Abstract
Background
US shows promise in evaluating clubfeet. In order to assess responses to therapy, the measurements of normal feet and clubfeet must be known.
Objective
To investigate the role of US measurement in quantitatively evaluating normal feet and clubfeet in children, and to assess changes in these feet with age.
Materials and methods
Patients <1 year old with unilateral or bilateral clubfoot deformity underwent US examination of the foot with specific attention to the medial malleolar to navicular (MMN) distance. Measurements were made in neutral and full adduction positions, and in the abduction position simulating the Ponseti maneuver. Children undergoing US for other reasons had the same imaging performed and served as controls.
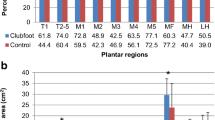
Results
A total of 127 feet in 66 children were evaluated (20 children had bilateral clubfeet, 25 had unilateral clubfoot, and 21 had normal feet). Clubfeet had significantly (P < 0.001) lower MMN measurements at all three positions than control feet. These distances increased with patient age for both normal feet and clubfeet, but the rate of increase was less for clubfeet.
Conclusion
Normal feet and clubfeet exhibit marked differences in MMN distances, as well as differences in rate of change over time. By understanding the age-dependent variability of normal feet and clubfeet, dynamic sonography can help assess clubfoot anatomy and could help to assess the effect of treatment interventions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobbs M, Morcuende J, Gurnett C et al (2000) Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot: an historical review. Iowa Orthop J 20:59–64
Aurell Y, Adlercreutz C, Andriesse H et al (2004) Repeatability of sonographic measurements in clubfeet. Acta Radiol 45:622–627
Aurell Y, Johansson A, Hansson G et al (2002) Ultrasound anatomy in the normal neonatal and infant foot: an anatomic introduction to ultrasound assessment of foot deformities. Eur Radiol 12:2306–2312
Kuhns L, Koujok K, Hall J et al (2003) Ultrasound of the navicular during the simulated Ponseti maneuver. J Pediatr Orthop 23:243–245
Aurell Y, Johansson A, Hansson G et al (2002) Ultrasound anatomy in the neonatal clubfoot. Eur Radiol 12:2509–2517
Tolat V, Boothroyd A, Carty H et al (1995) Ultrasound: a helpful guide in the treatment of congenital talipes equinovarus. J Pediatr Orthop B 4:65–70
Roye B, Hyman J, Roye D (2004) Congenital idiopathic talipes equinovarus. Pediatr Rev 25:124–130
Katz D, Albanese E, Levinsohn E et al (2003) Pulsed color-flow Doppler analysis of arterial deficiency in idiopathic clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop 23:84–87
Furdon S, Donlon C (2002) Examination of the newborn foot: positional and structural abnormalities. Adv Neonatal Care 2:248–258
Ponseti I (ed) (1996) Congenital clubfoot: fundamentals of treatment. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Ippolito E (1995) Update on pathologic anatomy of clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop B 4:17–24
Noonan K, Richards B (2003) Nonsurgical management of idiopathic clubfoot. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 11:392–402
Dobbs M, Rudzki J, Purcell D et al (2004) Factors predictive of outcome after use of the Ponseti method for the treatment of idiopathic clubfeet. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86A:22–27
Morcuende J, Dolan L, Dietz F et al (2004) Radical reduction in the rate of extensive corrective surgery for clubfoot using the Ponseti method. Pediatrics 113:376–380
Herzenberg J, Radler C, Bor N (2002) Ponseti versus traditional methods of casting for idiopathic clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop 22:517–521
Simons G (1977) Analytical radiography of clubfeet. J Bone Joint Surg Br 59B:485–488
Bansal V, Daniel J, Rai J (1988) Radiological score in the assessment of clubfoot. Int Orthop 12:181–185
Chami M, Daoud A, Maestro M et al (1996) Ultrasound contribution in the analysis of the newborn and infant normal and clubfoot: a preliminary study. Pediatr Radiol 26:298–302
Cahuzac J, Navascues J, Baunin C et al (2002) Assessment of the position of the navicular by three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging in infant foot deformities. J Pediatr Orthop B 11:134–138
Pirani S, Zeznik L, Hodges D (2001) Magnetic resonance imaging study of the congenital clubfoot treated with the Ponseti method. J Pediatr Orthop 21:719–726
Saito S, Hatori M, Kokubun S et al (2004) Evaluation of calcaneal malposition by magnetic resonance imaging in the infantile clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop B 13:99–102
Gigante C, Talenti E, Turra S (2004) Sonographic assessment of clubfoot. J Clin Ultrasound 32:235–242
Maiza D, Themar-Noel C, Legrand I et al (1995) Ultrasonographic approach to the neonatal foot: preliminary study. J Pediatr Orthop B 4:123–128
Napiontek M (1995) Intraoperative ultrasound for evaluation of reduction in congenital talipes equinovarus. J Pediatr Orthop B 4:55–57
Hamel J, Becker W (1996) Sonographic assessment of clubfoot deformity in young children. J Pediatr Orthop B 5:279–286
Goldner J, Fitch R (1994) Classification and evaluation of congenital talipes equinovarus. In: Simons G (ed) The clubfoot. Springer, Berlin, pp 120–139
Wallander H, Aurell Y, Hansson G (2007) No association between residual forefoot adduction and the position of the navicular in clubfeet treated by posterior release. J Pediatr Orthop 27:60–66
Dimeglio A, Bensahel H, Souchet P et al (1995) Classification of clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop B 4:129–136
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank John Hayes, PhD, and Stacy Hoshaw-Woodard, PhD, for statistical support and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coley, B.D., Shiels, W.E., Kean, J. et al. Age-dependent dynamic sonographic measurement of pediatric clubfoot. Pediatr Radiol 37, 1125–1129 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0601-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0601-3