Abstract
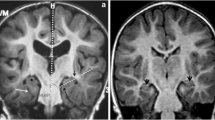
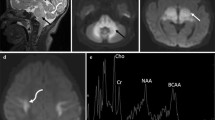
Citrullinaemia is a rare inborn error of urea cycle metabolism. We describe the MRI findings in a 16-year-old boy with type I citrullinaemia during an episode of acute hyperammonaemic encephalopathy and compare them to his previous follow-up MRI studies. MRI revealed bilateral high signal intensity in the cingulate, perirolandic, parietal and temporoinsular cortex, the subcortical white matter and left thalamus. Diffusion-weighted imaging showed high signal intensity and low apparent diffusion coefficient values in the frontoparietal lobes. To our knowledge, MRI findings in an adolescent with type I citrullinaemia have not been previously reported. Since our patient’s neuroradiological findings showed greater similarity to type II citrullinaemia, we think his brain injury during this acute episode was probably age-related and independent of the type of citrullinaemia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brusilow SW, Horwich AL (2001) Urea cycle enzymes. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS et al (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1909–1963
McMurray WC, Mohyuddin F, Rossiter RJ et al (1962) Citrullinuria: a new aminoaciduria associated with mental retardation. Lancet i:138
van der Knaap MS, Valk J (2005) Magnetic resonance of myelination and myelin disorders. Springer, New York, pp 360–368
van der Knaap MS, Valk J (2005) Magnetic resonance of myelination and myelin disorders. Springer, New York, pp 25–36
Majoie CB, Mourmans JM, Akkerman EM et al (2004) Neonatal citrullinemia: comparison of conventional MR, diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor findings. AJNR 25:32–35
Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Cheng SF et al (2003) Brain MR imaging in neonatal hyperammonemic encephalopathy resulting from proximal urea cycle disorders. AJNR 24:1184–1187
Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Cheng SF et al (2003) Brain MR imaging in acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy arising from late-onset ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. AJNR 24:390–393
Au WL, Lim TC, Seow DC et al (2003) Serial diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in adult-onset citrullinemia. J Neurol Sci 209:101–104
Chen YF, Huang YC, Liu HM et al (2001) MRI in a case of adult-onset citrullinemia. Neuroradiology 43:845–847
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Longo, D., Delfino, L., Genovese, E. et al. MRI findings in an adolescent with type I citrullinaemia. Pediatr Radiol 38, 237–240 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0650-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0650-7