatr Surg Int 2:172–176
Spigland N, Brandt M, Yazbeck S (1990) Malrotation presenting beyond the neonatal period. J Pediatr Surg 25:1139–1142
Jamieson D, Stringer DA (2000) Small bowel. In: Babyn P (ed) Pediatric gastrointestinal imaging and intervention. Decker, Hamilton, Ontario, pp 311–332
Bonadio WA, Clarkson T, Naus J (1991) The clinical features of children with malrotation of the intestine. Pediatr Emerg Care 7:348–349
Lin J, Lou C, Wang K (1995) Intestinal malrotation and midgut volvulus: a 15-year review. J Formos Med Assoc 94:178–181
Seashore J, Touloukian R (1994) Midgut volvulus. An ever-present threat. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 148:43–46
Long F, Kramer S, Markowitz R et al (1996) Intestinal malrotation in children: tutorial on radiographic diagnosis in difficult cases. Radiology 198:775–780
Rescorla F, Shedd F, Grosfeld J et al (1990) Anomalies of intestinal rotation in childhood: analysis of 447 cases. Surgery 108:710–715
Berdon WE, Baker DH, Bull S et al (1970) Midgut malrotation and volvulus. Which films are most helpful? Radiology 96:375–384
Andrassy RJ, Mahour GH (1981) Malrotation of the midgut in infants and children: a 25-year review. Arch Surg 116:158–160
Ford EG, Senac MO Jr, Srikanth MS et al (1992) Malrotation of the intestine in children. Ann Surg 215:172–178
Taybi H, Lachman R (1990) Radiology of syndromes, metabolic disorders, and skeletal dysplasias. Yearbook Medical Publishers, Chicago, IL
Applegate KE, Goske MJ, Pierce G et al (1999) Situs revisited: imaging of the heterotaxy syndrome. Radiographics 19:837–852; discussion 853–834
Koplewitz B, Daneman A (1999) The lateral view: a useful adjunct in the diagnosis of malrotation. Pediatr Radiol 29:144–145
Katz ME, Siegel MJ, Shackelford GD et al (1987) The position and mobility of the duodenum in children. AJR 148:947–951
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sizemore, A.W., Rabbani, K.Z., Ladd, A. et al. Diagnostic performance of the upper gastrointestinal series in the evaluation of children with clinically suspected malrotation. Pediatr Radiol 38, 518–528 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-0762-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-0762-8